Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Feet (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Bones, Ligaments, and More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
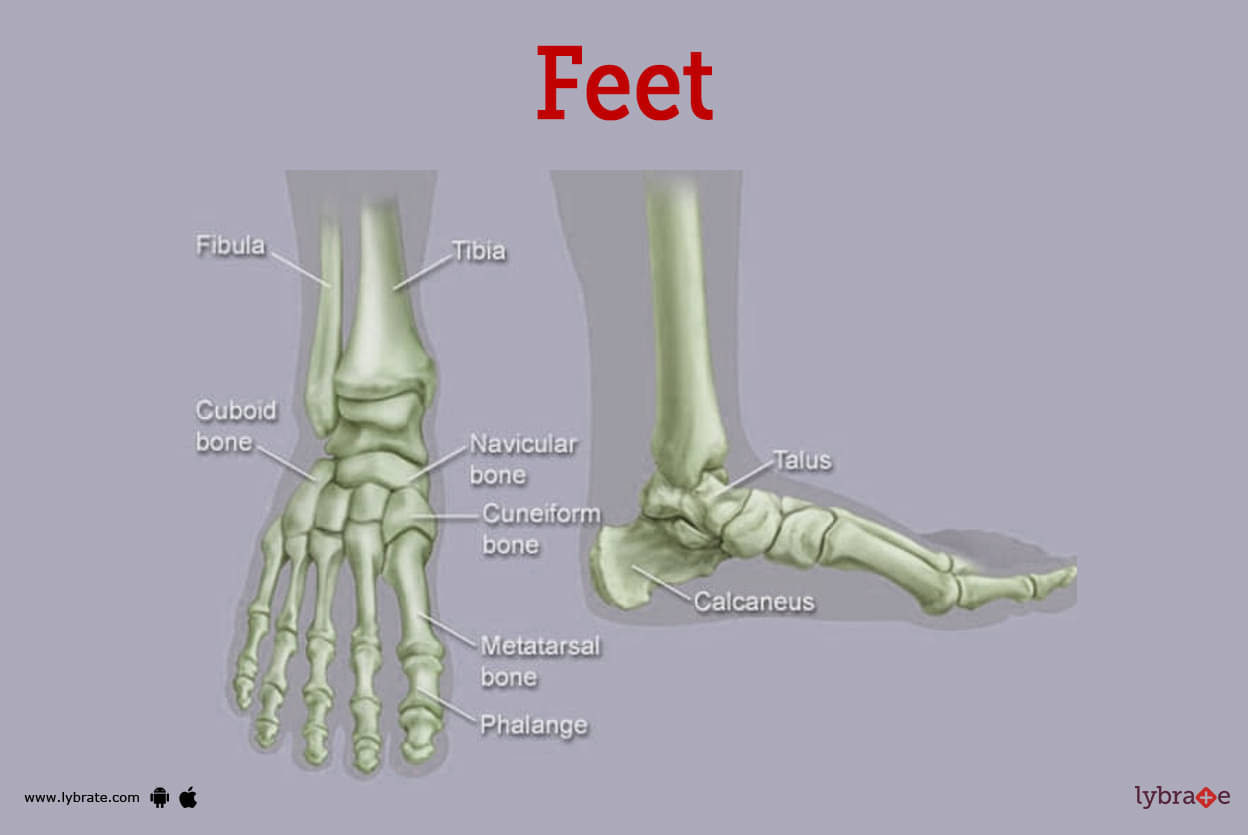
Feet Image
- Our feet are made up of bones, joints, muscles, and other connective tissues that allow us to stand up straight and do things like walk, run, and jump. The toes, the middle, and the heel are all separate parts of the foot.
- In the forefoot are the five phalanges of each toe and the five longer bones of the foot (metatarsals).
- In the middle of the foot, the bones that come together to make the arches are set up like a pyramid. This group includes the navicular bone, the three cuneiform bones, and the cuboid bone.
- The back foot makes up both the heel and the ankle. The talus bone supports the other ankle bones, the tibia and the fibula. The biggest bone in the foot is the calcaneus, which is also called the heel bone.
- The muscles, tendons, and ligaments that run along the bottoms of the feet allow the feet to move and balance. Running, jumping, and standing on your toes all require a healthy Achilles tendon, which is the tissue that connects the heel to the calf muscle.
Feet Function
The feet are a complex structure of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the weight of the body and allow for movement. Some of the main functions of the feet include:
- Feet support the weight of the body: The feet support the weight of the body, allowing it to remain upright and balanced. It is capable of balancing the weight of the full body in a variety of orientations and situations
- Feet help to maintain balance: The feet help to maintain balance by adjusting to changes in surface level and movement.
- Propulsion: The feet help to propel the body forward when walking or running by pushing off the ground. The ability to move around is the primary objective served by the limbs that comprise the foot.
- Feet helps to absorb shock: The feet help to absorb shock when the body is in motion, protecting the bones and joints of the lower extremities from impact. The structure of the foot is developed to be able to absorb shock, which the body experiences during walking
- Sensory functions: The feet have a high concentration of sensory receptors that help to detect changes in surface level and provide feedback to the brain about the body's position in space.
Overall, the feet are a vital part of the body's musculoskeletal system, providing support, balance, and movement.
Feet Diseases
- Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia, a ligament that runs along the bottom of the foot. Pain in the arch and heel, which is typically worse in the morning, are symptoms.Osteoarthritis Of The Feet: The degeneration of cartilage in the feet is a common symptom of osteoarthritis, which is caused by ageing as well as normal wear and tear. Osteoarthritis can cause a number of issues in the feet, including pain, swelling, and deformity.
- Gout: Gout is an inflammatory condition that causes severe pain and swelling in the joints. The crystals that cause gout deposit themselves in the joints on a periodic basis. Gout typically manifests itself in the joint of the big toe.
- Athlete's Foot: Athlete's foot is a fungal infection that affects the feet and can cause the skin to become dry, flaky, red, and irritated. Athlete's foot can be avoided by washing the feet regularly and maintaining a dry foot environment.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of autoimmune arthritis that leads to joint inflammation and damage over time. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints in the feet, including the toes, the ankle, and the foot itself.
- Bunions (Hallux Valgus): A bunion, also known as a hallux valgus, is a bony prominence that forms next to the base of the big toe and can cause the big toe to rotate inward. It's possible for anyone to develop bunions, but hereditary factors or shoes that aren't a good fit are typically to blame. Injury to the Achilles Tendon: Pain in the back of the heel could be an indication of a problem with the Achilles tendon. The injury may come on suddenly, or it may be a constant ache (tendinitis).
- Diabetic Foot Infection: Infections of the feet are common in people who have diabetes, and these infections can be more serious than they initially appear to be. People who have diabetes should check their feet every day for any signs of injury or infection that may be developing, including redness, warmth, swelling, and pain.
- Edema of the Feet: Some degree of edema in the feet is common in people who have varicose veins and may be normal after periods of standing for extended periods of time. Edema in the feet is one of the symptoms that can indicate problems with the heart, kidneys, or liver.
- Callus Of Feet: A callus is a buildup of tough skin over an area of the foot that experiences frequent friction or pressure. Calluses are common on the balls of the feet or the heels of the feet and can be uncomfortable or painful.
- Corns Of Feet: Corns, much like calluses, are the result of an excessive buildup of tough skin in areas of the feet that experience excessive pressure. Corns are painful growths that have the appearance of a cone with a point at the top.
- Heel Spur: A heel spur is an abnormal growth of bone that occurs in the heel and can be the source of excruciating pain when walking or standing. People who suffer from plantar fasciitis, have flat feet, or have high arches in their feet have a greater risk of developing heel spurs.Ingrown toenails are characterised by one or both sides of a toenail growing into the surrounding skin. It is possible for ingrown toenails to cause excruciating pain and even infection.
- Flat Feet: Flat feet, also known as fallen arches, occur when the natural arch in the foot collapses as a result of standing or walking, which can lead to other issues with the feet. Should the need arise, flat feet can be treated with orthotics in the form of shoe inserts.
- Onychomycosis: Onychomycosis, also known as nail fungal infection, is a condition in which fungus causes the fingernails or toenails to become discoloured or crumbly. Infections of the nail bed can be challenging to treat.
- Mallet Toes: Mallet toes are caused when the joint in the middle of a toe becomes rigid and unable to straighten, causing the toe to become deformed and point downward. If the mallet toe is not accommodated by special footwear, the wearer may experience irritation as well as other foot problems.
- Metatarsalgia: Pain and inflammation in the metatarsal region of the foot is referred to as metatarsalgia. The most common triggers for this condition are strenuous physical labour or footwear that is too tight.
- Claw Toes: Claw toes are caused by an abnormal contraction of the toe joints, which gives the toes a claw-like appearance. Claw toe is a painful condition that, in most cases, requires a change in footwear.
- Fracture: The metatarsal bones are the bones in the feet that are most likely to fracture as a result of either an accident or excessive use. A fracture may be indicated by the presence of pain, swelling, redness, and bruises.
- Plantar Wart: Warts on the plantar surface of the foot are caused by a viral infection that can lead to the formation of a callus that has a dark spot in the middle of it. Plantar warts are often excruciatingly painful and challenging to treat.
- Morton's Neuroma: A Morton's neuroma is a growth that typically forms between the third and fourth toes and is comprised of nerve tissue. Altering one's footwear can frequently alleviate the symptoms of a neuroma, which include pain, tingling, and a burning sensation.
- Pyogenic Osteomyelitis: Acute pyogenic osteomyelitis is a serious form of bone inflammation that can be brought on by a bacterium or another kind of microorganism. The infection caused by staphylococcus aureus that is most widely known.
Feet Tests
- Physical Examination Of Feet: An examination of the feet by a medical professional may reveal the presence of an feet fracture, a sprain, or another ailment.
- Feet X-Ray For Scanning Bones Of Feet: An X-ray film of the feet is often taken while trying to diagnose a fracture, arthritis, or any number of other conditions that may affect the joint.
- Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography: It stands for contrast enhanced computed tomography, in which high resolution images are produced using a 3 dimensional flow of X-rays around the organs. It is a gold standard diagnostic technique for many of the disorders of the liver, spleen, brain, kidneys and other vital organs.
- MRI: It stands for magnetic resonance imaging, for which high resolution imaging is done by using a super magnetic conductor and a central processing unit, which involves resizing and impartial diagnosis of disorders of bones, heart, spleen, kidney and other vital organs.
- Serum Calcium Test For Diagnosing Hyper And Hypocalcemia Are Feet: A calcium blood test determines how much calcium is currently present in your blood. It is possible that a wide variety of medical issues, such as bone disease, are present if the amount of calcium in the blood is either too high or too low.
- Serum Urea And Creatinine For Diagnosing Gout Symptoms Of Feet: They determine the metabolic nitrogenous substances. Uric acid accumulates in the blood and between the joints, causing inflammation and reducing bone mineral density.
- Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) Antibody For Diagnosis Osteomyelitis Of Feet: Levels are often high in rheumatoid arthritis, but they can be raised in other rheumatologic illnesses associated with inflammatory arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus. Which can also lead to foot discomfort
- RA Factor For Diagnosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A blood test can detect the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF). Rheumatoid factor is an autoantibody that the body's immune system produces. Autoantibodies like RF are destructive because they mistakenly attack healthy cells and tissues instead of pathogens. It leads to more painful friction between the foot's bones
- CRP Levels For Checking Symptoms Of Arthritis: C-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammatory marker, has been linked to an increased risk of fractures. Fractures and foot discomfort can both be predicted by measuring CRP levels in the blood.
- Serum Vit D3 For Checking Hypercalcemia: A blood test can tell you how much vitamin D is in your body, so you can make sure you have an ideal amount for your health. Vitamin D status refers to the quantity of this essential vitamin that a Calcium, a mineral crucial to bone development, is regulated in the body in a roundabout way.
- Dexa Scan For Osteoporosis Of Feet: The most common and trustworthy technique is a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. DEXA imaging employs low-dose x-rays. It's considered one of the best ways to detect bone breaks and arthritis.
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) For Checking Strength Of Feet: The results of this test can aid in the diagnosis of foot-related bone issues by providing insight into the bone's composition.
Feet Treatments
- Orthotics: Orthotics are shoe inserts that can help with a variety of foot problems. Orthotics can be made to order or purchased in standard sizes.Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve the flexibility, strength, and support of the feet and ankles through a variety of exercises.
- Rice Therapy: Rest, Icing, Compression (with an athletic bandage or similar), and Elevation is the RICE therapy protocol. In most cases, the RICE protocol rest, ice, compression, and elevation is all that's needed to treat an injury to the foot.
- Feet Immobilization: Most foot fractures necessitate casting the affected foot in order to prevent further movement. Some medical experts think that immobilisation might help with foot sprains as well.
- Feet Arthroscopic Surgery: The doctor will drill a hole in the patient's lower leg and implant a screw to unite the bones. This helps to stabilise the sprained high foot and promotes healing. The screw will be taken out after the incision has closed.
- Feet Fusion Surgery: Surgery to fuse the bones of the feet together will limit movement in the feet. It is possible that surgical fusing of the feet might ease the intense pain of severe foot arthritis.
- Feet Replacement Surgery: There are orthopaedic specialists that do replacement surgery on the foot, but the results aren't always as good as they are with knee replacements.
- Chopart Amputation: However, chopart amputation, which eliminates the forefoot and midfoot while preserving the talus and calcaneus, should not be carried out in the presence of ischemia. Because the majority of the tendons supporting the foot joint have been destroyed, the heel is no longer supported, making this amputation highly risky.
- Triple Arthrodesis: Surgery called a triple arthrodesis involves the fusing of three joints in the foot: the talocalcaneal (TC), talonavicular (TN), and calcaneocuboid (CC). The term 'foot fusion' describes this surgical operation.
- Dilwyn Evans Procedure: The Evans technique is a surgical treatment used to treat mechanical instability of the ligaments in the lateral foot. If your child has a clubfoot, the Dilwyn Evans therapy may help (procedure).
- Ponseti Method: An accelerated Ponseti operation, in which all procedures, five casts, and Achilles tenotomy are completed in a single week, has been proposed.
Feet Medicines
- Antifungal Medicines For Athlete's Foot: It is treatable with antifungal medications that can be applied topically or taken orally. few of the examples are luliconazole itraconazole, clotrimoxazole, fluconazole etc.
- NSAIDs For Reducing Foot Pain Of Feet: These drugs are used to treat aches and pains in other regions of the body. Ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen sodium are some examples of typical medications that are classified under this category. Ibuprofen and Naproxen, together with Indomethacin Ketorolac Diclofenac Meloxicam Celecoxib.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for Osteomyelitis Of Feet: Platelet-rich plasma, more frequently referred to as PRP, is a combination of numerous growth factors that is injected into a joint, most commonly the foot. PRP is recognised by its acronym, PRP. This not only helps reduce inflammation, but it also promotes the body's natural ability to mend damaged tissue, which is a significant benefit.
- DMARDs For Reducing Pain Of Feet: Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatics treat rheumatic diseases. Therapies limit disease progression. Autoimmune illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis are treated with this drug. DMARDs include methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib. DMARDs baricitinib and tofacitinib.
- Nutritional Supplements For Promoting Bone Growth Of Feet: Nutritional supplements, such as glucosamine and chondroitin, are often prescribed by medical professionals in order to alleviate a patient's discomfort and speed up the healing process in the joints. vitamin D and calcium supplements may be prescribed.
- Pregabalin For Reducing Peripheral Pain Of Feet: It is an anticonvulsant that is utilised in the treatment of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain. When combined with other seizure medications, it can also be used to treat partial-onset seizures.
- Bisphosphonates For Bone Growth In Feet: They are a type of medication that belongs to a class that can either stop or significantly slow the process of bone loss, which results in stronger bones. The primary purpose of bisphosphonates is to inhibit osteoclasts, which are cells found in bone that are responsible for the removal and reabsorption of minerals like calcium (the process is known as bone resorption). zoledronic acid. Alendronate and risedronate were both components of the treatment.
- Hyperuricemia Treatment Drugs For Treating Gout Symptoms Of Feet: Medications like Allopurinol, which blocks xanthine oxidase, Febuxostat, which blocks xanthine oxidase in the kidneys, Probenecid, which blocks the reabsorption of uric acid in the kidneys' proximal convoluted tubules (PCT), and Rasburicase, a recombinant uricase that converts uric acid to a water-soluble form,
- Antibiotics For Osteomyelitis And Myositis Of Feet: Bacterial diseases of the feet muscles, such as myositis, are treated with antibiotics. Cellulitis is one of the most frequent reasons people take antibiotics. Vancomycin and the cephalosporins are two prevalent examples.
- Corticosteroids for Feet: Patients who suffer from specific kinds of myositis that present in the feet muscle may be given prescriptions for cortisone-like medications such as prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone, as well as other pharmaceuticals that are comparable to cortisone.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously