Fetal Pole (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Jun 28, 2023
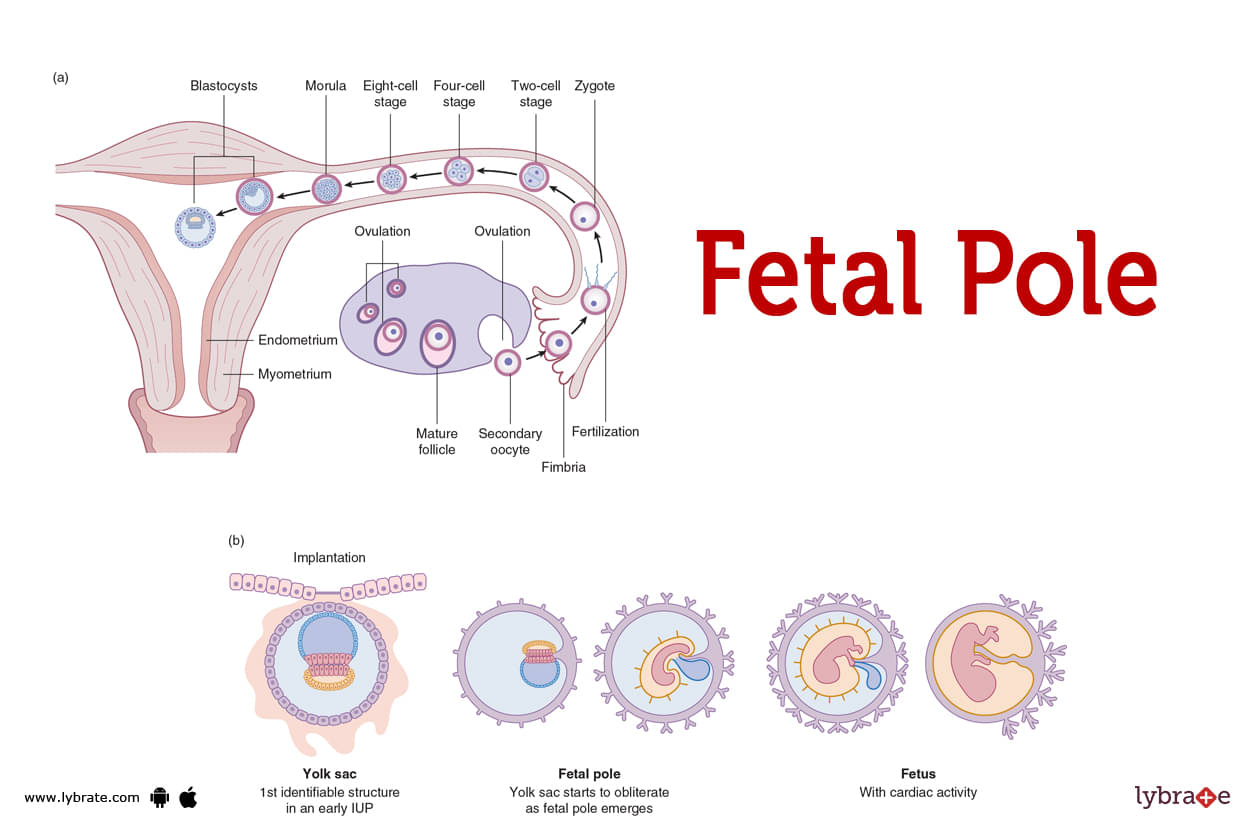
Fetal pole Image
One of the earliest phases of an embryo's growth during pregnancy is a Fetal pole. The development of the Fetal pole into a foetus occurs in a healthy pregnancy. The Fetal pole can be seen and measured during an early prenatal ultrasound.
This includes information about the embryo's location, gestational age, potential difficulties, and whether there is more than one embryo. The Fetal pole grows into a foetus, then a newborn, during a healthy pregnancy. It is also called an embryo or embryonic pole.
Is a Fetal pole a baby?
A Fetal pole is not yet a baby, according to medical terminology. Until roughly the 10th week of pregnancy, it is an embryo. It subsequently develops into a foetus and undergoes Fetal development till birth.
Where is the Fetal pole located?
The yolk sac is a tiny pouch found adjacent to the Fetal pole. All of its nutritional needs are met by those. There's a yolk sac and Fetal pole in there somewhere. The gestational sac resides in the uterus throughout a typical pregnancy.
What does a Fetal pole look like?
The pole of a foetus is skewed. The crown, or embryonic head, is located at one end. On the opposite end is a tail-like appendage known as the rump.
How big is an embryo?
The size of a Fetal pole is directly proportional to the stage of gestation at which it is formed. The length of an embryo is determined by measuring from the crown to the rump (crown-to-rump length, or CRL). When an embryo is found for the first time, it may only be one or two millimeters in size. By the tenth week of pregnancy, it will have grown to a length of approximately 30 millimeters.
When does the Fetal pole appear?
After approximately 5 to 6 weeks of pregnancy, a Fetal pole can typically be seen using vaginal ultrasound imaging. However, depending on what type of ultrasound that was performed and the orientation of your uterus, it is possible that it will not be detected for several weeks.
What comes first, Fetal pole or heartbeat?
A heartbeat is usually visible about six weeks of pregnancy, after the Fetal pole is seen.
Fetal Pole Functions
The Fetal pole can be observed and measured via prenatal ultrasonography. Early in pregnancy, the photos can provide crucial information to medical professionals, such as:-
- The size of the Fetal pole can be used to estimate gestational age, especially if you don't remember when you last had a period or if it has been a while since your last one.
- If you are pregnant with more than one baby, there will be more than one Fetal pole.
- Where in the body the pregnancy is: For example, a healthy pregnancy should occur within your uterus, not in your fallopian tubes.
- Whether there is a problem with the pregnancy: If the Fetal pole is small or can't be seen, it could mean that the dates were wrong or that the baby died.
Fetal pole Conditions and Disorders
- Blighted ovum: An embryonic pregnancy, or blighted ovum, occurs when a fertilized egg settles in the uterus but it does not develop into an embryo. An early miscarriage results from this.
- Too early: You might not be able to view the embryo if the pregnancy isn't far enough along. Inaccurate estimates of gestational age are common, especially when your menstrual cycles were erratic.
- Miscarriage: You could have experienced a miscarriage if an ultrasound is unable to see a Fetal pole or gestational sac. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a Fetal pole is discovered somewhere other than your uterus. This is a medical emergency, not a feasible pregnancy.
- Fetal growth restriction (FGR): It occurs when an unborn baby (foetus) is smaller than predicted for the number of weeks in the pregnancy (gestational age). A missed miscarriage is diagnosed when a Fetal pole with no heartbeat and a crown-rump length more than 7 millimetres is detected. It happens when the embryo dies or fails to grow, but the body does not miscarry.
- Unknown pregnancy location (PUL): This condition is characterised by a positive pregnancy test despite the absence of intrauterine or extrauterine pregnancy symptoms. Typically, this is not a conclusive diagnosis.
A yolk sac tumour is an unusual kind of cancer that is also known as a germ cell tumour. After birth, cancer begins in the cells which line the yolk sac and becomes a tumour.
What does it mean if the Fetal pole is missing?
If the ultrasound doesn't find the Fetal pole when it should, you may have to do the test again in a few days. If the Fetal pole isn't there, it could mean a few things, such as:
- Blighted ovum: A blighted ovum, also called anembryonic pregnancy, happens when a fertilised egg implants in the uterus but it doesn't grow into an embryo. This makes the pregnancy end too soon.
- Too early: You might not be able to observe the embryo if the pregnancy is too early. Gestational age is an estimate that might be off by a few weeks if your periods have been erratic. Ultrasound may indicate a miscarriage if it fails to detect a Fetal pole and/or a gestational sac.
An ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed when a Fetal pole is discovered in a location other than the uterus in a pregnant woman. It is not a pregnancy that can continue normally because of this issue, which is a medical emergency. In addition to these locations, a gestational sac may also be present in the cervix, fallopian tube, ovary, and abdomen.
What if I have a Fetal pole with no heartbeat?
You will miscarry if your provider doesn't observe a heartbeat and your Fetal pole is over 7 mm. Your healthcare practitioner will help you understand. They may prescribe further testing.
Fetal pole Tests
- Fetal ultrasound: The best method for determining FGR is using ultrasonography to estimate Fetal weight. Images of the unborn child in the womb are produced by ultrasound using sound waves. You and the baby won't be harmed by sound waves.
- Doppler ultrasound: measures the amount of blood flowing to the placenta and to the infant via the umbilical cord. Reduced blood flow might indicate that the baby has FGR.
- Maternal blood screen: Protein levels and circulating free Fetal DNA in mother's circulation may be measured using blood tests. A Fetal chromosomal abnormality is more likely if the findings are abnormal.
- Screening for maternal serum: Blood testing in the second trimester may detect chromosomal abnormalities and/or spina bifida.
- Echocardiogram of the foetus: This is a targeted fetal heart ultrasound of the Fetal heart that may be done in some high-risk pregnancies or if an anomaly ultrasound reveals a cardiac abnormality.
- Fetal MRI: In situations of probable birth abnormalities, especially of the foetus' brain or nervous system, this may be prescribed.
- Serum-fetoprotein (AFP): It is a valuable diagnostic for diagnosing yolk sac tumours. Amniocentesis to search for genetic reasons of IUGR (and occasionally to assess the lung maturity of the foetus).
Fetal pole Treatments
- Dilation & Curettage (D&C): D and C is a type of surgery that removes the placental tissues from the uterus. Your doctor will open the cervix and use surgical equipment and suction to eliminate the pregnancy tissues from the uterus. This is done while the person is asleep or under general anaesthesia.
- Chemotherapy: Patients will often need at least three rounds of chemotherapy. One of the best measures of how well chemotherapy is working is whether or not tumour markers decrease the following treatment.
- Salpingostomy: During a salpingostomy, an ectopic pregnancy is surgically removed and the fallopian tube is permitted to heal on its own. It is a surgical procedure in which both the tube and the ectopic pregnancy are removed.
Fetal pole Medicines
- Oral medicines combined with surgery: In the treatment of anembryonic pregnancy, the use of misoprostol in conjunction with surgical therapy is thought to be more beneficial.
- HCG therapy: It is the most prevalent kind of hormone treatment for managing unplanned pregnancies when the pregnancy's location is unclear. For the purpose of forecasting the results of PUL, it is possible to utilise either a single serum hCG test or a series of serum hCG measures.
What can I do to keep a Fetal pole healthy and viable?
The Fetal pole has a lot of issues that are unavoidable. For instance, there is no way to eliminate genetic issues that might cause a miscarriage after you are pregnant or to modify the position of an ectopic pregnancy.
However, a number of strategies can help you and your embryo achieve the highest level of health possible:
- Consult your doctor about any medication or over-the-counter prescription drugs or supplements you are taking.
- Get plenty of fluids.
- Avoid mercury-containing foods, raw eggs or meats, and unpasteurized dairy products.
- Consume a daily prenatal vitamin.
- Follow a healthy diet containing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Cut back on the coffee.
- Don't smoke or use anything with tobacco.
- Do not consume alcoholic beverages or recreational drugs.
Table of content
Find Gynaecologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors