Gout: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Feb 24, 2023
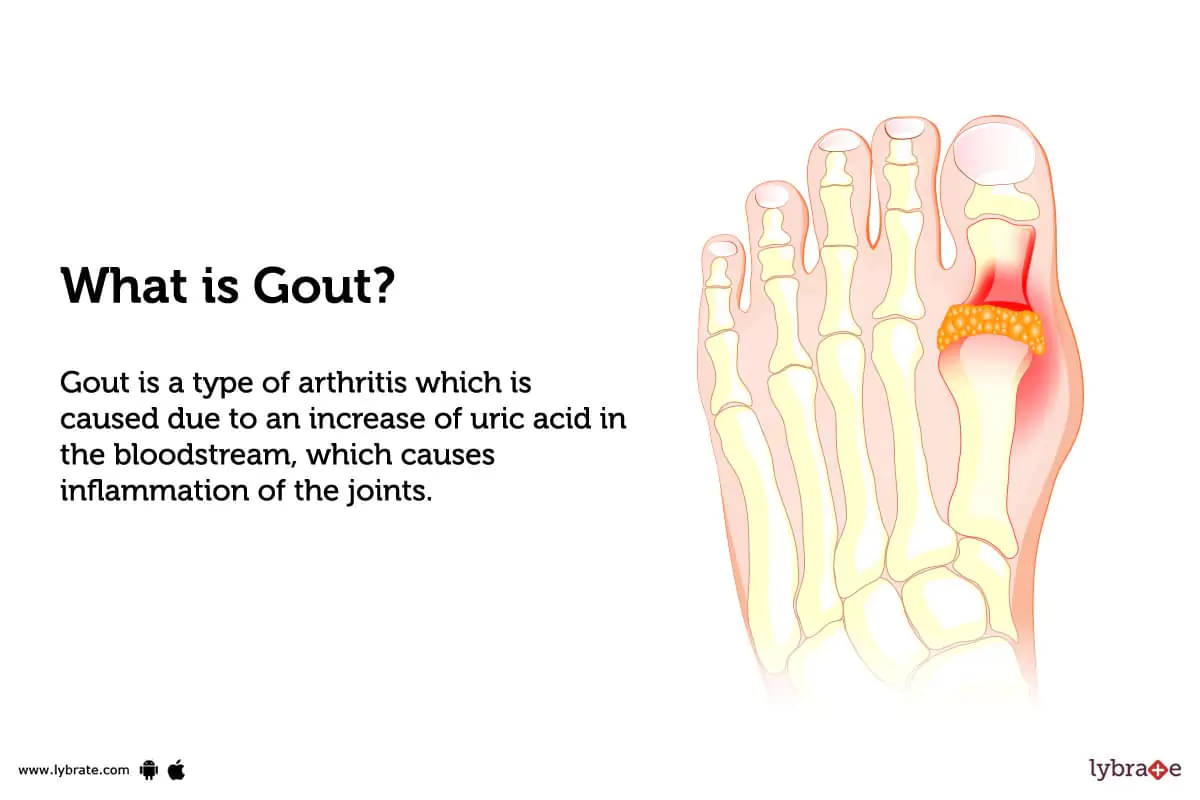
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis which is caused due to an increase of uric acid in the bloodstream, which causes inflammation of the joints. It is usually an extremely painful condition, and can cause excruciating joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Gout often affects the big toe but can also affect many other parts of the body such as the elbow, heel etc.
Types of Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by deposits of uric acid crystals in the joints. It can occur in various forms:-
- Acute gout: This is the most common form and it involves intense joint pain, swelling and redness caused by sudden crystal buildup in the joints.
- Asymptomatic gout: Also known as 'silent gout', this is when uric acid builds up in your body asymptomatically - without any noticeable symptoms.
- Chronic gout: This type occurs when deposits of uric acid crystals remain for long periods of time in the joint, causing recurrent episodes of pain and swelling over a period of months or years.
- Tophaceous gout: Tophi are deposits of uric acid crystals that form painful lumps just under the skin near an affected joint.
What causes Gout?
- Gout is caused due to increased levels of uric acid in the bloodstream, which can lead to the formation of uric acid crystals in joints, causing inflammation and pain in them.
- Uric acid is produced when purines, which are found naturally in certain foods and drinks we consume, are broken down by enzymes in our bodies.
- Other factors that can contribute to gout include genetics, existing health conditions such as obesity or kidney problems and high alcohol consumption.
- Medications like diuretics may also increase your risk of developing gout as they affect how your kidneys process uric acid levels.
What are the symptoms of Gout?
- Gout often presents as sudden and intense pain in the affected joint(s), usually presenting during the night and causing a lot of discomfort.
- Painful swelling, redness and tenderness in the joints are also common symptoms of gout.
- Other signs and symptoms might include chalky deposits, fatigue, fever and occasional deformity of the affected joints.
- If left untreated, an attack can last for days or weeks at a time before subsiding completely or recurring periodically with very similar flares.
How can you prevent Gout?
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat a proper healthy balanced diet, don't prefer food that is high in purines and uric acid.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Increase intake of complex carbohydrates instead of processed food.
- Drink enough fluids as it will help to eliminate uric acid out from the body.
- Avoid crash diets that increase the risk for developing gout.
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and decrease uric acid levels.
- Take medications recommended by your doctor.
Gout - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical exam: During physical examination, the doctor may check for joint inflammation, tenderness, and redness. He or she may also check for lumps around affected joints that can indicate the presence of tophi (chalky deposits of uric acid).
- Blood tests: To confirm the diagnosis of gout, your doctor may order a blood test to check uric acid levels in your blood. High levels can indicate gout, although normal levels can be seen in patients with certain types of arthritis as well as in healthy adults.
- Joint fluid analysis: If a physical exam and blood tests do not provide enough evidence to diagnose gout, then your doctor may order a joint fluid analysis to look for monosodium urate crystals in the synovial fluid (the fluid between joints) collected by aspiration or arthrocentesis.
- X-rays: X-rays are usually not helpful when diagnosing gout since they typically do not show any signs of inflammation or other changes associated with the disease. It can also be used to rule out conditions that are having similar symptoms for example bone fractures and some types of arthritis.
- Ultrasound scans: Ultrasound scans are another imaging technique used in diagnosing gout by pinpointing any areas where swelling or inflammation is present due to monosodium urate crystal deposits within soft tissues such as tendons and ligaments surrounding affected joints.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRIs may also be used to diagnose gout by catching any signs of inflammation that might otherwise go unnoticed on traditional X-rays or ultrasounds scans. The images from an MRI can also help confirm the presence of tophi if noted on a physical exam but not yet visible via other imaging techniques.
What are possible complications of Gout?
- Joint damage: Chronic gout can cause serious joint damage, including loss of cartilage, inflammation of the tendons, and the formation of deformities in severe cases.
- Tophi: accumulation of uric acid crystals may form around joints is known as tophi. These usually appear as firm, rounded lumps below the skin overlying the joint.
- Kidney Stones: Uric acid stones are kidney stones that may form due to high uric acid levels in the body.
- Kidney Damage: High levels of uric acid can also lead to chronic kidney disorders like nephropathy or azotemia.
- Cardiovascular Disease: People with gout also have an increased risk for developing cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure and heart attack/stroke due to inflammation associated with gout attacks or persistently elevated levels of uric acid in the blood.
Home Remedies for Gout
- Applying a paste of turmeric powder, black pepper powder and ginger juice on the affected area may reduce the symptoms of gout.
- Drinking warm water with lemon juice and honey can help to control uric acid level in the bloodstream.
- Eating raw banana or drinking its milkshake can be beneficial for reducing joint pain caused by gout.
- Taking warm oil massages on the affected area will improve circulation and reduce inflammation.
- Boiling fenugreek seeds in water and drinking it can help in detoxifying the body and lowering uric acid levels.
What to eat in Gout?
- Low-purine foods, such as most fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products.
- Chia seeds, olive oil and salmon.
- Bananas
- Root vegetables like turnips, potatoes.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Lean poultry and fish with low mercury levels.
- Legumes such as kidney beans, lentils.
- Honey instead of sugar.
What not to eat in Gout?
- Foods high in purines, such as organ meats, alcoholic beverages (especially beer), anchovies, sardines, mackerel and scallops, should be avoided.
- Other foods to avoid with gout include red meat and fatty foods.
- Processed foods and refined sugars should also be avoided. Examples of these include white breads, potatoes and certain fruits that are high in fructose.
Gout Treatment
- Uric Acid Lowering Therapy: This is the main form of treatment for gout and aims to reduce the levels of uric acid in the body. This is usually done by taking medications such as allopurinol or probenecid.
- Percutaneous electrocautery: This procedure involves using an electric current to burn away the tophi deposits that can form in response to high uric acid levels.
- Open synovectomy: During this procedure, the surgeon will make a small incision and remove the deposits of uric acid within the joint cavity, providing relief from pain and inflammation associated with gout.
- Arthroscopic synovectomy: In this minimally invasive technique, an arthroscope is inserted into your affected joint and tiny tools are used to cut away the buildup of uric acid crystals within it, reducing symptoms of gout.
- Surgery to remove a chronically infected bursa: If you have chronic gout-related bursitis (inflammation) over a long period of time, your surgeon may recommend surgically removing it from your joint along with any crystals of uric acid or inflammatory tissue that may accompany it.
Which doctor to consult for Gout?
A doctor experienced in treating joint pain and inflammation, such as a rheumatologist, should be consulted when experiencing gout.
A rheumatologist specialises in diagnosing and managing arthritis, autoimmune diseases and other musculoskeletal conditions.
Which are the best medicines for Gout?
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs are used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with gout attacks. Examples include ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, and sulindac.
- Corticosteroids: This class of drugs is used to suppress the immune system in order to reduce the swelling and pain associated with gout flares. Examples include prednisone, methylprednisolone, and dexamethasone.
- Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors: These medications work by inhibiting the production of uric acid in the body which helps prevent or reduce gout flares. Examples include allopurinol and febuxostat.
- Colchicine: This medication is used to prevent or reduce the frequency of gout flares by increasing the solubility of uric acid in the bloodstream, thus reducing its concentration in joint fluid which can cause inflammation from gout attacks.
- Other Medications: Other non-specific medications that can be used for treating symptoms related to gout include analgesics for pain relief (such as acetaminophen) and antihistamines for itch relief (such as diphenhydramine).
How long does it take to recover from Gout?
Recovery from gout depends on several factors, including patient compliance with treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Generally, it may take about 3-4 weeks for symptoms to resolve completely.
What is the Cost of Gout treatments in India?
The cost of gout treatments in India depends on the severity of the case and the treatment method chosen.
Generally, medicine to treat gout costs anywhere between ₹100 to ₹5000 depending on which medicine is prescribed and dosage required.
Surgery for severe cases can cost up to ₹70,000 depending on the complexity of the procedure and cost of hospitalisation or post-surgery care required.
What are side-effects of Gout treatments?
- The most common side-effects of gout treatments include nausea, dizziness, constipation, and headaches.
- Other more severe side-effects may include muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, fainting, and swelling of the face or throat.
- Rarely, more severe side-effects such as liver toxicity and kidney damage can occur.
Gout - Outlook / Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to Gout then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'joint damage, tophi, kidney stones' in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors