Hematoma: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
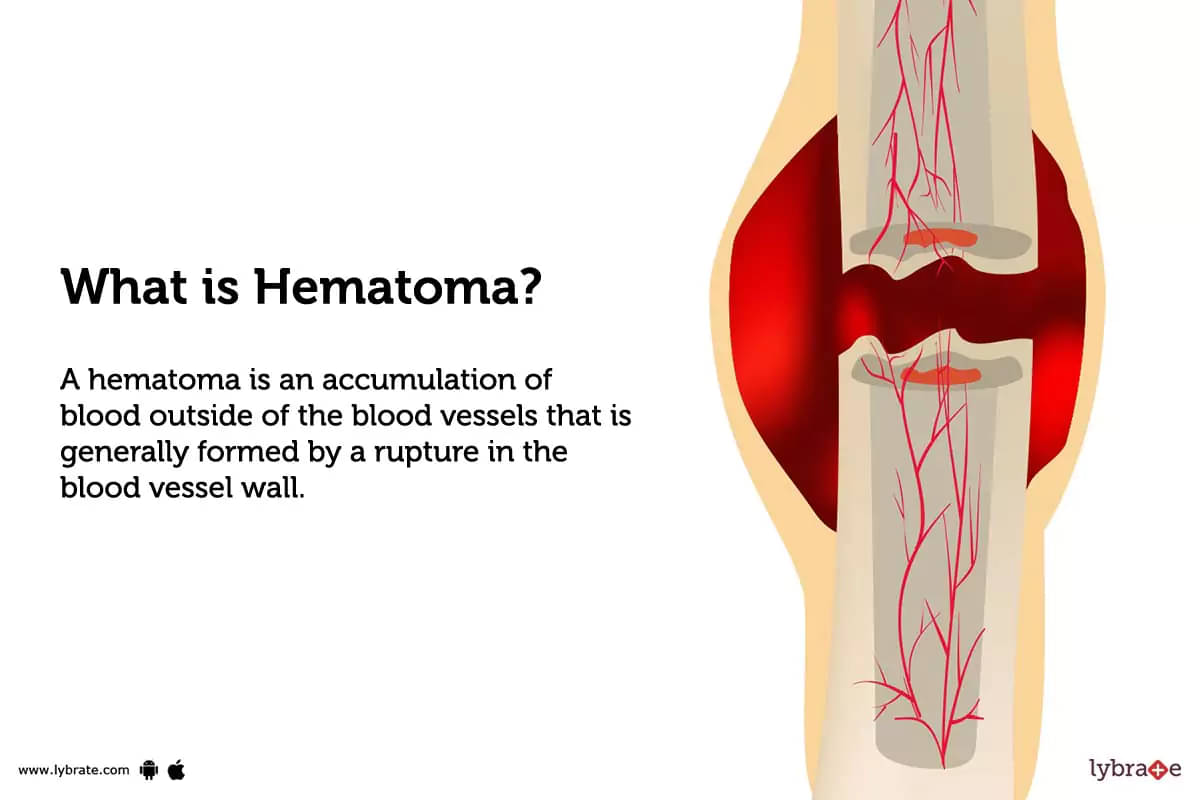
What is Hematoma?
A hematoma is an accumulation of blood outside of the blood vessels that is generally formed by a rupture in the blood vessel wall. Hematomas can occur anywhere in the body, but are most commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes. They can be caused by injury, surgery, or certain medical conditions such as clotting disorders.
Types of Hematoma
- Intracranial hematoma: This type of hematoma is a blood clot that forms inside the skull, either on the surface of the brain or between the skull and brain tissue.
- Subdural hematoma: This form of hematoma arises when blood accumulates between the dura mater (the meninges' outermost layer)) and the arachnoid membrane (the intermediate layer of three membranes that envelop and safeguard the brain and spinal cord).
- Subarachnoid Hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs when blood collects in the subarachnoid space (the space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater).
- Epidural Hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs when blood collects between the dura mater and inner table of skull bone (innermost layer).
- Retroperitoneal Hematoma: This type of hematoma occurs when blood accumulates in the retroperitoneal space that lies behind your abdominal cavity and in front of your spine.
What causes Hematoma?
It is usually caused by trauma, such as a blow to the head, or by an underlying medical condition that causes bleeding.
In certain situations, an injection or medical treatment that destroys a blood vessel might potentially cause this condition.
What are the symptoms of Hematoma?
The symptoms of a hematoma might vary depending on the afflicted area's location and size. Common symptoms include:
How can you prevent Hematoma?
To prevent hematoma, it is important to take precautions such as wearing protective gear when engaging in contact sports or other activities where blunt force trauma is a possibility, and being aware of any medical conditions that may increase the risk of hematoma.
Additionally, controlling blood pressure, avoiding taking certain medications that can increase bleeding, and seeking medical attention for any injury that breaks the skin are all important preventive measures.
Hematoma - Diagnosis and Tests
- Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body and can be used to detect and diagnose hematomas.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: This scan employs X-rays and computer technologies to generate pictures of the body's inside. It can be used to detect and diagnose hematomas, as well as to determine the size and location of the hematoma.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This test employs a combination of powerful magnets, radio waves, and a computer to generate detailed pictures of the inside of the human body. It is also capable of detecting and diagnosing hematomas.
- Blood tests: In some cases, a blood test may be used to check for clotting disorders or other underlying medical conditions that may be causing the hematoma.
What are possible complications of Hematoma?
- Common complications of hematomas include infection, swelling, pain, and tissue death.
- Severe complications may include organ damage or in rare cases death due to blood loss.
Home Remedies for Hematoma?
- Apply a warm compress: Soak a cloth in warm water and gently apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time. This may help reduce swelling and speed up healing.
- Take turmeric: Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory spice commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine as an effective home remedy for reducing hematoma swelling.
- Use castor oil: Castor oil has been used for centuries as a treatment for hematomas, thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties. Soak a cloth in castor oil and apply it directly to the affected area several times a day until the swelling goes down.
- Try Gotu Kola: Gotu Kola is an herb used by Ayurvedic practitioners to treat hematomas due to its ability to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of damaged tissues.
- Eat ginger: Ginger is another powerful anti-inflammatory that can be used to reduce the size of hematomas over time thanks to its active compounds called gingerols which act as natural painkillers and anti-inflammatories in the body when consumed regularly
What to eat in Hematoma?
- Lean proteins: chicken, turkey, fish, beans, and tofu
- Fruits and vegetables: spinach, kale, broccoli, apples, oranges
- Whole grains: brown rice, oats, quinoa
- Healthy fats: olive oil, nuts and seeds
- Water
What not to eat in Hematoma?
It is essential to avoid meals loaded with salt, sugar, and saturated fats while treating a hematoma.
Foods such as processed meats, fried foods, sugary snacks and desserts, and fatty dairy products should be avoided.
Hematoma Treatment
- Ice Therapy: The use of an ice pack to the afflicted area may reduce pain and swelling. Ice should never be applied directly to the skin as it can cause frostbite; instead, wrap an ice pack in a towel and apply it for 15-20 minutes at a time several times a day.
- Elevation: Elevating the afflicted region above the level of the heart may help decrease swelling by enabling gravity to assist in the drainage of excess fluid.
- Compression: Wrapping a bandage around the affected area may also help reduce swelling by providing compression that limits fluid from accumulating in the area. This should not be too tight as doing so could restrict circulation or increase pain in the area.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen may help alleviate the pain and inflammation caused by hematoma development.
- Incision and Drainage: This surgical procedure involves making a small incision in the affected area and draining any accumulated fluid or blood.
- Evacuation of Hematoma: This procedure involves surgically removing the hematoma using a needle or scalpel to make an incision in the affected area.
- Embolization: A catheter is placed into a vein in the arm or leg, and employing x-ray imaging, it is directed to the hematoma. The catheter releases a clotting agent which can stop further bleeding, allowing for healing of the hematoma.
- Ventricular Shunt Placement: This procedure is used in cases where there is pressure buildup inside of the head due to a large hematoma that cannot be drained with other treatments. A shunt is placed between two ventricles in order to relieve pressure and allow for drainage of fluid buildup from within the brain or spinal cord.
- Drainage: This involves inserting a needle into the hematoma in order to drain out the fluid.
Which doctor to consult for Hematoma?
Depending on the severity and location of the hematoma, it is usually best to consult a doctor, preferably an orthopedic surgeon or general practitioner.
Which are the best medicines for Hematoma?
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs): These medicines can help reduce pain and swelling associated with hematoma. Ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin are a few examples of them.
- Corticosteroids: These are a type of steroid that can be used to reduce inflammation and swelling in the area affected by the hematoma.
- Vasoconstrictors such as epinephrine, which can be used to constrict blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the area of the hematoma in order to reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Blood thinners such as aspirin or warfarin, which may be used to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of further bleeding if the hematoma is caused by a blood vessel injury.
How long does it take to recover from Hematoma?
Generally, minor hematomas take 1-2 weeks to heal, while larger and deeper ones may take up to several months.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
Generally, treatment can reduce the size of a hematoma, however, the effects may not be permanent.
What are the post- treatments guidelines?
Post-surgical treatment guidelines for a hematoma include:
- Applying ice or cold compresses to reduce swelling and pain.
- To help avoid infection, keep the place dry and clean.
- Elevating the injured region helps to lessen discomfort and swelling by raising it above the level of the heart.
- Using over-the-counter painkillers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to help treat pain and inflammation.
- Wearing loose clothing or a bandage over the area to provide support and comfort while it heals.
- Having regular follow-up visits with a doctor or healthcare provider to monitor healing progress and check for signs of infection or other complications.
What is the cost of Hematoma treatments in India?
Generally speaking, a simple procedure to drain a hematoma can cost around 2000-3000 rupees, while more complex surgeries may cost upwards of 10,000 rupees.
Many hospitals also offer discounted packages for patients who need multiple treatments.
Moreover, the cost of various hematoma treatments may be partially or entirely covered by insurance providers.
What are side-effects of Hematoma treatments?
The most common side effects of hematoma treatments are pain, infection, and bleeding.
Other less common side effects include swelling, bruising, and skin discoloration.
There is a slight possibility that the medication may cause an allergic response.
Hematoma - Outlook / Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to Hematoma then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like ' infection, swelling, pain, and tissue death' in which treatment courses can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find General Physician near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors