Hypothalamus (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
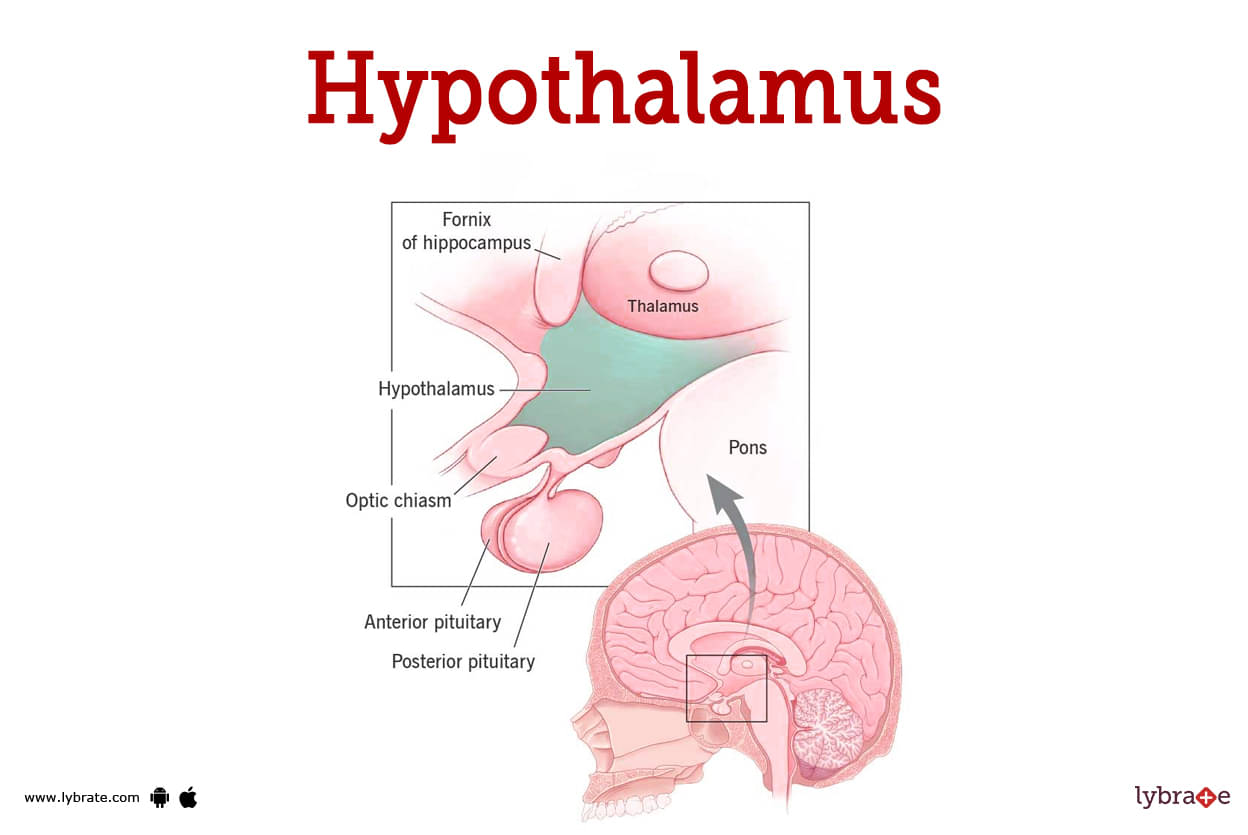
Hypothalamus Image
The hypothalamus is a structure located deep within the brain. It is the primary connection between your endocrine and neurological systems. Your hypothalamus keeps your body in a steady condition known as homeostasis.
It is the floor of the diencephalon (forebrain) with numerous neurosecretory cells that produce a variety of hormones to govern pituitary gland secretion. It also has a few of these nerve cells, whose axons end in the posterior pituitary gland and produce hormones.
Functions of Hypothalamus
The ability of hypothalamic endocrine secretion is to monitor metabolite and hormone levels in the body based on information acquired by the brain.
Hypothalamic hormones produced into the bloodstream go to the pituitary via the hypothalamus physeal portal circulation.
Hormones released both releasing and inhibiting hormones, which controlled the action of several Adenohypophysis hormones, i.e. Pituitary gland.
The hormones secreted by hypothalamus are (TRH) Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone, (CRH/ARh) Corticotropin Releasing Hormone, (GnRH) Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone, (GH-RH/SRH) Growth Hormone Releasing
Hormone/Somatotropin,GH-IH/SOMATOSTATIN) Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone, (PRF) Prolactin Releasing Hormone, (PIF) Prolactin Inhibiting Hormone, (PIF) Prolactin Inhibiting Hormone, and also (MRIH) Melanocyte Inhibiting Hormone).
Hypothalamus Disorders
- Precocious Puberty: it involves Onset of puberty at age more than two standard deviation lower than normal onset
- Central Precocious Puberty: Early maturation of the hypothalamic pituitary-gonadal axis.
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Due to failure of GnRH release ( causes seen below) - leutinizing and follicle stimulating hormone decreased below normal levels.
- Laron Dwarfism: Defective growth hormone receptor (decreased linear growth, increased growth hormone, decreased intrinsic growth factor) some of the symptoms includes Short height, small head, characteristic fades with saddle nose and prominent forehead, delayed skeletal maturation, small genitalia and Increased insulin sensitivity (resistant to diabetes and cancer).
- Hypothalamic Obesity: Injury to the hypothalamus can cause problems with hunger. People who have hypothalamic obesity can have symptoms like, Sudden and excessive weight gain also having symptoms of uncontrolled appetite and also having low metabolism.
- Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea: This condition is sometimes called secondary amenorrhea and happens when you stop having your period.Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea can also be caused by a brain tumor.
- Cushing Syndrome: When your body does not receive enough energy from meals, it might result in elevated cortisol levels. The stress hormone cortisol blocks signals between the brain and ovaries, leading to inadequate hormone production. This affects ovulation and leads to absent periods.
- Central Diabetes Insipidus: The hypothalamus is destroyed by the immune system in this extremely unusual autoimmune disease. Antidiuretic hormone, also known as vasopression, is produced in the hypothalamus and helps the kidneys filter water and keep you hydrated. When the hypothalamus is injured, it stops producing enough antidiuretic hormone, leading to increased urination and thirst.
- Kallman Syndrome: Hypothalamic dysfunction, like Kallman syndrome, can cause a delay in or complete absence of puberty, as well as an impaired or nonexistent sense of smell. Diseases that affect the hypothalamus, such as this one, tend to run in families. It means you won't have enough hormones for sexual development.
- Prader-Willi Syndrome: An insufficiently active hypothalamus is at the root of this genetic disorder. This can cause Intellectual disabilitie, Poor growth, Irresistible urge to eat, Small genitals ,Obesity and Behavioral problems
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone: It is characterised by elevated antidiuretic hormone levels and abnormally low electrolyte levels (SIADH). Damage to the hypothalamus, usually from a stroke, infection, or cancer, is the usual culprit. Too much of this hormone can cause low sodium levels and lead to Weakness, Throwing up, Tiredness, Headaches, and Trouble in thinking.
- Craniopharyngioma: they are benign tumours which grow above the pituitary gland at the hypothalamic axis. they can form cysts which can be solid and hollow.
- Secondary/Tertiary (Central) Hypocortisolism: Central hypoadrenalism may be defined as hypocortisolemia secondary to a deficiency in ACTH. The most common cause of central hypoadrenalism remains exogenous glucocorticoid use.
- Rapid-Onset Obesity with Hypothalamic Dysfunction, Hypoventilation, and Autonomic Dysregulation (ROHHAD): a severe form of paediatric autonomic dysfunction that is extremely uncommon, this condition is marked by a fast growth in weight, as well as a decrease in breathing and a decline in the control of the body's regular metabolic activities.
- Craniopharyngioma: a benign growth that can form as a solid cyst or are also discovered as hollow sacks filled with fluid is called a which is located at the base of the hypothalamus and in close proximity to the pituitary gland.
- Primary Cns Lymphoma: It is a form of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma in which the irregularities and anomalies of the metaplasia are confined to the regions of the brain in which malignant cancer cells from the lymph tissue are found in the brain and in various areas of the spinal cord. Additionally, this form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma affects the central nervous system.
- Metastatic Brain Tumour: It is a secondary kind of brain tumour that can arise from primary cancers located in any part of the body. In this type of brain tumour, the main tumours metastasis, and the cells that transmit the disease from one part of the body to another migrate to the brain.
- Dermoid Tumour: When there is oncogenic activity in the epidermal or dermoid cells in the areas of the brain, then there is evolution of dermoid cyst in the brain and or spinal cord. It is a non-cancerous lesion that is characterised by the presence of uncommon benign and slow-growing masses.
- Pituitary Adenoma: It is a non-cancerous growth of the lesion on the part of the predatory gland and which is not spreading to any other part of the body. They are generally present at the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland and does not invade any other surrounding tissue. They are slow growing tissues which remain dormant for a considerable amount of time.
- Meningioma: They are the most common forms of brain tumours that originate from the arachnoid capsules; they are also slow growing in nature and surround the different parts of the brain if presenting at the base of the skull; they affected the parts of the midbrain and pituitary gland; they also affected the spinal cord or the brain stem. This type of tumour is not cancerous; it is formed from the membrane that covers the spinal cord and the brain and is also called the meninges.
- Ependymoma: They are the malignant tumours that grow in the portion of the brain or any part of the spine; they are an aberrant growth of the glial cells; they are rare in origin and can be depicted as primary tumours; they are found in the brain and in any section of the spine.
- Oligodendroma: They are the brain tumours that are generated by the abnormal development of the glial cells, which then leads to the production of calcium deposits in the glial cells, which causes bleeding and the formation of various cysts, the origin of which may be solid or semi solid.
- Hemangioblastoma: It is a primary brain tumour in origin, and it is a type of benign and highly vascular brain tumour. It does not spread by any other form of infection, but it does spread because of the gradual and benign growth of the vascular tumour in the central nervous system.
Hypothalamus Tests
- Physical Examination: A physician is able to carry out particular physical examinations in order to check the coordination of the hands and legs, as well as the coordination of the eye movements and the speech. These examinations include the testing of reflexes, as well as the testing of the integrity of the joints and the power of the muscles, and the testing of any palpebral pain that may be present in the body.
- CT Scan: During a computed tomography scan, which is more often referred to as a CT scan, several X-ray images of the patient are obtained. With the assistance of a computer, these X-ray images are then transformed into complete photos of the patient's hypothalamus.
- MRI: In order to offer a comprehensive diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (often known as an MRI scan) is a type of imaging technology that may provide exceptionally detailed pictures of the hypothalamus and other areas of the head. The radio waves used in an MRI scan are encased in a magnetic field during the scanning process.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA is an acronym that stands for magnetic resonance angiography. Magnetic resonance angiography is a kind of MRI scan that focuses on the hypothalamic arteries. An MRA scan may detect a blood clot or another possible cause of a stroke.
Hypothalamus Treatments
- Craniospinal Irradiation: Craniospinal irradiation (CSI) is a radiation therapy used to treat central nervous system cancers that have a high risk of spreading to the brain's subarachnoid space. Typically, lateral/anterior oblique cranial and posterior spinal fields are used with low energy megavoltage photons.
- Surgical Resection Of Tumours: The first treat ment for a brain tumor is often surgery. The goal of brain tumor surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing harm. For many patients with intracranial tumors, accurate surgical resection is a mainstay of their treatment paradigm
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: In order to treat tiny brain tumours and functional problems, stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), a non-surgical radiation therapy, is increasingly being employed in neurosurgery. It is a non-invasive therapy that targets the tissue with extremely focussed radiation beams.
- Craniotomy: In order to relieve pressure from within the skull, this procedure is carried out by a surgeon, who makes a hole in the side of the head by drilling through it. It is carried out in cases when there is an infection that is creating an abnormally high level of pressure in the hypothalamus and the brain.
- Lumbar Drain: When a drain is inserted into the fluid that surrounds the spinal cord, the fluid in the lumbar area will begin to drain. It is possible that the hypothalamus and spinal cord will experience less stress as a result of this.
- Radiation Therapy: If the cancer has already advanced to the hypothalamus, radiation therapy may be able to reduce symptoms and stop the growth of the disease.
Hypothalamus Medicines
- Thrombolytics for Hypothalamus Infarcts: If these therapies are given during the first few hours following the beginning of symptoms, they have the potential to lessen the severity of some types of strokes, and in some cases, they may even be able to cure them entirely.
- Antiplatelet agents for Thrombolysis of Clots: Antiplatelet medications are one kind of treatment that can reduce the likelihood of a blood clot being formed. Antiplatelet drugs like aspirin and clopidogrel are two examples of the types of treatments available (Plavix). As a direct consequence of this, there is a possibility that the risk of having a stroke will be reduced.
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: These are some of the pharmaceuticals that have demonstrated some potential for enhancing patients' cognitive capacities, ranging from moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. They do not have any impact in preventing Alzheimer's disease or delaying its course in any way.
- Analgesics for Migraine and Headaches: Analgesics are drugs that are taken to alleviate pain in addition to lowering the number of prostaglandins that are produced by the body. It is recommended that the medications be used no later than forty-eight hours following any cardiovascular incident that causes discomfort at the time.
- Diuretics for maintaining Hypothalamus Blood Pressure: Furosemide, Torsemide, Bumetanide, Hydrochlorothiazide, and Metolazone are diuretics that reduce fluid transportation by increasing urine output and so reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. Also for relieving cerebral edema the medicine known as mannitol is useful.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 7 functions of the hypothalamus?
What hormone does the hypothalamus produce?
What can cause damage to the hypothalamus?
How is hypothalamic disorder diagnosed?
Can hypothalamus disorders be cured?
How do you reset your hypothalamus naturally?
How do you know if you have a hypothalamus problem?
What diseases affect the hypothalamus?
How can I fix my hypothalamus naturally?
Can hypothalamus be repaired?
Table of content
Find Endocrinologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors