Kidneys: Image, Function, Diseases, Treatments and Medicines
Last Updated: Apr 07, 2023
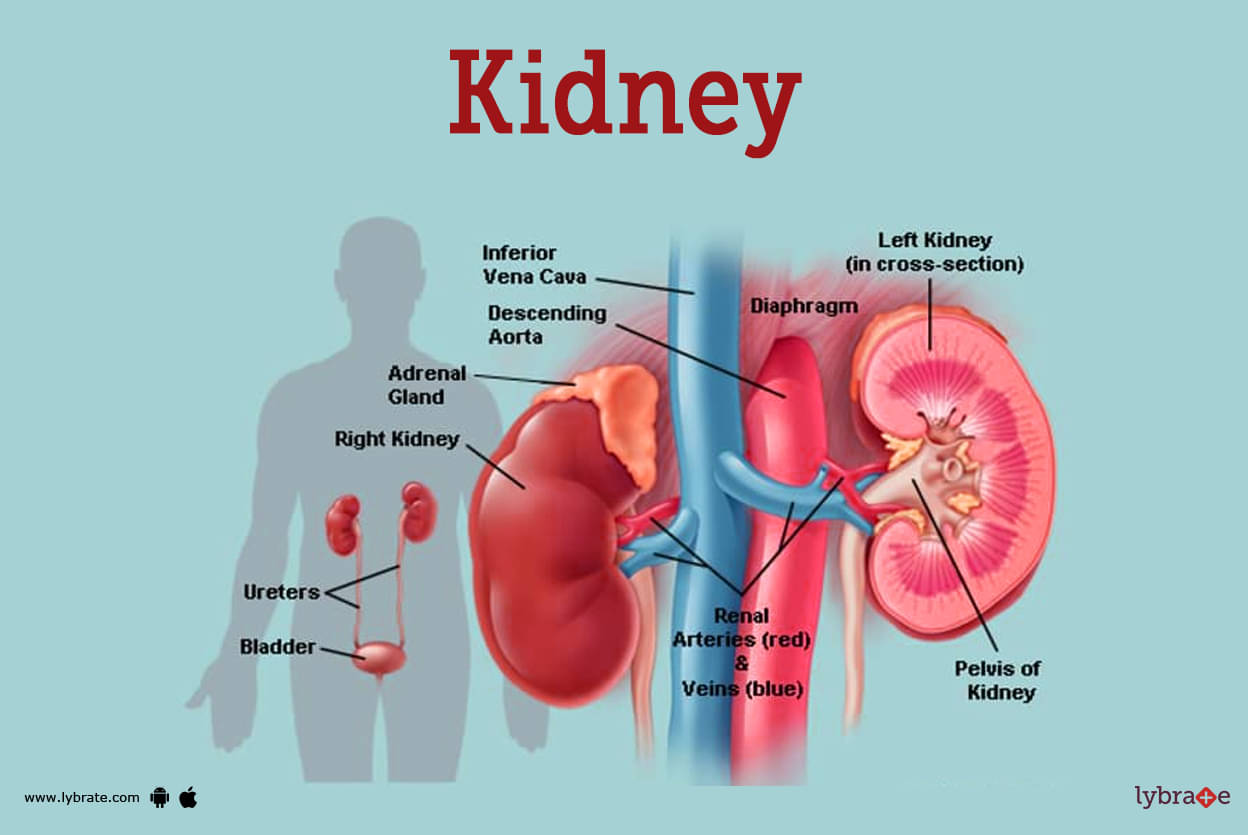
Kidneys Image
Two bean-shaped organs, the kidneys are each roughly the size of a fist. One is on either side of your spine, directly below the rib cage. Around half a cup of blood is filtered by healthy kidneys every minute, with the extra water and waste products exiting the body via urine.
Two skinny muscle tubes known as ureters, one on either side of your bladder, carry urine from your kidneys to the bladder. Your bladder collects and stores your urine. The kidneys, ureters, and bladder make up the urinary tract.
Kidney Functions
Kidney is the most important organ for regulation of metabolic waste material and PH balance of our blood. it constitutes of various parts each of which performs a specific function consisting of corpuscles, tubules, pyramid, collecting ducts ,calyces etc
- Renal Corpuscle: After entering a nephron, blood travels to the renal corpuscle, also known as a Malpighian body. The renal corpuscle has two extra structures:
- Renal Tubules: The renal tubules consist of a series of tubes that extend from the Bowman capsule to the collecting ducts. Each tubule consists of many segments. By the time fluid reaches the tubule's end, it has been diluted and filled with urea.
- Renal Cortex: It is the outer part of the kidney. It consists of the glomerulus and tubules that are convoluted. It is encircled by the renal capsule, a layer of fatty tissue, on its outer margins. Together, the renal cortex and capsule protect and house the kidney's interior components.
- Renal Medulla: It is the kidney's inner, smooth tissue. It encompasses both the Henle loop and renal pyramids.
- Renal Pyramids: The renal pyramids are tiny structures composed of nephrons and tubules. These tubules provide the kidney with fluid. This fluid then flows away from the nephrons and toward the structures within the kidney that collect and transport urine.
- Collecting Ducts: Each nephron's terminal end contains this structure in the renal medulla. This is the location where filtered fluids leave the nephrons. Once the fluid reaches the collecting duct, it continues to the renal pelvis.
- Renal Pelvis: It is a funnel-shaped region in the kidney's innermost portion. It serves as a conduit for fluids on their route to the bladder.
- Calyces: The calyces are located in the first portion of the renal pelvis. These are little compartments in the shape of cups that catch fluid before it enters the bladder. Additionally, here is where excess fluid and waste produce urine.
- Hilum: The hilum is a tiny aperture on the kidney's inner border, where it curls inward to form its distinctive bean-like shape.
- Ureter: Urine is pushed into the bladder via the ureter, a muscular tube.
Kidney Diseases
- Acute Renal Injury: Acute kidney injury (AKI), commonly referred to as acute renal dysfunction (ARF), is an episode of renal failure or damage that occurs suddenly and lasts for a few hours or days. Chronic Renal Failure: Because of regular impairment of kidney functions the infrastructure of kidney undergoes changes which is considered as CRF. Usually, a major medical condition like diabetes, high blood pressure, or cardiovascular disease will cause complications.
- Urinary Tract Infection: UTIs are infections of the urinary system, which can affect the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra (UTI).Female individuals are more prone for UTI than males.
- Pyelonephritis: When some sort of infection is spread from kidney to the bladder this condition is called Pyelonephritis. In this situation discomfort in the abdomen and recurrent fever with symptoms of nausea and vomiting and burning micturition occurs.
- Glomerulonephritis: To damage the little filter inside your kidneys is known as glomerulonephritis (the glomeruli). It occurs because of complete targeting of our immune system by any sort of foreign infection. Although minor occurrences of glomerulonephritis could be adequately managed, the disorder can sometimes cause long-term renal issues in some people. Nephrolithiasis, Or Kidney Stones: Although ureteral calculi (ureterolithiasis) and renal calculi (nephrolithiasis) are particularly kidney calculi, they are frequently discussed together .
- Ureteric Calculi: Even after they have lodged in the ureter, ureteral calculi virtually invariably start in the kidneys. Calcium is a common component of renal calculi.
- Renal Colic Pain: Due to the acute ureteral blockage, dilatation, stretching, and spasm are the main causes of pain in renal colic.
- Nephrotic Syndrome: The kidney ailment nephrotic syndrome is characterised by an increase in the quantity of protein excreted in the urine.Nephrotic syndrome is typically brought on by harm to the collections of tiny blood capillaries in your kidney that remove waste and additional water from blood stream.
- Kidney Cysts: Cysts are fluid-filled, spherical, non-cancerous sacs. The cysts can get very large and come in a variety of sizes. Your kidneys can become harmed if you have a lot of cysts or big cysts.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease: Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a hereditary disorder that causes clusters of cysts to form mostly within your kidneys, leading to enlargement and decreased kidney function over time.
- Acute Renal Failure: Acute kidney failure is the sudden inability of the kidneys to remove waste from the circulation. A harmful buildup of waste products and an unbalanced chemical composition of your blood may result from your kidneys losing their filtering capacity.
- Chronic Kidney Failure: Renal function declines progressively in patients with chronic kidney disease, often known as chronic kidney failure. If your chronic kidney disease has progressed, your body might build up dangerous levels of fluid, electrolytes, and wastes.
- End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): It is also known as end-stage kidney disease or renal failure, develops when chronic kidney disease—the progressive loss of kidney function—reaches an advanced stage. Your kidneys no longer function as they should to support your body's needs if you have end-stage renal disease.
- Papillary Necrosis: An illness of the kidneys known as renal papillary necrosis causes all or some of the renal papillae to die. The kidney papillae are the regions where the collecting duct apertures reach the kidney and also where urine passes into the ureters.
- Diabetic Nephropathy: In individuals with diabetes, a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the presence of excessive amounts of urine albumin excretion characterise the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy (DN), also known as diabetic kidney disease. One frequent consequence of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is diabetic nephropathy.
- Hypertensive Nephropathy: A medical ailment known as hypertensive kidney disease describes kidney damage by persistently high blood pressure.
- Nephrosclerosis: As hypertensive nephrosclerosis, it shows symptoms It should be separated from renovascular hypertension, a type of secondary hypertension with an entirely different mechanism of aetiology.
- Pyonephrosis: Due to ureteral blockage, pyonephrosis is a suppurative infection of the upper urinary system. It frequently leads to renal function loss and suppurative damage to the renal parenchyma. Patients are typically symptomatic, however 15% of patients may continue to be asymptomatic. If a severe infection in the pyonephrosis is not promptly treated with surgery, it may result in urosepsis and jeopardise life.
- Hydronephrosis: The swelling of a kidney brought on by a buildup of urine is known as hydronephrosis. It occurs when there is an impediment or blockage preventing urine from flowing freely from the kidney into the bladder. You can have hydronephrosis in one or even both kidneys.
- Cancer Of The Kidney: When metaplasia activity occurs in the Kidney it is termed as carcinoma of kidney. Each side of your spine has a kidney, which is located behind your abdominal organs.
- Interstitial Nephritis: A kidney condition known as interstitial nephritis causes the gaps between the renal tubules to swell (inflamed). Your kidneys may have trouble functioning as a result of this.
- Minimal Change Disease: This condition can also cause nephrotic syndrome. A collection of symptoms known as nephrotic syndrome includes protein in the urine, lower serum protein levels, high cholesterol, excessive triglyceride levels, and edema.
- Perinephric Abscess: It is collection of pus around the kidney, which involves cortical extension and hematogenous spread routes, mostly chances of occurrence because of the infection through E coli in which there is recurrent pain, fever and tenderness seen as a sign and symptom.
- Genitourinary Tuberculosis: It is a secondary infection of the kidneys spread by hematogenous spread of tuberculosis from the lungs. One of the primary organs involved in this is the kidney and prostate is also affected through it.
- Renal Agenesis: Renal agenesis is a birth defect in which one or both kidneys are absent at birth. If this disorder develops in only one kidney, it is known as unilateral agenesis; if it affects both, it is known as bilateral agenesis.
- Emphysematous Pyelonephritis (EPN): A serious infection of the renal parenchyma is the source of tissue gas buildup. EPN occurs more frequently in individuals with diabetes mellitus, particularly women. Its symptoms resemble those of acute pyelonephritis.
- Hyperuricemia: It leads to the formation of uric acid crystals in the glomeruli, which in turn generates inflammation of the renal parenchyma and renal failure.
Kidney Tests
- Urinalysis: A urine analysis can aid in the early detection of a number of kidney and urinary problems, such as diabetes, kidney stones, chronic kidney disease, and bladder infections.
- USG Kidney: This examination takes an image of the kidney using sound waves.It can detect obstructions such tumours or stones, and irregularities in kidney size and shape.
- CT scan: This imaging technique utilises x-rays to capture pictures of the renal system. If a UTI spreads to the kidneys, however, it might have devastating effects .Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography CECT: In this scan X-rays are used for diagnosing specific diseases of the kidney the image is enhanced through intravenous contrast dye better gives better prognosis For this test, intravenous contrast dye may be used, which kidney patients may find concerning.
- MAG 3 Study: It is a test used for diagnosis of renal perfusion in which mercapto acetyl glycine is involved . It is known as the gold standard for diagnosis of renal perfusion.
- MRI: Due to the combined importance of the anatomical and functional information offered, as well as the unique contrast patterns that may be detected non-invasively, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of healthy and diseased kidneys offers considerable potential. Imaging with several contrasts can reveal infiltrative kidney diseases.
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): Protein within foods you eat breaks down, producing urea nitrogen. BUN levels should be within 7 and 20. As renal function decreases, so does the amount of BUN in the blood.
- Ureteroscopy: A small telescope called a ureteroscope is passed into the urethra and bladder, up the ureter, and to the place in which the stone is located during ureteroscopy, a technique to treat kidney stones. The surgery typically takes one to three hours to finish and is usually done while the patient is under general anaesthesia.
- Kidney Biopsy: A kidney biopsy is a process in which a tiny piece of kidney tissue is surgically removed and studied under a microscope. You may use it to look for obstructions and structural flaws.Pressure Flow Study (Whittaker Test): In this the kidney is punctured percutaneously and contrast is injected into the pelvis simultaneously intrapelvic pressure is measured if there is an abnormal rise in intra pelvic pressure it should be suggestive of pelvic ureteric junction obstruction
Kidney Treatments
- Nephrostomy: An artificial opening between both the kidney and the skin known as a nephrostomy enables urinary diversion straight from the upper urinary tract (renal pelvis).
- Lithotripsy: Shock waves are used during the technique known as lithotripsy to dislodge kidney and ureter stones. Following the surgery, the minute stone fragments leave your body through your urine.
- Nephrectomy: The term 'nephrectomy' refers to the surgical procedure in which a kidney is removed or dissected. Along with other kidney disorders and traumas, kidney cancer is treated using this approach. Another use of nephrectomy is to withdraw a healthy kidney for transplantation from a donor, either alive or dead.
- Hemodialysis: A person whose kidneys are not functioning correctly undergoes hemodialysis, also known as haemodialysis or simply dialysis, to filter their blood. Whenever the kidneys are in a condition of renal failure, this type of dialysis removes wastes like creatinine and urea as well as free water in the body extracorporeally.
- Peritoneal Dialysis: It is a form of dialysis in which fluid and dissolving materials are exchanged with blood through the peritoneum in the abdomen of the patient. In patients with kidney failure, it is used to eliminate excess fluid, fix electrolyte issues, and get rid of pollutants.
- Kidney Transplant: Renal transplantation, often known as a kidney transplant, is the surgical procedure through which a healthy kidney is surgically implanted into a recipient who has chronic or irreversible kidney failure (ESRD)
- Cadaveric and Living Transplantation: Depending on where the donor organ comes from, kidney transplantation is often categorised as either living or deceased donor (previously known as cadaveric) transplantation. Living-donor kidney transplants can be further subdivided into 'living-related' and 'living-unrelated' transplants based on the donor and recipient's genetic similarity or dissimilarity.
- Open Stone Surgery: It is open surgery for extraction of complicated renal stones done since ancient times still now it is used for larger stone extraction and complicated renal surgeries
- Laparoscopic Cyst Ablation: It is a minimally invasive procedure for the removal of kidney cysts. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty corrects issues at the point where the ureter and kidney connect.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): Non-invasive lithotripsy, which employs shock waves to break up big kidney stones so they may move more readily via the urinary system, and nephrolithotomy are procedures used to treat kidney stones.
- DJ Stenting: A stent is an approximately 10-inch-long, hollow tube that extends from the kidney to the bladder to allow for normal urine flow. A cystoscope, a thin, flexible device, is inserted via the urethra by the surgeon.
- ESWL, Or Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy: It is a typical, non-invasive treatment for kidney and ureter stones, the tube that empties urine from the kidney to the bladder. It employs a source of energy that creates a shock wave directed towards the stone.
- Intracorporeal Lithotripsy: Lithotripsy is an intravenous procedure used to treat urolithiasis by breaking up and removing urinary stones. These operations are conducted in the urinary system using endoscopes.
Kidney Medicines
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics: Fluoro-quinolones (e.g.First-line therapy for acute, uncomplicated pyelonephritis is oral ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily for 7 days).
- Renal Specific antibiotics: Women who are pregnant and have urinary tract infections Antibiotics like nitrofurantoin, ampicillin, and the cephalosporins can be used with reasonable safety throughout the first trimester of pregnancy. Masculine urinary tract infections A fluoroquinolone or is advised for 7-14 days in treating a UTI in males with no evident complications.
- Diuretics: These medications are not only used to treat edema, but also other conditions that cause fluid retention, such as heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, and high blood pressure. Diuretics such as aldactone, bumetanide, torsemide, hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and metolazone are used by a wide variety of doctors.
- Statins: These are known as lipid-lowering medicines with additional positive features for reducing the progression of CKD, such as decreasing oxidative stress and inflammation. Some of the examples of statins are rosuvastatin, atorvastatin etc
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs): They belong to a class of drugs that inhibit the renin–angiotensin system and are believed to reduce proteinuria and albuminuria. Some of the drugs known to be found in market are Benazepril (Lotensin), Captopril (Capoten), Enalapril etc
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs): These are the drugs which decrease the functioning of angiotensin receptors decreasing the efficacy of RAAS mechanism. and improving the functioning of kidneys reducing inflammation. Some of the ARBs known to be used by expert physicians are andesartan (Atacand), eprosartan (Teveten), telmisartan, Losartan etc
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of action of these drugs involves inhibiting the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to sites of cellular and tissue damage. Some of the important corticosteroids includes methylprednisolone
- Alkalyzers: For the treatment of hyperuricemia, hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis , and also in the case of renal stones alkalizer or alkalizing agents are used which increases the pH level of kidneys reducing the renal inflammation, some of the examples of alkalizing agents are sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium citrate, magnesium hydrogen carbonate etc.
Table of content
Find Nephrologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors