Labrum tear: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 09, 2023
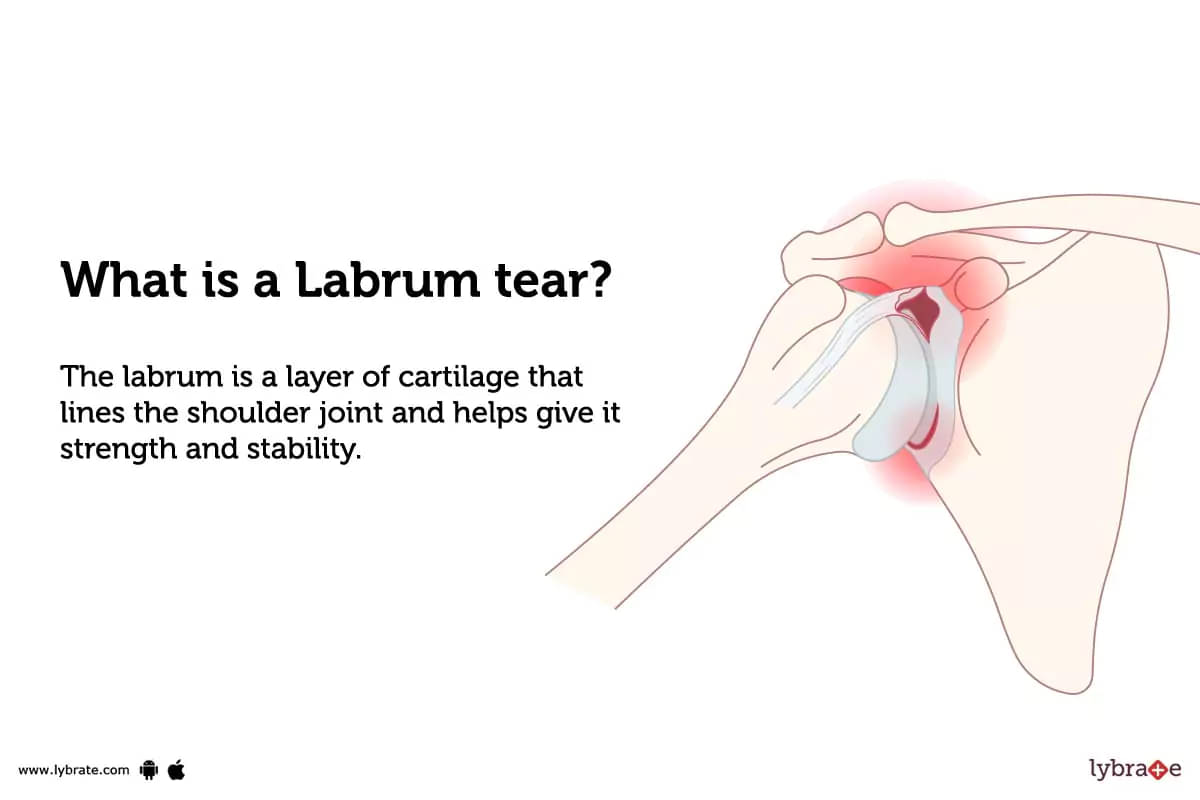
What is a Labrum tear?
The labrum is a layer of cartilage that lines the shoulder joint and helps give it strength and stability. A labrum tear is an injury to this cartilage, often caused by repetitive motion of the shoulder or a sudden event such as a fall.
Types of Labrum tear
- SLAP tear (Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior tear): A SLAP tear is a tear of the labrum at the junction of its superior and anterior attachments. It is typically associated with an injury to the biceps tendon or repetitive overhead motions, like throwing a ball.
- Posterior Labral Tear: This type of labrum tear occurs in the backside of the labrum, often as a result of trauma such as a dislocated shoulder or falling on an outstretched arm.
- Bankart Tear: This type of labrum tear usually takes place in front portion of the labrum at its junction with glenoid rim due to repeated violent motions like tackling or lifting heavy objects.
- Arcuate Ligament Injury (ALI): ALI typically occurs when there is an excessive backward stress to the shoulder joint, resulting in tearing of the arcuate ligaments which provide stability to both the front and rear portions of the labrums.
What causes Labrum tears?
- A labrum tear is typically caused by a traumatic event such as a dislocation, falling on an outstretched arm, or sports activities that involve repetitive or forceful use of the shoulder.
- Labrum tears can also be created over time due to degenerative wear and tear on the shoulder structure.
What are the symptoms of Labrum tear?
- Pain in the shoulder, especially when the arm is lifted away from the body or rotated.
- A feeling of shoulder instability or locking up in certain positions of the shoulder joint.
- A catching or grinding sensation when moving the shoulder joint.
- Weakness in certain shoulder movement patterns and difficulty completing full range of motion in certain directions of movement.
How can you prevent Labrum tears?
- Avoid overuse of shoulder joints-strengthen shoulder and core muscles with appropriate strength training exercises.
- Increase awareness and mobility of shoulder joints by doing shoulder stretches, increasing flexibility.
- Make sure to warm up thoroughly before physical activity and cool down after exercise as well.
- Monitor intensity, volume, and duration of physical activity to prevent overexertion or repetitive motion.
- Ensure proper techniques when playing sports, lifting weights or participating in other activities that involve shoulder movements.
Labrum tear - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical examination:The doctor will likely examine the injured area and press on it to check for sensitivity while flexing your hip or rotating it in different positions. They may also order X-rays or an MRI scan to diagnose a labrum tear.
- Arthroscopy:An arthroscopic procedure involves inserting a small camera into the joint to view the inside of the body and diagnose any problems.
- X-rays:X-rays will help show bone structures in your hip as well as provide information about any irregularities that could indicate a labrum tear such as fluid build up in your joint or bulging around the rim of your shoulder socket indicating possible injury to the ligaments and tendons.
- MRI scan:MRI scanning is the most common imaging technique used to detect labral tears, identify associated injuries, and measure cartilage damage in both hips (hips can differ).
- Ultrasound scan:Ultrasound scans help assess soft tissue injuries such as tendon attachments, muscle damage and inflammation but are less helpful when assessing labral tears since they do not create clear images of complex structures like bones and ligaments due to their dependence on movement (which is limited by pain).
What are possible complications of Labrum tear?
- Pain and instability:Labrum tears tend to cause pain in the shoulder joint area, accompanied by a decrease in range of motion and difficulty performing normal tasks.
- Weakness:Some people with labrum tears experience weakness in the shoulder as a result of decreased strength in the muscles around the joint.
- Reduced stability and coordination:Labral tears can cause instability, leading to less coordinated movements of the affected arm or arm muscles, which can lead to additional problems with sports activities or everyday activities.
- Bony impingement:Labral tears can cause increased friction between bones that comprise the shoulder joint, resulting in bony impingement which can be painful and restrictive on movement.
- Joint arthritis:Arthritis is often caused by deterioration of cartilage within a joint; labrum tears may predispose a person to developing arthritis because of ligament damage that disrupts normal movement patterns causing extra stress on other structures within the joint.
Home Remedies for Labrum Tears?
- Apply warm Castor oil or Aloe Vera gel compress to the affected area for 15 minutes twice a day.
- To reduce inflammation consume 1 teaspoon of turmeric powder daily with a glass of warm milk.
- Dip linseed in water overnight and apply them as poultices to the affected area in the morning.
- Drink honey, ginger and cinnamon tea 3 times a day to promote healing and reduce pain associated with Labrum tears.
- A diet rich in protein, Vitamin C, zinc and omega-3 fatty acids can aid in healing of torn labrum muscles and improve mobility of shoulders.
What to eat in Labrum tears?
- A diet for Labrum tears should include foods that are high in healthy proteins and carbohydrates, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, nuts, whole grains and fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids should be included in your diet such as salmon and other cold water fish, flaxseeds and walnuts to help reduce inflammation around the joint caused by labrum tear.
- Stay hydrated by consuming plenty of water throughout the day in order to keep your muscles strong and properly lubricated for better mobility of your shoulder joint affected with labrum tear.
What not to eat in Labrum tears?
- Fried and processed food:Fried and processed foods are usually high in unhealthy fats and sodium, which can be damaging to the muscles and joints. These foods can increase inflammation, making it harder for the body to heal after a labral tear.
- Dairy products:Dairy products are high in saturated fat as well as inflammatory proteins that can delay the healing process of a labral tear.
- Foods high in sugar:Sugary snacks, sugary drinks, condiments with high sugar content should all be avoided while recovering from a labral tear as they create extra strain on the body which can slow down recovery time.
- Alcohol:Alcohol is not only a depressant but is an inflammatory stimulant when consumed in excess amounts meaning that it can increase inflammation around the injured time slowing down the healing process for a labral tear.
Labrum tear Treatment
- Medication:Medications may be prescribed to further reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain associated with a labral tear.
- Rest:Rest is essential to aid in the healing and prevention of further damage.
- Physical therapy:An exercise program supervised by a physical therapist is essential for a proper recovery from labrum tear surgery or other treatments for this condition as it helps to reduce swelling and increase mobility while increasing strength in the shoulder area through stretching exercises and strengthening exercises.
- Arthroscopic Surgery:A minimally invasive procedure in which the surgeon repairs the labrum with a small camera, specialised tools, and tiny instruments inserted into small incisions in the shoulder joint.
- Open Surgical Repair:More invasive option that requires a larger incision through which the surgeon accesses the shoulder joint to repair the labrum.
- Debridement:Arthroscopic technique where excess tissue is removed from around the tear, allowing for more movement of shoulder joint and some pain relief, but not returning natural shoulder stability/function.
Which doctor to consult for Labrum tear?
It is recommended that you consult an orthopaedic doctor, who specialises in muscular and skeletal injuries, to obtain a diagnosis and treatment plan for a labrum tear.
Which are the best medicines for Labrum tears?
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):These drugs work by reducing inflammation and providing pain relief. Examples include ibuprofen, naproxen, celecoxib, and diclofenac.
- Corticosteroids:These drugs are cortisone-like medications used to reduce inflammation and can be used as injections or oral medications. Examples include prednisone, methylprednisolone, and triamcinolone.
- Opioids:These are strong pain medicines that may be used when NSAIDs or corticosteroids do not provide enough relief from the pain associated with labrum tear. Examples include codeine, hydromorphone, oxycodone and tramadol.
- Muscle relaxants:Muscle relaxants may be prescribed for the initial phase of the recovery process to help relieve painful muscle spasms associated with labrum tear. Examples include cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), diazepam (Valium) and carisoprodol (Soma).
How long does it take to recover from Labrum tear?
The amount of time that it takes to recover from a labrum tear varies widely, depending on the severity of the injury, the type and effectiveness of treatment, and the speed at which an individual heals.
Generally, recovery can take anywhere from three months to more than a year.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The results of the treatment for a labrum tear can be permanent, depending on the severity and cause of the tear. Surgery is usually necessary to restore function in the joint, and physical therapy can help to improve range of motion and flexibility, reduce pain and swelling, and aid in strengthening muscles that support the joint. With proper care and rehabilitation following surgery, full recovery without further damage can be expected.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Avoid high-impact activities such as running and participating in contact sports for at least six months to allow for full healing
- Keep your arm elevated when sitting or lying down to reduce inflammation.
- Ice the affected area several times a day or as recommended by a doctor.
- Perform a range of motion exercises as suggested by the physical therapist.
- Monitor symptoms closely, such as pain levels and any unusual swelling in the shoulder joint.
- Wear a brace or sling if required to avoid overuse and support the labrum.
What is the cost of Labrum tear treatments in India?
The cost of treatment for labrum tear in India can vary significantly depending upon the location and severity of the injury. Generally, treating a labrum tear can cost anywhere from ₹20,000 - 1 lakh depending on the extent of surgery and rehabilitation.
What are side-effects of Labrum tear treatments?
- Postoperative pain:Pain in the shoulder joint may occur after surgical treatment of a labrum tear, which can last up to several weeks.
- Nerve injury:An injury to the nearby nerves, such as the axillary nerve, is possible during labrum tear treatments.
- Hematoma:A collection of blood outside the blood vessels occurs sometimes during surgery for labrum tears and could lead to wound drainage and infection.
- Infection:In certain cases, an infection may arise at the surgical site or elsewhere in the body following a labrum tear procedure.
- Adhesions:Scar tissue can form around the repair site, which leads to a decrease in range of motion of the shoulder joint after healing from a labrum tear issue.
Labrum tear - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to labrum tear then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'weakness, bony impingement, joint arthritis' in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors