Lung Transplant: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
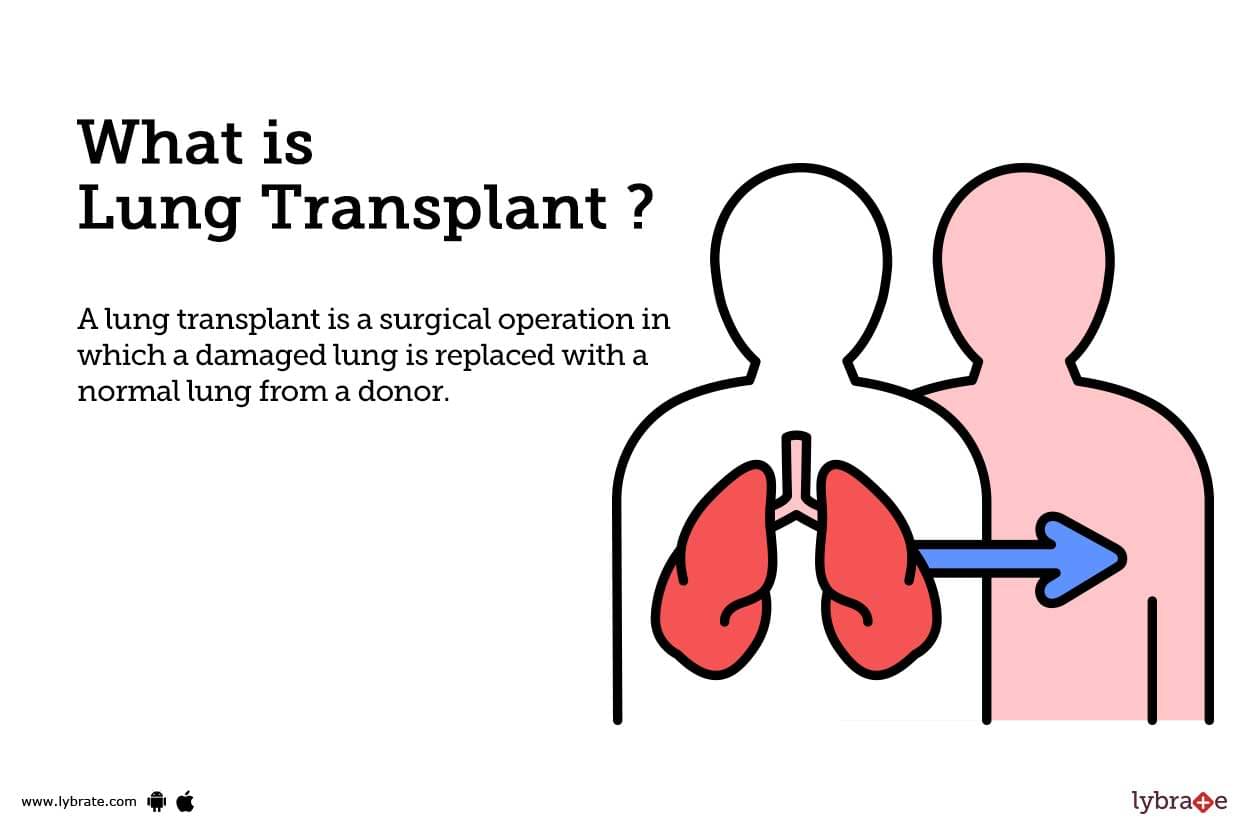
What is Lung Transplant ?
A lung transplant is a surgical operation in which a damaged lung is replaced with a normal lung from a donor. The donor might be alive or dead. The main goal of the transplant is to improve the quality of life for the patient by providing them with healthy and functioning lungs.
Lung transplants are typically used for patients with end-stage pulmonary diseases such as cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary hypertension.
Types of Lung Transplant
Lung transplants are classified into two types: single and double lung transplants.
- Single lung transplant: A single lung transplant is when only one of the patient’s lungs is replaced with a donor organ. Patients who have severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cystic fibrosis frequently require this sort of transplant.
- Double lung transplant: A double lung transplant involves the replacement of both lungs at the same time. This type of transplant is typically done for patients with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, or other conditions that have caused irreversible damage to both lungs.
Benefits of Lung Transplant
- Improved quality of life: A lung transplant can help improve a person’s quality of life by improving their breathing capacity, reducing their fatigue and increasing their ability to participate in physical activities.
- Increased lifespan: Patients with lung disorders like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis may benefit from lung transplants to live longer.
- Reduced symptoms: After a successful transplant, many patients experience a reduction in symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Improved oxygen levels: Patients who receive a lung transplant often have improved oxygen levels in their blood, which helps reduce the risk for other complications associated with low oxygen levels in the body, such as heart failure and stroke.
- Increased energy levels: After a successful transplant, many patients report an increase in energy levels due to improved breathing capacity and increased oxygen levels in the blood stream.
Why is Lung Transplant done?
A lung transplant is done when a person's lungs are no longer able to adequately provide the oxygen and other gases necessary for life.
There are a number of disorders that are capable of causing this, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (also known as COPD), cystic fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, and other uncommon lung diseases.
When all other treatment options have been exhausted, a lung transplant may be the only one left to attempt to improve the patient's quality of life or lengthen their life expectancy.
What are the risks of Lung Transplant ?
The following are some of the risks involved with getting a lung transplant:
- Infection: Following a lung transplant, a patient's body may become susceptible to infection from bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Rejection: The body’s immune system may recognize the transplanted lungs as foreign and attack them, leading to rejection of the transplant.
- Blood clots: Clotting of the blood vessels in or nearby the lungs can occur after a lung transplant, leading to serious complications such as stroke or heart attack.
- Bleeding: Bleeding can occur at the site where the donor lungs were attached to your body, or it can happen internally due to weakened blood vessels in your new lungs.
- Lung damage: Damage to your new lungs can be caused by infection, rejection or other factors that are not yet fully understood.
- Chronic organ dysfunction syndrome (CODS): This is a condition that affects many organ transplant patients and is characterized by inflammation of organs that don’t heal properly and cause ongoing symptoms such as fatigue and pain.
How do I prepare for Lung Transplant ?
- The process of getting ready for a lung transplant is a lengthy one that requires preparation on both the physical and the mental fronts. Before going through with this major operation, it is critical to have one's mind and body in the right state of preparedness.
- Before the transplant, you will need to undergo a series of tests to assess your physical condition and determine if you are a suitable candidate for the procedure. These tests may include blood tests, imaging studies (such as X-rays or CT scans), pulmonary function testing, and other specialized tests.
- In addition, your doctor will examine your medical history and talk to you about any possible hazards that may be linked with the surgery.
- In addition to these medical evaluations, it is important to make sure that you are emotionally prepared for the surgery as well.
- Discuss your concerns regarding the operation with your doctor.
- You should also make sure that you have a strong support network in place before undergoing the transplant, including family members or friends who can provide emotional support during this difficult time.
- Finally, it is important to take steps to ensure that your home environment is safe after the transplant so that you can recover properly from surgery.
- This may include making modifications such as installing grab bars in bathrooms or removing throw rugs from floors.
- Additionally, it is important to make sure that someone will be available at all times during your recovery period who can provide assistance if needed.
How Lung Transplant is done?
- The first step in the process of getting a lung transplant is to be evaluated by a team of specialists to determine if you are eligible for this type of surgery.
- Once you have been approved as an eligible candidate, you will then be placed on a waiting list until an appropriate donor organ becomes available.
- The actual transplant procedure begins with general anesthesia being administered to the recipient and donor organs being removed from both individuals.
- The donor's healthy lungs will then be carefully examined and prepared before they are transplanted into the recipient’s body.
- Depending on severity, the surgery takes four to six hours.
- Afterward, patients must remain in intensive care for several days while their bodies adjust to their new organs and medications are adjusted accordingly.
Steps to perform Before the procedure
- Ensure the patient is in sufficient health to undertake the surgery.
- Obtain informed consent from the patient.
- Perform a pre-operative workup including a physical exam, chest x-ray, and pulmonary function tests.
- Assess the patient’s eligibility for transplantation.
- Determine if there are any contraindications or risks associated with the procedure.
- To verify compatibility between the donor and recipient, get donor lungs and conduct crossmatching testing.
- Administer immunosuppressive medications to prepare the recipient for transplantation.
- Place a venous catheter in order to provide access for medications and fluids during surgery.
- Initiate anticoagulation therapy.
- Prepare surgical equipment and instruments needed for the procedure.
Steps to perform During the procedure
- A breathing tube is introduced into the patient's airway while they are under general anaesthesia.
- A chest tube is inserted to allow for drainage of excess fluid and air from the lungs.
- To reveal the heart and lungs, the surgeon performs a chest incision.
- The donor lung is removed from the donor and prepared for transplantation.
- The recipient’s lung is then removed, and the new donor lung is placed in its place with sutures, staples, or clamps to secure it in place.
- The surgeon reconnects all of the blood vessels that will supply oxygenated blood to the new lung, as well as any other necessary connections between organs or tissues that need to be reattached during transplantation surgery (such as trachea).
- Once all connections have been made, the chest cavity is closed with sutures or staples and a sterile dressing applied over it for protection against infection or other complications that may arise during recovery time after surgery has been completed.
- After surgery has been completed, medications will be administered to help control inflammation and reduce pain levels associated with recovery from transplantation surgery
Steps of perform After the procedure
- Keep an eye on the patient's temperature, pulse rate, and oxygen levels.
- Administer medications to help prevent infection and rejection of the new lung.
- Monitor the patient for any signs of rejection or infection, such as fever, difficulty breathing, or chest pain.
- Perform regular chest X-rays to check for any changes in the new lung tissue.
- Check for any fluid buildup in the lungs and perform a bronchoscopy if needed to remove it.
- Encourage deep breathing exercises to help strengthen the lungs and prevent pneumonia or other respiratory infections.
- Provide lifestyle advice on how to maintain a healthy lifestyle after transplantation, such as avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough restful sleep each night.
- Provide emotional support to help with adjustment issues after transplantation surgery
How much does Lung Transplant cost in India?
The cost of a lung transplant in India can vary significantly depending on the hospital, type of procedure, and other factors.
Generally, the cost of a lung transplant in India ranges from around Rs. 15 lakhs to Rs. 25 lakhs.
What to eat after Lung Transplant ?
- It is important to eat a healthy, balanced diet after a lung transplant. Eating well may aid in recovery and maintenance of health.
- Fruits, veggies, lean protein, healthy grains, and low-fat dairy items should all be prioritised. Eating a wide range of foods will help you acquire the nutrients your body needs for a speedy recovery.
- Consuming lots of fluids is also crucial following a lung transplant. Although water is ideal, other beverages, such herbal teas, could also be effective at keeping you hydrated.
- Finally, it is important to avoid alcohol after a lung transplant as it can interfere with your medications and weaken your immune system.
Is Lung Transplant safe?
Yes, lung transplant is generally safe.
However, there are risks associated with every medical operation.Lung transplant surgery carries with it the risk for infection, bleeding, and organ rejection.
Is Lung Transplant painful?
No, a lung transplant is not painful. Although there is a possibility of experiencing some discomfort during the process, in most cases, people do not describe it as painful.During the procedure, the patient will be sedated so that they do not experience any pain.
After the surgery, patients may experience some soreness or discomfort in their chest and throat area due to the incisions made during the procedure.
How long does it take to recover from Lung Transplant ?
- The recovery period following a lung transplant typically takes anywhere from 6-12 months.
- During this time, the patient will need to take medications and attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure that the transplanted lungs are functioning properly.
- Alterations to the patient's lifestyle, such as physical therapy and diet, may also be suggested in order to help the patient in regaining strength and mobility.
- It is important for patients to understand that recovery from a lung transplant is an ongoing process and that it can take some time before they begin to feel like their old selves again.
What are the side effects of Lung Transplant ?
The following are the most frequent side effects of a lung transplant:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Rejection of the transplanted organ.
- Damage to other organs from anti-rejection medicines.
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Blood clots in the lungs or legs (pulmonary embolism).
- Scarring in the airways (bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome).
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
- Kidney failure due to high doses of anti-rejection medicines.
Lung Transplant Aftercare
Aftercare for lung transplants typically involves:
- Physical therapy is important to help strengthen muscles weakened by the surgery and to help with breathing exercises.
- Medications are prescribed to prevent rejection of the new lungs and to reduce inflammation.
- Lung health may also be enhanced by modifying one's lifestyle, such as giving up smoking and preventing certain environmental toxins.
- To make sure the transplanted lungs are operating correctly, regular monitoring is required. Your doctor may also recommend pulmonary function tests or other tests depending on your individual situation.
- Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting enough restful sleep, and avoiding stress can all help promote good health after a lung transplant.
Conclusion
Patients who get a lung transplant may see an improvement in their quality of life as well as an increase in their likelihood of survival. Before deciding to proceed with this surgery, it is important to consult with an experienced medical group to go through the advantages and disadvantages of the operation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Pulmonologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors