Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Lungs (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, Treatment and More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
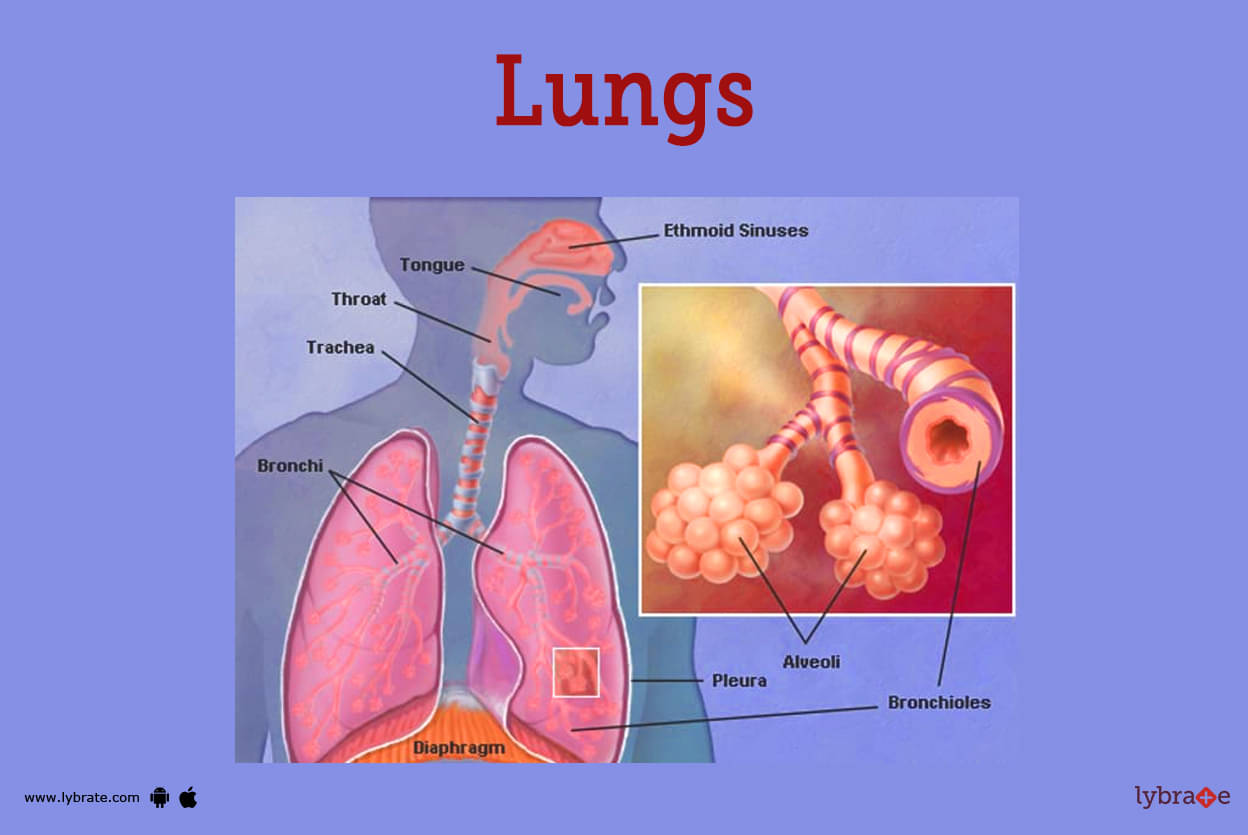
Lungs Image
- Lungs are the respiratory organs of the human body which are found in a pair and located on either side of the thorax region or chest region.
- The trachea, often known as the windpipe, is responsible for directing air that has been inhaled into the lungs to the numerous bronchi that make up the pulmonary system. Bronchi were further split into bronchioles at this point.
- The alveoli are microscopic structures that are further subdivided into branches that are known as the bronchioles. They are sometimes referred to as air sacs.
- Air sacs are locations throughout the body that are responsible for the absorption of oxygen molecules from the surrounding air, which are then distributed to various regions of the body, and the exhalation of carbon dioxide gas from the body. Co2 is a byproduct of the metabolic processes that occur in the body.
- The space between the alveolar sacs is filled by interstitium.It is a very thin layer that can be found between two alveoli. There is a presence of blood vessels in the interstitium.
- The lungs have a cap-like structure called the pleura, which is a thin coating of tissue. These tissues line the chest cavity, helping to keep the lungs from collapsing, making breathing more comfortable, and also serving as a lubricant.
Lungs Functions
- It takes O2 from the surrounding and transfers it to the bloodstream.
- It also removes Co2 from the body.
- Through lungs the individual takes more than 6 million breaths per year .
- Mucus is located at the lining of the lungs, which acts as a barrier to prevent foreign particles from entering the alveoli.
Lung Diseases
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ( C.O.P.D): A condition known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (C.O.P.D) causes damage to the lungs, which leads to difficulties in inhaling and exhaling air, which in turn leads to a feeling of being short of breath. Cigarette smoking is the most common factor in this.
- Emphysema: Emphysema is a kind of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that is typically brought on by a smoking habit. In this condition, the alveolar sacs are compromised, which leads to the accumulation of air within the lungs and, as a result, makes it difficult to take in breath and let it out.
- Chronic Bronchitis: It is a variety of C.O.P.D which is also caused by smoking. It is the continuous episodes of production of cough in lungs which leads to difficulty in inhalation as well as exhalation of air.
- Pneumonia: This is the condition of lungs in which the lungs are infected with bacteria such as streptococcus pneumoniae . Some cases of pneumonia are reported due to viruses too.
- Asthma: It is the condition in which The bronchi of lungs become inflamed which results in convulsions which leads to shortness of breath and wheezing. Allergens, some viral infections , dust particles are the common causes of Asthma.
- Acute Bronchitis: It is the condition that occurs due to the viral infection in bronchi. Cough is taken as the major symptom for acute bronchitis.
- Pulmonary Fibrosis: It is a variety of interstitial lung disease . In this condition the breath becomes short due to the stiffness in lungs. The stiffness is due to damage in alveolar sacs.
- Sarcoidosis: It is the condition in which small tissues of lungs become inflamed . Sarcoidosis can occur to other parts of the body too. This disease can usually be seen in X-rays.
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome: It is a condition that occurs when a person carries over weight. These overweight causes difficulty in expansion of the pleural wall. If a person carries extra weight with him on a regular basis then it can cause c.o.p.d.
- Pleural Effusion: It is a condition in which the alveolar sac and pleural space are filled with fluid. Severe pleural effusion includes symptoms of breathing problems.
- Pleurisy: It is the condition of lungs in which the pleura of lungs shows inflammation. Pleurisy is due to autoimmune disorders, infection and pulmonary embolism.
- Bronchiectasis: It is a condition of the lung in which the bronchi show unusual expansion with inflammation after repeated infections. The main symptom of this condition includes coughing with a large amount of mucus.
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): It is a rare lung condition in which cysts are formed on all surfaces of the lungs. Emphysema shows the same symptoms that LAM shows. The cases of LAM are mostly seen in women who conceive pregnancy.
- Cystic Fibrosis: It is a condition of the lungs in which the mucus is not cleared easily in air passage which results in presence of extra mucus. This excess mucus develops conditions like pneumonia and pneumonia throughout their life. It is a genetic condition.
- Interstitial Lung Disease: It is a condition of lung disease in which the lining between alveolar sacs are infected by some diseases. Prolongation of this condition can lead to permanent fibrosis in lungs.
- Lung Cancer: It is a condition of the lungs in which carcinoma cells activate. This activation is mostly due to smoking.
- Tuberculosis: It is a condition of lungs which is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis. Some of the symptoms of this disease include weight loss, fever , night sweats , and chronic cough.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): It is a condition in which lungs are severely injured by some sort of illness. Patient might need ventilation for his/her survival.
- Coccidioidomycosis: It is a pneumonia-like condition that occurs in lungs. It is commonly caused by fungi known as Coccidioidea. Mostly this disorder is asymptomatic but sometimes it can show flu.
- Histoplasmosis: This pneumonia-like condition of lungs is caused by fungi called Histoplasma capsulatum. Mostly it shows mild symptoms of flu and cough.
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (allergic alveolitis): It is an allergic reaction which is mostly caused by inhalation of dust particles or other allergens. The workers of dry field, farmers are the major group who are mostly affected by this condition.
- Influenza: It is a viral infection. Fever , body aches, and cough are the common symptoms of this disease. In older people influenza can cause life threatening problems.
- Mesothelioma: It is a type of carcinoma. This disorder was reported several decades ago.
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough): It is a highly communicable disease of bronchi. It is caused by Bordetella pertussis. It mostly causes continuous coughing. It could be prevented by a booster vaccine i.e. Tdap vaccine in adolescents.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: This condition can lead to high pressure of blood in blood vessels which is circulated from heart to lungs. If you do not find any cause for this condition then this is known as idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.
- Pulmonary Embolism: It is a condition in which a clot of blood from a vein of leg separates and moves to the heart. The heart sends this clot to the lungs by blood pumping. Difficulty in breathing and Sudden shortness of breathing are some of the major symptoms.
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome: It is commonly known as Covid 19. It is a pneumonia-like condition. First case discovered in China in 2002.
- Pneumothorax: This condition is due to the injury in the thorax region. It is an abnormal condition in which air enters the area of pleural spaces of lungs.
- Carcinoid Tumour: Enterochromaffin cell proliferation can give rise to well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours. Although the small intestine is where it is seen most frequently, it can also be detected in the lungs and the stomach.
- Dermatomyositis: It is a damage to the myocytes that is immune-mediated. It has been linked to occult cancers, such as those of the lungs, breast, ovaries, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys.
- Cryptococcus: There is round yeast present, and it has thick capsules. Pigeons are known to be carriers of this disease. The inhalation of fungus into the lungs. There is a possibility that the brain and meninges will be affected by hematogenous spread.
- Hemothorax: Bruising and bleeding as a result of a ruptured aorta or myocardium, or from the lung parenchyma or intercostal vessels.
- Pulmonary Contusion: Happens within the first 48 hours after a chest injury ( alveolar haemorrhage).
- Choriocarcinoma - Proliferation of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast without chorionic villi, also known as molar pregnancy, which accounts for fifty percent of all pregnancies, as well as normal pregnancies. - Common metastases to vagina and lungs.
Lungs Test
- Chest X-ray: It is the most common test used for identification of fluid that is present in chest or pneumonia and other problems.
- Computed Tomography (CT scan): This test uses X-rays with a computer and it provides more clear and detailed information about lungs.
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): This test is used to identify the problems in lungs capacity and problem of lungs during inspiration and expiration.
- Spirometry: It is a test which is used to check how rapidly and the amount of air that we could breathe out.
- Sputum Culture: It is a test in which the mucus which comes out during coughing is culture which helps to identify the bacteria which results in disease like pneumonia or bronchitis.
- Sputum Cytology: This test is used to identify lung cancer. In this test sputum is investigated under a microscope for abnormal cells.
- Lung Biopsy: This test is used to examine the condition of lungs. In this test a biopsied tissue from the lung is used for diagnosis purposes.
- Flexible Bronchoscopy: It is a test which uses an endoscope . This endoscope is inserted in air ways till bronchi,so the physician is able to identify the problems associated with lungs.
- Rigid Bronchoscopy: In this a rigid metal tube is inserted in airways from the mouth. It is better than flexible bronchoscopy. For this Anesthesia is mandatory.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI Scan): In this the high resolution images of lungs are created by radio-waves. MRI scanner is mandatory for this kind of test.
Lung Treatments
- Thoracotomy: It is a chest surgery in the thorax region. Done to deal with some dangerous conditions of lungs that are diagnosed by lung biopsy.
- Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): This is a chest wall surgery which is used to cure various disorders of lungs . This endoscopy is done prior for a clear view.
- Chest Tube (Thoracostomy): In this the extra fluid from chest wall is drained out through an incision which is made in chest wall.
- Pleurocentesis: In this treatment a needle is inserted in the wall of the chest to suck out fluid that surrounds the lung. Before pleurocentesis a tissue sample is examined properly and its cause.
- Lung Transplant: It is a surgical process in which the infected lung is replaced by uninfected lungs from the donor. Some of the diseases which may need lung transplantation are C.O.P.D, pulmonary hypertension, fibrosis in pulmonary region etc.
- Chemotherapy And Radiation Therapy: surgery is not able to cure carcinoma in lungs. Somehow chemotherapy and radiotherapy can reduce the symptoms of carcinoma of the lungs. It could increase the life of patients too.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Many diseases including Covid -19 requires a ventilator bed which helps the patients in breathing. In this the ventilator bed pumps are inserted in the mouth or in the neck of patients to help them in breathing.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): In this the pressure of air through a mask is applied by a machine which helps the airways open and prevent it from collapsing in various conditions like sleep apnea, C.O.P.D.
- Lung Resection: It is a surgical process in which the infected tissue is cut and removed surgically. Done in mostly cases of Benign tumours.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Treatment for dyspnea should focus on alleviating the underlying condition(s) that manifested as the breathing difficulty. If your oxygen saturation drops significantly while you're sleeping, resting, or exercising, you may need supplemental oxygen. Improvements in exercise tolerance due to pulmonary rehabilitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (C.O.P.D).
Lungs Medicines
- Antibiotics: These are the medicines which are used to check the bacterial growth in lungs and treat those bacterial infections such as pneumonia. However, these meds are ineffective against viral lung disease . Common medicines are Amoxicillin.
- Antiviral Medicine: These meds are used to treat many viral lung diseases but these are ineffective against viral bronchitis. Amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, oseltamivir, ribavirin, acyclovir, ganciclovir, and foscarnet are common drugs among this class of medicines.
- Bronchodilators: Inhaling these medications is the most popular method for increasing the amount of air that may travel through the respiratory system. Patients who are suffering from COPD may experience a reduction in symptoms such as wheezing and shortness of breath as a result of this. Beta-2 agonists, which include salbutamol, salmeterol, formoterol, and vilanterol, are the types of bronchodilators that are prescribed to COPD patients by medical professionals at the highest frequency.
- Corticosteroids: This class of medicine is used to treat the inflammation of lungs that occurs during various C.O.P.D conditions. It could be taken in both forms i.e. through inhaler or in the form of pills. cortisone, prednisone and methylprednisolone are some of the examples of this class of meds.
- Vasodilators: The hypertension that can develop in the lungs can be treated with medicines from this category. Long-term treatment with this medication is recommended. Several examples of medications that fall into this category include Alprostadil IV, Corlopam, and Deponit.
- Analgesic: This kind of medication is prescribed to patients suffering from a variety of lung pains in order to provide relief.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to remove mucus from lungs naturally?
There are numerous effective ways to remove mucus from the lungs: use a humidifier, drink lots of water, gargle with warm water and use a good nasal spray to clear phlegm.
How to clean lungs?
The best method to keep your lungs healthy is to stay away from dangerous chemicals like air pollution, and cigarette smoke and also exercise frequently and eat a nutritious diet.
How to detox lungs?
Techniques for thoroughly clearing the lungs include breathing exercises, postural drainage, and chest percussion.
How to clean lungs after smoking?
Drink plenty of water, exercise regularly, eat a healthy diet and drink warm fluids to clean your lungs after smoking.
How to increase lung capacity?
Exercises like pursed lip breathing, belly breathing, interval training, quitting smoking, drinking lots of water, and being active, etc. can all help the lungs function more effectively.
How many lobes in lungs?
The right lung is made up of three lobes: right upper, right middle, and right lower. The left upper lobe and left lower lobe are the two lobes that make up the left lung.
What are the structural and functional unit of lungs?
The structural and functional component of the lung is the alveolus.
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Pulmonologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously