Muscular System (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
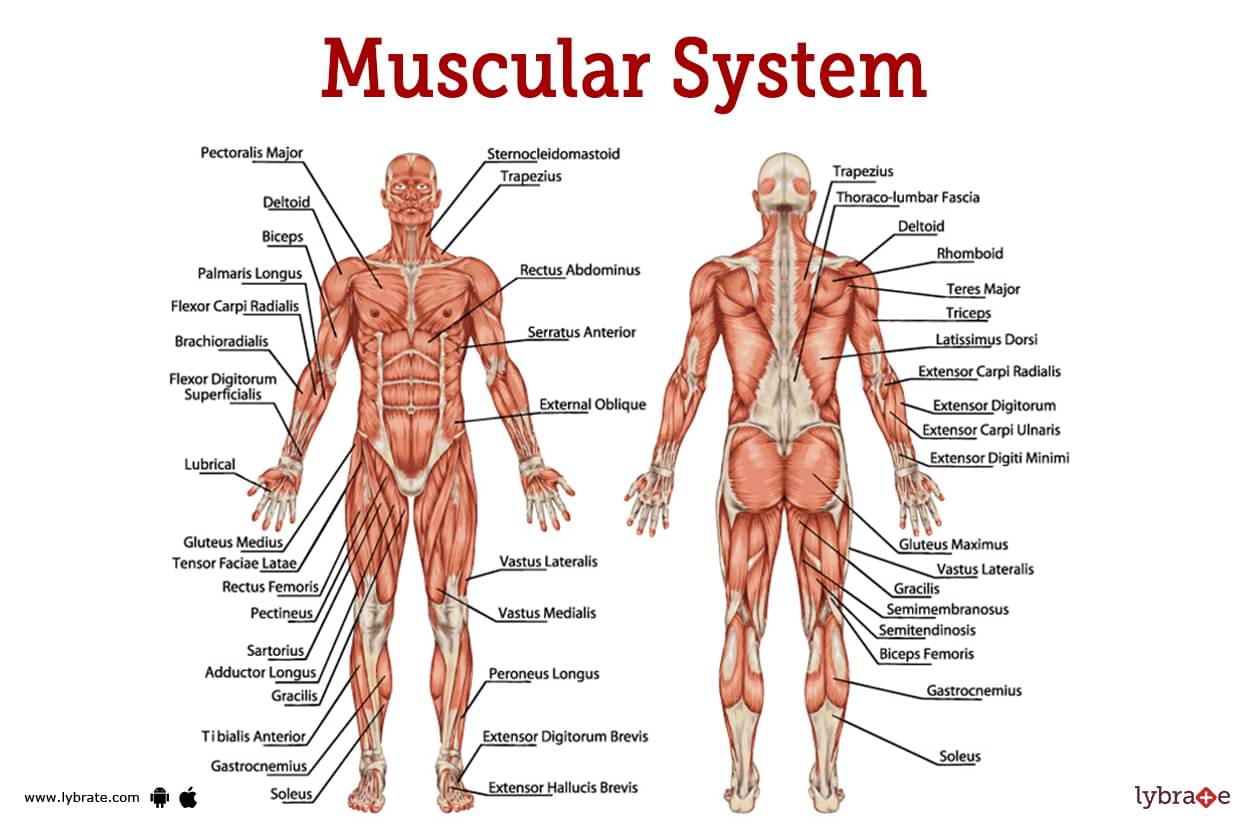
Muscular System Image
Human muscular system, the voluntary muscles of the skeleton that regulate movement, posture, and balance. Human muscle is classified into striated (or skeletal), smooth, and cardiac muscle.
- Smooth muscle is present in blood vessel walls in the urinary bladder, intestines, and stomach.
- Cardiac muscle is involuntary and controls the heart's rhythmic contractions. Human smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are arranged similarly to other vertebrates.
This article discusses the skeletal muscles of the human body, focusing on muscular motions and alterations caused by upright position.
The article muscle discusses smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and muscle contraction physiology. Muscular disease describes muscle problems.
The next sections describe significant muscle groups and their activities to help you comprehend gross human muscular anatomy. Coordinated muscle groups govern bodily motions.
- Neck: Neck motion includes rotation, flexion, extension, and sidebending (i.e., the motion used to touch the ear to the shoulder). Action might be ipsilateral or contralateral to the contracting muscle. Rotation is a key cervical (neck) spine motion.The sternocleidomastoid muscle turns the neck. The sternocleidomastoid muscles flex the neck and elevate the sternum to help with vigorous breathing.The anterior and middle scalene muscles on the sides of the neck rotate the neck and raise the first rib. Back of the neck muscles splenius capitis and cervicis rotate the head. The cervical spine also bends sideways.Cervical side bending involves the sternocleidomastoid muscles. The posterior scalene muscles bend the neck to the side and raise the second rib. Splenius capitis and cervicis help side bend the neck. Iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis are massive, deep back muscles. All three side-bend the neck ipsilaterally.
- Skeletal muscle: A muscle of this sort is responsible for generating bodily motion. Skeletal muscles, of which there are more than 600, account for around 40% of a person's total mass. Groups of muscles work together to move the skeleton in response to impulses from the neurological system. There is some degree of will involved in producing these signals and actions, but they are still not completely automatic. We humans, however, can move without paying attention to each individual muscle.
- Cardiac muscle: Muscle in the heart occurs automatically. The walls of the heart are made up of this kind, and in response to brain instructions, they beat steadily and rhythmically, pumping blood throughout the body. Although this muscle group is responsible for generating the electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract, they may be altered by other factors, such as hormones and nervous system stimulation (which is why, for example, a frightened person's heart rate rises).
- Smooth muscle: The walls of your hollow organs, airways, and blood arteries are all composed of smooth muscle. Moving like waves, it helps transport items like food and urine through the digestive and urinary systems. Similar to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle is involuntary and only contracts in reaction to external stimuli or nerve signals.
Muscular System Functions
Neurological signals cause muscle cell electrical changes. Calcium is released into cells, causing a muscular twitch. Neuromuscular illnesses can result from synapse problems. Proper diet and exercise maintain cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles healthy.
Muscular System Conditions
- Muscle pain: Muscle soreness refers to the discomfort caused by overworked muscles. Myofascial discomfort, caused by trigger points in the muscles, is commonly experienced in the primary upper back muscles. Muscular irritation and upper back pain are the result of weak muscles and repetitive motions.
- Sprains: Ankle ligament ruptures are typically the result of a sudden motion of the foot. Future discomfort and swelling could be avoided with the use of rehabilitation treatments.
- Strain: A pulled bicep is the result of overstretching and tearing the tendons and/or muscle fibres in the biceps. Pain and edema are possible complications.
- Bruise : A bruise is the medical word for a cut or rupture in the muscular tissue. Symptoms include swelling and a rise in pressure around the muscle that has been injured.
- Cancer Of The Muscle: This disorder, which can impair the calf muscle, is extremely uncommon. Cancer of the calf muscles is called sarcoma in the medical community. Metastatic carcinoma, which begins in another region of the body and progresses to the calf, is another potential cause of this illness.
- Muscle Cramps: Calf cramps are among the most excruciating pains one may experience. Any number of medical conditions, such as pregnancy or dehydration, might be the root cause of these pains.
- Parkinson’s disease: Mobility and coordination issues develop as a result of the disease, which is characterised by the slow degeneration of nerve cells in a substantial area of the brain. One of the earliest symptoms of Parkinson's disease is trembling in the hands.
- Multiple sclerosis: Degenerative changes in the myelin sheath of the exons lead to fatal redistribution of the neuronal pathways and variable neuronal degeneration in this progressive disease of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system.
Muscular System Test
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Magnetic Resonance Imaging is the most common abbreviation used to describe it. The goal of this test is to gain a thorough understanding of the calf muscles and other soft tissues of the body. Using a powerful magnet and a computer, this technique can detect the delicate architecture of a patient's soft tissues.
- Computed Tomography: A computed tomography (CT) scan is the more popular name for this diagnostic test. In order to get a good look at the calf muscles and any other muscles connected to or near the calf muscles, this test used X-ray waves and a computer.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasonography, which utilises high-frequency sound waves, is used to evaluate the calf muscle for diagnostic purposes. These sound waves can travel into the calf muscle and its accompanying ligaments and tendons to provide doctors an accurate digital representation of the muscle's structure.
- Phlebography: This process is also known as venography. A venogram will be performed immediately after a particular dye is injected into the patient's veins or bone marrow.
- Biceps ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves are produced by reflecting a device placed on the skin off the components of the biceps. Because the impulses are turned into pictures on a television screen, medical experts may view inside body structures. An ultrasonography of the biceps may indicate problems with the tendon.
- SERUM calcium test: A calcium blood test indicates the concentration of the mineral in your blood. Bone disease, thyroid disease, parathyroid abnormalities, renal disease, and other medical conditions can all be signs of high or low blood calcium levels.
- Serum Urea and creatinine: They aid in the identification of nitrogenous compounds generated as a metabolic byproduct. Urea is produced primarily as a result of the breakdown of dietary and cellular protein. When calcium deposits as crystals in the bone, its density decreases.
Muscular System Treatment
- Open reduction and internal fixation: When the distal third of the humerus is fractured, the bone is displaced from its position, requiring open reduction and internal fixation of the bone as well as nerve exploration to prevent damage.
- Closed reduction and slab: When a humerus fracture occurs, the first line of treatment is to return the fractured part to its original position and apply a slab to prevent additional movement until the injury is healed.
- RICE Therapy: Rest, Icing, Compression (with an athletic bandage or something similar), and Elevation (RICE) is an injury-treatment programme that comprises multiple methods. Like most injuries, a palm laceration responds well to the RICE treatment protocol of rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
- Palm Immobilisation: The majority of palm fractures require casting to prevent additional movement. Immobilisation is recommended by some medical authorities as a therapy for diseases such as palm sprains.
- Physiotherapy for myositis: Contraction and release Inflammation of the biceps muscles can be treated with physical therapy; when conducted by a skilled physiotherapist, this modality improves the prognosis for even patients with chronic injuries.
Muscular System Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Muscular System: Cortisone-like medicines such as prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone are sometimes prescribed to individuals with specific kinds of myositis that present in the foot muscle.
- Analgesics for pain in Muscular System: Analgesics, sometimes known as painkillers, include drugs like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and aspirin. They're used to alleviate discomfort.
- Muscle relaxants for stiffness in Muscular System: A practitioner treating a patient's illness may administer muscle relaxants such as metaxalone, methocarbamol, orphenadrine, or carisoprodol.
- Antibiotics for infection in Muscular System: The majority of sinus infections do not require antibiotic treatment and will improve even if not treated. Medical experts often only prescribe antibiotics for sinus infections that do not clear on their own. Common names include Augmentin (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid), Zithromax (azithromycin), and Levaquin.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in Muscular System: Nutritional Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin, which are often prescribed by doctors, can help relieve joint discomfort and speed up the healing process. Calcium and vitamin D supplements may be recommended.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Muscular System: Antiviral medications aid the immune system in combating viral infections. These drugs can reduce the intensity of symptoms and the length of time an illness is caused by a virus. The immune response modulator and the cyclovirus, valacyclovir, famciclovir, penciclovir, cidofovir, foscarnets, and so on are only a few examples.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Muscular System: When applied to patients with locally advanced breast cancer, neoadjuvant combination chemotherapy is an efficient therapeutic choice. Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, and 5-Fluorouracil are the components of this chemotherapy regimen. Next comes radiation therapy for the breasts and then surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are 5 diseases of the muscular system?
What are the common disorders of the muscular system?
What is the treatment for muscular system diseases?
Can muscle disease be treated?
What is the cause of muscular system diseases?
What are 3 diseases of the muscular system?
What are the effects of the muscular system?
What causes muscle loss and weakness?
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors