Nasopharynx (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
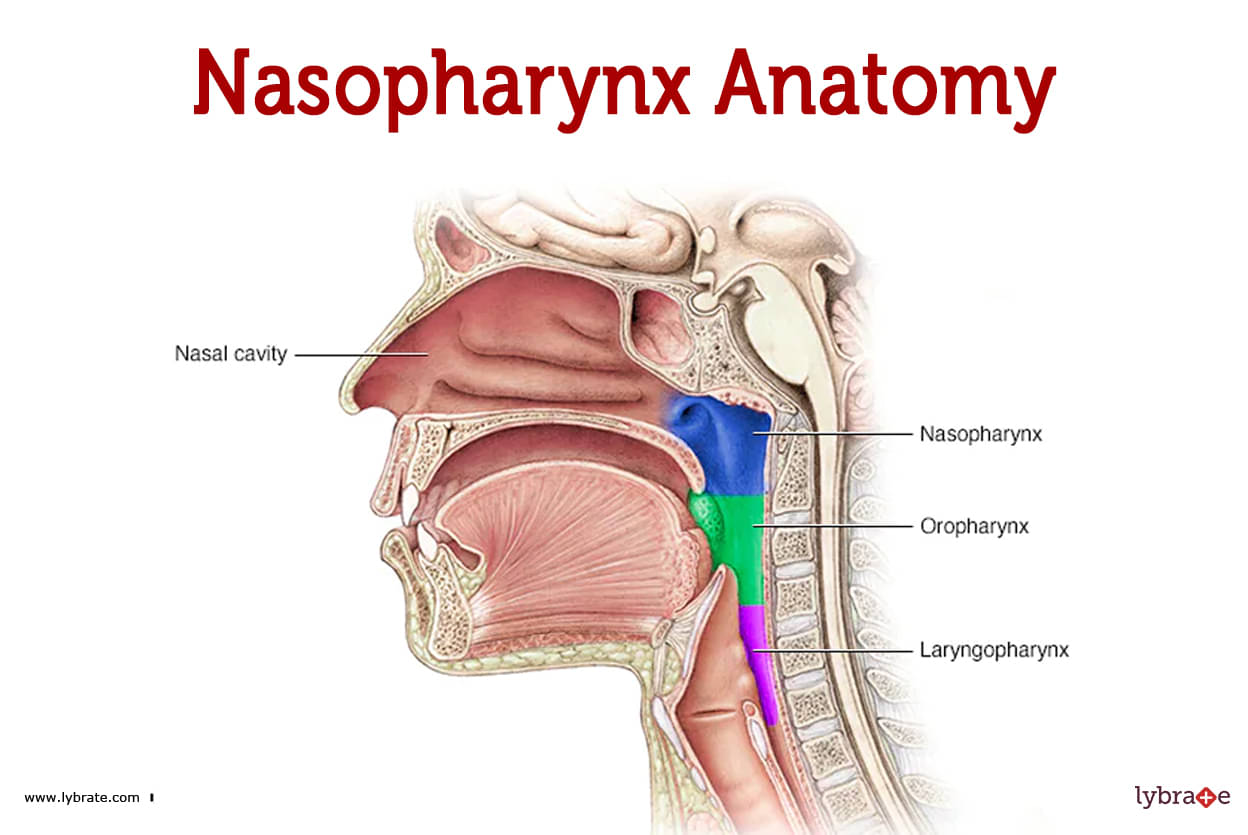
Nasopharynx Image
Nasopharynx refers to the area at the top of the throat (pharynx) that links the nasal cavity to the trachea and bronchi. The adenoids within aid in fighting off infection. The eustachian tubes drain fluid and maintain a healthy pressure balance between the ear and the nasal passages. Nasopharynx issues include things like the common cold and swollen adenoids.
The nasopharynx is the area of your throat closest to your nose (pharynx). Located directly above the ceiling of your mouth and behind your nose, it is a muscular box. The nasopharynx is the passageway through which air travels from the nasal cavity to the trachea and, from there, to the lungs.
Nasopharynx Functions
The nasopharynx is an important part of the respiratory system because it facilitates airflow from the nose to the lungs. It opens the airway between the nose and the lungs.
What does the nasopharynx do?
- The nasopharynx is the anatomical structure that sits at the base of the tongue and at the top of the back of the throat. Its primary use is to improve the quality of the air you're breathing.
- The nasopharynx is the passage through which air travels from the nasal cavity to the pulmonary artery and pulmonary capillary system. Ciliated hairs and mucus in the nasopharynx act as a filter to remove dust, pollen, and other particles from the air. This aids in the prevention of irritation to the airways.
- Humidification of the air you breathe in is another function of the nasopharynx. So, it's a good way to maintain your lungs and throat healthy by increasing the humidity in the air.
What connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx?
The nasopharynx and middle ear are joined by a tiny, tubular structure called the Eustachian tube. The ear canal's primary job is to make sure the pressure behind and in front of the eardrum stays the same. It accomplishes this by creating a passage for air to travel from the middle ear to the nasal cavity.
What closes the nasopharynx during swallowing?
When we swallow, a structure called the soft palate in the rear of the mouth slides upward and closes off the nasal passageway. As a result, we are less likely to choke on food or liquids that make it up our nostrils. When we swallow, the soft palate acts like a door to seal off the nasopharynx. This is crucial since ingesting anything that enters the nasopharynx might cause serious illness.
Where is the nasopharynx located?
The area of your skull known as the nasopharynx can be found towards the base. It's between the soft palate and the nasal septum.
Your nasal cavity communicates with the upper portion of your pharynx through the nasopharynx. The lower end is linked to the oropharynx (throat), which in turn communicates with the hypopharynx (throat) and the trachea (windpipe) and the lungs.
What does the nasopharynx contain?
Your nasopharynx involves several important structures:
- Eustachian tubes: Your nasopharynx is connected to the middle ears via these tubes. They help to drain excess fluid from the ear and normalise the ear pressure.
- Adenoids (nasopharyngeal tonsils): These glands play an important role in the immune system, which defends the body against harmful microorganisms and viruses.
How big is the nasopharynx?
A person's nasopharynx size might differ from person to person. The length is around 4 centimetres, and the width is about 2 cm.
Nasopharynx Conditions and Disorders
- Nasopharyngitis: Nasopharyngeal inflammation, most often known as the common cold. Symptoms include a runny nose, congestion, and a sore throat, and are typically brought on by a viral infection.
- Sinusitis: Sinusitis is an infection and inflammation of the sinuses, which are hollow cavities within the facial bones that are filled with air. A stuffy nose, face pain, and a headache are all possible side effects of sinusitis.
- Adenoiditis: The adenoids are a group of tiny glands in the back of the nose and upper throat that can become inflamed. Symptoms of adenoiditis include congestion, nasal obstruction, and the need to breathe via the mouth instead.
- Tonsillitis: The tonsils, a pair of tiny lymph nodes at the base of the tongue, become inflamed. A scratchy throat, trouble swallowing, and enlarged tonsils are all potential signs of tonsillitis.
- Pharyngitis: An infection in the pharynx, the area of the throat that lies below the oral cavity and the nasal cavity, causes this inflammation. Symptoms of pharyngitis include a sore throat, swallowing difficulties, and enlarged tonsils.
- Nasopharyngeal cancer: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is a rare kind of cancer. A lump in the neck, a change in one's voice, or trouble swallowing are all possible results.
- Benign nasopharyngeal tumour: This tumour is extremely uncommon and typically affects young people. It rarely causes death and rarely spreads to other parts of the body. However, as it develops, it can cause painful symptoms such as epistaxis (nosebleeds) and abnormalities in vision. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma is one such example.
- Enlarged adenoids: Your adenoids may swell due to chronic infections, allergies, or irritants. Although enlarged adenoids are most frequent in kids, adults are not immune to developing them. Nasal congestion, mouth-breathing, snoring, sleep apnea, recurrent ear infections (otitis media), and sinus infections are all symptoms (inflamed sinuses). Antibiotics, adenoidectomy, and corticosteroids are all potential treatments (surgery to remove your adenoids).
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Inflammation of the blood vessels in the nasal cavity, lungs, and kidneys is a symptom of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, an uncommon condition. Sometimes doctors will refer to it as Wegner's granulomatosis. Sinus infections and nosebleeds may be associated symptoms. Treatment typically entails taking immunosuppressants like corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide.
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Nasopharyngeal cancer occurs when the lining cells of the nasopharynx multiply uncontrollably and cause obstruction of the nasal airway. Issues with breathing, speech, or hearing may be symptoms. Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or surgery may be part of the treatment plan, and more options are being investigated.
- Nasopharyngeal cyst: Mucus is the contents of this extremely unusual cyst (fluid). It is often discovered incidentally during testing for other diseases. However, it can lead to a stuffy or runny nose, a headache, an ear infection, and, in extremely rare cases, spinal fluid leakage through the nose. A nasopharyngeal cyst can be removed surgically at the discretion of your doctor.
- Allergic rhinitis: Allergies rhinitis are reactions to harmless items like pollen, mildew, or animal dander. Congestion, sneezing, and a constantly wet nose are some of the symptoms it might bring on.
- Epistaxis: A nose bleed has occurred. Dry air, nose picking, and nasal injuries are just some of the things that might bring on this condition.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: This is a sleep condition in which a person has trouble breathing because their airway becomes clogged. Its symptoms include excessive snoring, daytime sleepiness, and mood swings.
- Nasal polyps: These benign tumours develop in the mucosal lining of the nasal cavity or sinuses. A stuffy nose, obstructed nasal airflow, and diminished smell are all symptoms that may result from them.
- Deviated septum: Septal deviation occurs when the wall between the nostrils (the septum) is misaligned. Its symptoms include a runny nose, a stuffy nose, and nasal congestion or obstruction.
How to remove food stuck in the nasopharynx?
If you're having trouble clearing your nasopharynx of food, a good cough may assist. Inhale deeply and forcefully let out your breath while generating a 'hacking' noise:
- Try coughing: If you're having trouble clearing your nasopharynx of food, a good cough may assist. Inhale deeply and forcefully let out your breath while generating a 'hacking' noise.
- Try drinking water: If food is stuck in your throat, drinking a glass of water may help flush it out.
- Use the Heimlich maneuver: A person may need to use the Heimlich manoeuvre to remove food that has become lodged if they are having difficulty breathing. Wrap your arms around the person's waist while standing behind the one who has food lodged in their nasopharynx. Raise one fist and position it above the individual's belly button. Then, use your fist to help clear the meal by pushing in and up firmly.
Nasopharynx Tests
Here are some brief definitions of common nasopharynx tests:
- Nasopharyngoscopy: The nasopharynx is examined by inserting a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera (called an endoscope) into the nasal passages.
- Nasal endoscopy: It's a diagnostic procedure in which a thin, flexible tube (an endoscope) equipped with a camera is put into the nose and used to take images of the nasal cavity.
- CT scan: This imaging procedure takes photos of the body's internals using X-rays and a computer. The nasal cavity and the voice box can be scanned using CT.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a form of imaging examination that employs strong magnets and radio waves to produce clear photographs of an organ or tissue deep within a patient's body. The nasal cavity and voice box can be scanned with an MRI.
- Biopsy: A small amount of tissue is taken from the back of the throat (nasopharynx) and analysed under a microscope to determine the results of the test. Cancer and other diseases can be diagnosed with a biopsy..
- Allergy testing: This is an allergy test that can identify whether or not a person is sensitive to specific chemicals. Allergic rhinitis, for example, can be pinpointed with the help of allergy testing (hay fever).
Nasopharynx Treatments
- Surgical intervention: Surgical removal of foreign bodies or structural abnormalities in the nasopharynx is sometimes required to alleviate symptoms.
- Humidification: Using a humidifier can help to add moisture to the air, which can help to reduce dryness and irritation in the nasopharynx.
- Nasal irrigation: The nasal passages are rinsed with a saline solution, which can remove excess mucus and other irritants.
- Nasal sprays: Certain nasal sprays contain anti-inflammatory and anti-swelling drugs that can help alleviate nasopharyngeal symptoms.
- Allergy treatment: Nasopharynx issues may be helped by allergy medication or allergy injections if allergies are a contributing factor.
Nasopharynx Medicines
- Prednisone, dexamethasone, and triamcinolone are all examples of steroids used to treat nasal and throat inflammation.
- Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and aspirin are all effective analgesics for Nasopharyngeal discomfort.
- Cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol, and methocarbamol are examples of effective muscle relaxants for Nasopharynx stiffness.
- Penicillins, cephalosporins, and macrolides are all examples of effective antibiotics for Nasopharyngeal infections.
- Acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are three effective antiviral medications for treating a Nasopharynx infection.
- Medications that work to relieve swelling and congestion in the nasal passages are known as nasal decongestants, and they are useful for relieving pressure and pain in the nasopharynx.
- Pain and discomfort can be alleviated by anti-inflammatory medicines, which work by reducing inflammation in the nasopharynx.
When should I call a healthcare provider?
You should call your healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of the following symptoms:
- Severe or persistent nasal congestion or difficulty breathing through your nose
- Green or yellow discharge from your nose
- Severe or persistent headaches
- A fever or other signs of illness
- Facial pain or pressure
- A loss of sense of smell or taste
- A lump or growth in your nose
Remember, it's important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as they may indicate a more serious issue. Your healthcare provider will be able to diagnose the problem and provide the necessary treatment to help you feel better.
How can I keep my nasopharynx healthy?
A healthy nasopharynx can be maintained through a combination of the following:
- You can help stop the transmission of germs and protect yourself from illness by washing your hands often.
- Keep your nasal passages wet and your mucus thin by drinking lots of fluids.
- Stay away from things that could aggravate your condition, like smoke, strong fragrances, and harsh chemicals.
- If dryness and irritation of the nasopharynx are issues, a humidifier may be used to increase moisture in the air and alleviate the symptoms.
- Use nasal irrigation to flush away mucus and other irritants stuck in your nose.
- Be sure to get your shots: Protect yourself from diseases that can enter the body through the nose and throat by getting vaccinated against respiratory infections.
- If you suffer from allergies, it is important that you take the steps recommended by your doctor to control the symptoms, such as utilising an air purifier or allergy medicine.
Table of content
Find ENT Specialist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors