Patellar Tendonitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 06, 2023
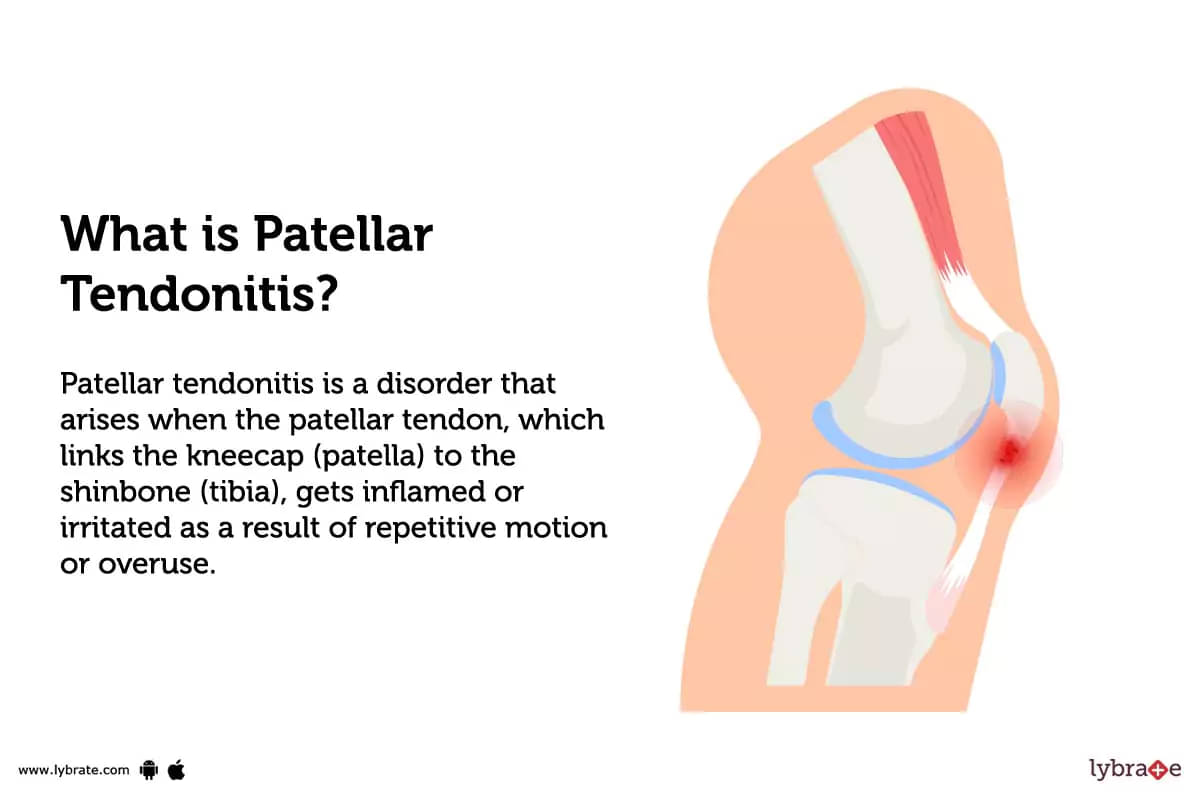
What is Patellar Tendonitis?
Patellar tendonitis is a disorder that arises when the patellar tendon, which links the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia), gets inflamed or irritated as a result of repetitive motion or overuse.
Types of Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis can be classified into four types, depending on the severity and location of pain:
- Anterior Patellar Tendonitis: This type of patellar tendonitis is marked by pain at the front of the knee near the kneecap. It occurs when the patellar tendon is overused or strained due to repetitive jumping and running activities.
- Infrapatellar Tendonitis: This type of tendonitis causes pain underneath the kneecap, usually due to irritation caused by kneeling or squatting. It can be associated with inflammation or degeneration of the infrapatellar fat pad beneath the knee joint.
- Medial Patellar Tendonitis: Also known as 'jumper’s knee', this type occurs when there is too much stress on one side of the kneecap due to activities such as running and jumping. Pain on both sides of the kneecap, as well as swelling around it, are symptoms.
- Posterior Patellar Tendonitis: This type of patellar tendonitis causes pain at the back of the knee due to strain on the posterior aspect of the patella from activities such as running uphill or downhill, squats, or lunges.
What causes Patellar Tendonitis?
Patellar tendonitis is caused by overuse or repetitive tension on the patellar tendon. Other causes of patellar tendonitis include:
- Poor technique during activities.
- Weak thigh muscles
- Tight hamstring muscles
- Sudden increases in training intensity.
What are the symptoms of Patellar Tendonitis?
- Pain around the kneecap on the front of the knee.
- Difficulty with activities that require knee extension or increased strain on the patellar tendon.
- Tenderness and swelling in the affected area.
- A popping or cracking sensation when straightening or bending the knee.
- Weakness in the muscles around the kneecap.
How can you prevent Patellar Tendonitis?
- Invest in proper shoes: Properly fitting and well-cushioned shoes can help prevent over-pronation and provide support to the knee joint.
- Strengthen Quad Muscles: Strong quadriceps muscles can increase the stability of the patella and reduce the strain on your tendon.
- Stretch after exercise: Gentle stretching right after high intensity physical activity can help keep the muscles and tendons loose, reducing your risk of injury.
- Change up your workouts: Incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine helps reduce strain on any single muscle group or joint.
- Compression Sleeves & Braces: Wearing supportive compression sleeves or braces when exercising may help decrease stress on the knee and tension in the tendon, helping to protect it from injury.
Patellar Tendonitis - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical Examination: The doctor will feel the tendon for tenderness and swelling, as well as check the range of motion in the knee and leg.
- X-ray: An X-ray may be taken to ensure that there are no other conditions causing the patient’s symptoms.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI scan can help determine the extent of the damage to the tendon and surrounding tissue.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound is used to view soft tissue structures, such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles in detail. Additionally, it may assist in identifying any tears or inflammation in the patellar tendon.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be done to rule out other conditions that could be causing the patient’s symptoms (such as arthritis).
What are possible complications of Patellar Tendonitis?
- Chronic tendonitis: Constant inflammation of the patellar tendon resulting in pain and/or swelling.
- Tendon 'thickening': A buildup of scar tissue around the injured area leading to reduced range of motion and difficulty with activities that require jumping or landing.
- Partial tear of the patellar tendon: Where partial tears to the tendon occur making it difficult for the affected person to perform activities normally.
- Total rupture of the Patellar Tendon: This is considered a severe injury and can require surgery to repair, often leading to a long road to recovery for full function to return.
Home Remedies for Patellar Tendonitis
- Apply a warm compress to the affected area for 10-15 minutes several times throughout the day.
- Take an Ayurvedic formulation such as Nirgundi oil, or Mahanarayan oil, and massage gently into the area around the tendon.
- Consume one cup of ginger tea every day to decrease inflammation and enhance circulation.
- Use Yoga postures such as Vriksasana (Tree Pose) and Uttanasana (Standing Forward Bend) to help strengthen and stretch the patellar tendon.
- Take an Ayurvedic supplement such as ashwagandha or boswellia to reduce inflammation and support joint health.
What to eat in Patellar Tendonitis?
- Proteins: Lean meat, fish, eggs, nuts and seeds, dairy.
- Fruits & Vegetables: Green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, broccoli.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, Steel-cut oats.
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocados.
- Spices: Turmeric, ginger.
- Herbal Teas & Drinks: Green tea.
What not to eat in Patellar Tendonitis?
- Foods high in sugar and saturated fats: These may result in swelling, gaining weight, and other conditions that aggravate tendonitis.
- Refined carbohydrates: Because they may raise blood sugar and induce inflammation, foods like white bread, spaghetti, and chips should be avoided.
- Artificial sweeteners: These have been discovered to obstruct the creation of collagen, which is necessary for healthy tendons.
- Fried food: Fried foods are full of trans fats which are known to harm the body’s immune system response and increase risk of chronic diseases like tendonitis.
- Alcohol: Alcoholic beverages can interfere with healing process in tendon injury and aggravate the already injured tissue of knee joint vicinity.
Patellar Tendonitis Treatment
- Ice or Cold Therapy: Make regular 20-minute applications of a cold pack or ice wrapped in a towel throughout the day.
- Compression: Compress the region with an elastic bandage to reduce swelling.
- Arthroscopic Debridement: This procedure involves making small incisions in the knee and using a camera to remove any scar tissue buildup that may be causing the tendonitis.
- Grafting: If the injury has caused irreparable damage, grafting may be done to provide a new tendon over the affected area.
- Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) injections: These help promote tissue regeneration by harnessing the body’s own healing capabilities with a concentrated injection of platelets and growth factors.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): ESWT is a non-invasive technique used to break down scar tissue and stimulate blood flow around the affected area to reduce inflammation.
Which doctor to consult for Patellar Tendonitis?
A doctor that specializes in musculoskeletal problems, such as an orthopedist, or a sports medicine physician can diagnose and provide treatment for this condition.
Which are the best medicines for Patellar Tendonitis?
How long does it take to recover from Patellar Tendonitis?
Recovery from patellar tendonitis can be a long and difficult process, with treatment taking anywhere from a few weeks to several months or even up to a year.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
- Patellar tendonitis treatment aims to reduce pain, improve joint function and strength.
- While not permanent, the effects of treatment are generally long lasting.
- Non-surgical options such as rest, physical therapy, stretching and bracing can provide relief from symptoms for weeks or even months; however, to maintain long-term relief from patellar tendonitis, individuals typically need to maintain an active lifestyle that includes low-impact activities and a gradual exercise routine.
- Surgery can provide more permanent relief but is usually a last resort option used when other methods have not provided long-lasting relief.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Initially stay off the injury for a few days to allow the tissue to heal.
- Use an ice pack for around 15 minutes every three to four hours to relieve pain and swelling.
- Gradually increase activity level but avoid activities that require repeated flexing of the knee joint or jumping until symptoms resolve.
- Stretch and strengthen exercises such as straight leg raises and quadriceps sets should be done regularly under the guidance of a physical therapist to ensure proper form and body mechanics are used during exercise routines.
- If necessary, use a brace or support bandage while exercising or engaging in activity that will help provide added stability and support while participating in activities with increased risk of trauma or injury leading to reformation of patellar tendonitis symptoms.
- Massage along the patellar tendon can greatly help with reducing inflammation as well as increasing range of motion around the knee joint if done with trained professionals.
What is the cost of Patellar Tendonitis treatments in India?
Generally, these treatments include physiotherapy, ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, medications and in some cases, surgical treatments.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapist visits can cost from ₹250 to ₹1,500 per session.
- Ultrasound Therapy: Treatment sessions are typically charged around ₹800 to ₹2,000 per session.
- Electrical Stimulation: This may be charged at around ₹2 per session.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications and injectable corticosteroids prescription may cost between ₹100 - ₹300.
- Surgery: Depending on the patient’s condition and the complexity of the surgery, a surgical treatment may range from ₹600 to upwards of several lakhs of rupees.
What are side-effects of Patellar Tendonitis treatments?
The most common side effects of treatment for patellar tendonitis include:
- Temporary swelling
- Pain and discomfort at the site of injection.
- Skin discoloration
- A feeling of warmth or burning sensation in the area where the injection was given.
- There is a small risk of infection and nerve injury.
Patellar Tendonitis - Outlook/ Prognosis
It is important to see a doctor if you have any Patellar Tendonitis symptoms, since they may lead to more serious conditions including 'chronic tendonitis, tendon thickening, total rupture of the Patellar Tendon' the treatment for which can last anywhere from a few months to many years.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors