Pelvic Bones (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Disorders, and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
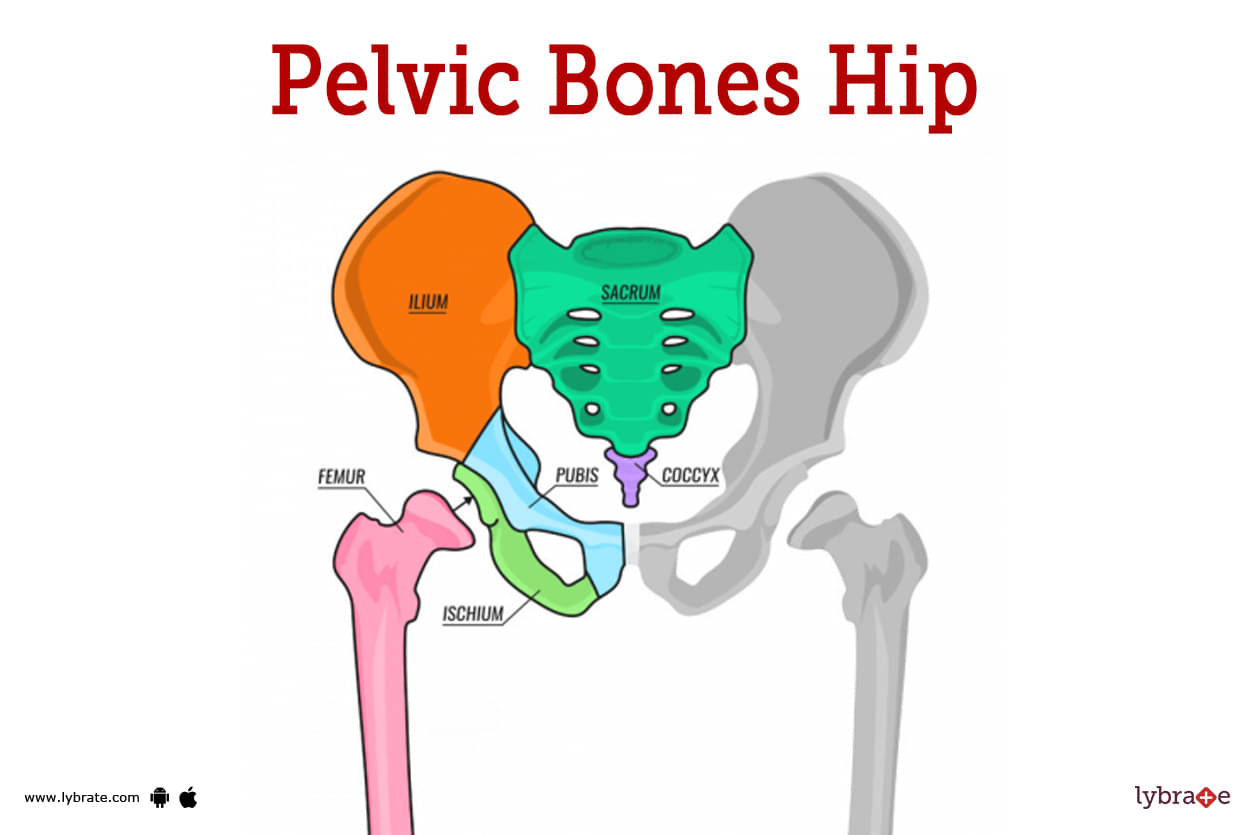
Pelvic Bone Image
The lowest part of a woman's abdomen is called the pelvic bone, and it may be found in the space in between her hip bones. It is sometimes referred to as the bone of the pubic symphysis.
The pelvic region, sometimes known simply as the pelvis, is a ring of bones that are located at the base of your spine. Also, blood vessels and nerves could be in this part of the body.
The hip bones, the tailbone (which is also called the coccyx), and the triangular bone that sits at the base of the sacrum make up the pelvis.
Pelvic Bone Functions
It lends a hand in the stabilisation of muscles and protects the organs that are situated in the lower abdomen. The pelvic girdle's function is to transfer the weight of the body to the lower limbs so that proper locomotion may be carried out. This is accomplished by transferring the weight of the body to the lower limbs.
The most significant advantage it provides during labour is that it makes it simpler for the infant to exit the body through the birth canal, which is situated inside the pelvic girdle. This is the most important method in which it facilitates the process of labour and delivery. It also helps support the organs inside the abdomen.
Pelvic Bone Diseases
- Tailbone/coccyx fracture: A fracture of the tailbone may occur because the tailbone is situated at the very end of the spine. A baby's tailbone could get sprained or even broken if they come out of the birth canal at the wrong angle or go through the process too quickly.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a type of rheumatic disorder that is characterised by symptoms including pain in the muscles and musculoskeletal system, as well as stiffness and localised discomfort in some parts of the body. Fibromyalgia is characterised by these symptoms because it is caused by an autoimmune disorder. pelvic inflammatory disease: Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (also known as PID) is a disorder that may be brought on by a prolonged infection, which is often sexually transmitted and can lead to scarring that affects the pelvic organs. PID is an abbreviation for chronic pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Pelvic congestion syndrome: The illness known as pelvic congestion syndrome may be the source of pain localised in the pelvic region. It is characterised by swollen veins surrounding the uterus and ovaries that are similar in appearance to varicose veins. These veins are found in the pelvic region.
- Osteitis pubis: Osteitis pubis is an inflammation that takes place in the pubic symphysis, which is a moveable joint found at the front of the pelvis. This condition may affect both men and women. It's probable that you'll have symptoms like back pain and discomfort in the front of your pelvis if you have this condition. This ailment is often brought on by activities that place repeated stress on the pelvic region, such as kicking a soccer ball, which is an example of one such activity. Despite the fact that getting enough rest is necessary for the healing process to proceed normally.
- Pelvic bone hydatidosis: It is possible for the uterus, the broad ligament, and the adnexa to be affected by the condition that is known as pelvic bone hydatidosis. This condition is characterised by the presence of several cystic space-occupying lesions in the pelvic cavity. It is possible to develop symptoms such as pain in the abdominal region, swelling, sensations of pressure in the local area, and chronic sinus formation. These symptoms are all conceivable.
- Osteogenesis imperfecta/OI: this is also known as brittle bone disease, is a genetic (inherited) disorder characterised by bones that break easily without a specific cause.Pelvic inflammatory disease: Pelvic inflammatory disease is a condition that may damage a woman's reproductive organs and is given its own name by the same name. The majority of instances of this syndrome are brought on by an infection that is transmitted sexually. Most of the time, symptoms like pain in the stomach and lower abdomen and a discharge from the cervix can be seen.
- Pelvic fracture: A pelvic fracture may be brought on by a jarring experience that involves a lot of energy, such as being in a car accident. This type of bone fracture can also be caused by a fall from a great height, which increases the risk of serious injury. Fractures to the pelvis may result in significant bleeding, in addition to other injuries that need prompt medical treatment, and they should be treated as soon as possible. This is because the pelvis is located so near to the main blood vessels and organs in the body.
- Fibrous dysplasia: It is possible for this illness, which is known as fibrous dysplasia, to present itself in a number of different parts of the body, including the pelvis. This condition arises when abnormal fibrous tissue takes the place of healthy bone structure. Scar tissue that does not form very often leads the bone to become weaker, which in turn may cause the bone to alter shape and increases the risk of fractures. As a result of this, the bone is more likely to break. Scar tissue has the ability to alter the form of the bone, which can increase the risk of the bone breaking.
- Symphysis pubis dysfunction: Symphysis pubis dysfunction refers to symptoms you feel when the joint between your left and right pelvic bones (pubic symphysis) allows for more movement than usual. The term 'symphysis pubis dysfunction' refers to the symptoms that arise when the joint that connects your left and right pelvic bones (called the pubic symphysis) is able to move more freely than it normally would.
Pelvic Bone Tests
- Stool test: During a stool test, a sample of the patient's poop is looked at under a microscope for microscopic blood. This is done to check for cell abnormalities that could be caused by cancer.
- Lower gut endoscopy: An expert will do a lower endoscopy on a patient by putting a lighted tube into the patient's digestive system. This allows the expert to look for signs of injury or infection in the rectum and either part or all of the patient's colon.
- Ultrasound lower abdomen: An ultrasound is a diagnostic process that uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of a patient's internal organs in order to identify any breaks or abnormalities. These photos may be used to determine whether or not the organs are functioning normally.
- CT scan lower abdomen: A CT scan is a type of computed tomography (CT) that examines the abdomen and pelvis in order to create a picture of a cross-section of the body for the purpose of determining whether or not a fracture is present. The purpose of this examination is to determine whether or not a broken bone is present. To get comprehensive photographs of the body, the subject must be photographed from a number of perspectives.
- MRI lower abdomen: In magnetic resonance imaging, which is more commonly called 'MRI,' large magnetic fields, radio waves, and a computer are used to make detailed pictures of the bones and organs in the pelvic area.
- BMD lower abdomen: The screening for bone density, which is a specialised kind of testing that is aimed at measuring an individual's bone strength, makes use of X-rays as one of the diagnostic tools.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy: A diagnostic laparoscopy is a technique that allows for a direct examination of the organs and tissues located in the abdominal cavity and pelvis.The specialist will first create a tiny incision in the patient's abdomen, and then he or she will insert a thin tube that is attached to a small camera that is known as a laparoscope. This will allow the specialist to examine the patient's internal organs. Because of this, the doctor is able to inspect the patient's pelvic organs in search of any abnormal tissues or signs of infection that may be present.
- X ray lower abdomen: Radiation is used in the process of imaging that is known as x-rays, which collects images of the skeleton. If a pelvic fracture is suspected or confirmed, X-rays are needed to find out which part of the pelvis is broken and how bad it is.
- Blood screening: Examining the patient's blood is one of the most important ways to confirm a diagnosis of bone cancer and find out how far along the disease is.
- Biopsy for evaluation of infection: A qualified medical practitioner may perform a technique known as a biopsy in order to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. For this test, a small piece of bone tissue needs to be taken from the area that is hurt and then looked at under a microscope.
Pelvic Bone Treatments
- Closed reduction internal fixation: in this surgical procedure the bones which are fractured are fixed by a orthopaedic surgeon without cutting the skin open and fixing the bone using different instruments
- Pauwels osteotomy: it is a surgical procedure for treating nonunion or malunion of the femoral neck blade plate concluding to internal fixation of the high femoral osteotomies. it is a reliable method to treat fracture of the neck of femur and it is also considered as a conservative approach for the treatment of femur
- Dynamic hip screw insertion: this is a type of surgical procedure in which screw hip insurgents are performed with recurrent of the fixation of neck or femur fractures. It is also a rigid fixation and the hips screws are used for intertrochanteric fractures.
- Gallows traction: it is a type of preventive fixation procedure in which hip dysplasia is treated which can also be a reason for fracture of the hip bone in this procedure our incubator frame is used for traction of the lower hip bone which could be made of a thermoplastic material this method is used for treatment of fracture of thigh bone in young children and in children going through the phase of puberty
- Hip spica cast: it is a type of orthopaedic cast used for the immobilisation of the hipbone when there is any sort of injury to the hip muscles or tendons or any fracture in the hip bone it is used to facilitate the healing of injured hip giants and or also helpful in treatment of and promoting growth of the fractured hip bones.
- kuntscher nail: it is a specified type of nail known for interlocking intermediary regions of the femoral shaft with the hipbone and helpful in providing better mechanical stability to the femur
Pelvic Bone Medicines
- Analgesics for relieving pain in pelvic bone: Aspirin, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen are all examples of analgesics, and they are all capable of providing at least some relief from pelvic pain. Other examples of analgesics are paracetamol and naproxen.
- Antibiotics for infection of the lower gut and colon: In the event that the physician concludes that an infection is the primary reason for the patient's distress, antibacterial medication will most likely be prescribed in order to treat the condition. Antibiotics such as amoxicillin, ampicillin, and penicillin are the most common kinds.
- Antibiotics for pelvic inflammatory disease: the medicines for infection for pelvis infection are doxycycline, metronidazole, azithromycin, clindamycin, levofloxacin, ceftriaxone, and zithromax which have some side effects but still important for treating infection.
- Muscle relaxants for gluteal pain: A patient may be prescribed muscle relaxants such as metaxalone, methocarbamol, orphenadrine, or carisoprodol by a specialist.
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors