Penis (Male Anatomy): Diagram, Function, Diseases, and More
Last Updated: Jun 28, 2023
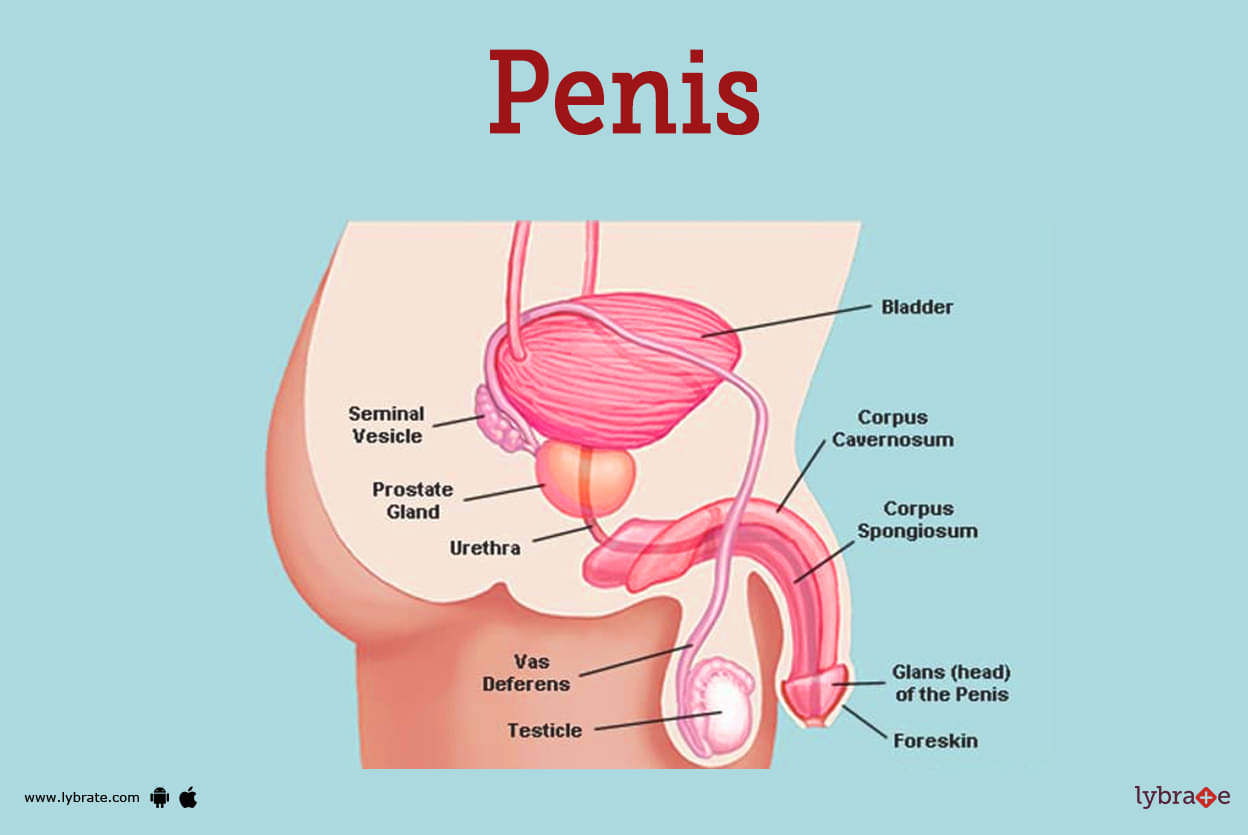
Penis Image
The penis is the male copulatory organ. During puberty it reaches its full size. For urine the Penis acts as a channel for passage.Penis Shaft is the interlink between urethra and pubic bone.The following parts constitute the penis.
- Glans penis: It is the head as well as the most sensitive end of penis. Foreskin is the outer layer of glans penis which encloses mucosa which is generally moist in nature and pink in colour. If foreskin is surgically removed then it leads to transformation of mucosa to dry from moist. Glans is also known as bell end.
- Corpus Cavernosum: These tissues are present adjacent to the penis. In these tissues the blood streams run which causes erection of the penis.
- Corpus Spongiosum: These are the mass of sponge-like tissue present along the front of penis and it marks the end of the glans penis. During erection the blood circulation increases in these tissues which perisit the opening of urethra. From the body, urethra which remains in the corpus spongiosum carries out the urine .
Penis Functions
The primary functions of the penis are Urinary and sexual activity are the two basic roles that the penis plays in the body.Erection and ejaculation are the two processes that make up the sexual function of the penis.
- Urination: Urination is the process through which urine (also known as pee) is expelled from the body. This takes place when urine travels from the bladder to the urethra and then finally to the meatus. When the detrusor muscle inside the wall of the bladder contracts, urine is expelled from the body. The exterior sphincter muscle, which is located between the penis and the bladder, is a controllable muscle that may either prevent urine from leaking out or allow urine to leak out.
- Erection: The penis becomes more rigid as a result of sexual desire and/or physical stimulation, which is referred to as an erection. Erections happening while you sleep and just after you wake up are both perfectly natural occurrences. When there is a greater amount of blood flowing into the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum, this results in an erection. The arteries that supply the erectile tissues will dilate (widen) during an erection, which will cause the penis to engorge (fill up with blood) at this time. The swelling puts pressure on the veins that are normally responsible for blood circulation out of the penis. This 'traps' the blood and assists in maintaining an erection during the activity.
- Ejaculation: Ejaculation refers to the process by which semen is expelled from the penis. Orgasms, which are a type of sexual reaction, are almost always present when this occurs. Ejaculation is characterised by a sequence of synchronous, involuntary muscular contractions, including the following
The release of sperm from the penis during ejaculation is known as 'ejaculation.'.In most cases, it is followed by a sexual reaction that is referred to as an orgasm. Ejaculation is characterised by a sequence of synchronous, involuntary contractions of the muscles.
Penis Diseases
- Erectile Dysfunction: E.D. is the disorder of penis which is mostly due to Atherosclerosis, which results that penis is not able to conceive its rigidity. Hence the male is not able to satisfy the female during coitus. There are many reasons for erectile dysfunction such as damage to the blood arteries of penis due to excess mastrubation and other reasons.
- Premature Ejaculation: It is the recurrent ejaculation during sex within one minute. Ejaculation time may different to person to person depending upon the country he is living in and the nutritional food he is eating.
- Delayed Ejaculation: It is the condition which marks delay in or absence of orgasm .
- Priapism: It is the unusual prolonged and unwanted persistence of erection. Some severe conditions include pain with Priapism. This disorder could be due to over use of medicine given for erectile dysfunction. This can be easily treatable by consultants.
- Hypospadias: It is the Congenital anomaly with abnormal ventral opening of male urethra .It is often associated with abnormal foreskin or urethral meatus.This defect can be treatable through surgery.
- Phimosis: Phimosis is due to the infection of penis in which the foreskin of penis does not retract to show glans penis.
- Paraphimosis: Retracted foreskin that cannot be returned to normal position . This condition usually occurs due to the forcible retraction of the foreskin.
- Balanitis: Appearance of redness on penis with pain and looseness of tissues are the symptoms of Balanitis. Balantis is mostly due to the infection in penis which results in inflammation of the glans penis.
- Balanoposthitis: It is a type of Balanitis, in which infection occurs in the foreskin of an uncircumcised man.
- Chordee: It is a congenital condition in which abnormal bend is present in the end of male copulatory organ. It can be cured through surgery.
- Peyronie's Disease: It is the unusual bend of the shaft of the penis. It could be due to injury or other medical conditions.
- Urethritis: It is inflammation of the urethra due to infection in it which results in persistence of pain during urination, mastrubation and during coitus. The most common causes of Urethritis is Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea.
- Gonorrhea: During coitus the affected female infect the male sexual organ by bacteria N. gonorrhea which results in urethritis.
- Chlamydia: Chlamydia is mostly asymptomatic in approx 40 percent males . It is a bacterial infection that occurs due to coitus with an infected person which leads to urethritis.
- Syphilis: Syphilis causes ulcers that are painless or less painful.This bacteriological disease is also spread during coitus.
- Herpes: It is a disease that is passed on via sexual contact that is caused by the HSV-1 and HSV-2 viruses. Additionally, it is capable of causing an infection in the circulatory system.
- Genital Herpes: It is a variety of herpes. Itching, burning, and blisters are its common symptoms.
- Micro Penis: Micropenis is a congenital disease. Hormonal imbalance is its major cause, which leads to an abnormally small penis.
- Penis Warts: The most common STD which can spread easily is genital warts. Its causative agent is HPV (Human papillomavirus).
- Penis Cancer: HPV increases the risk of penile cancer while circumcision decreases it. It is a rare disease in countries like the U.S.
- Paraphilias: Sexual arousal to atypical situations, fantasies, individuals, or acts.
- Pedophilia: Sexual interest in children (generally less than 13 years old) occurs while an individual is generally a minimum of 5 years older than the person of interest.
- Transvestic: Sexual arousal from cross dressing.
- Epispadias: It is the Congenital opening of the urethra on the dorsal surface of penis.
- Bacterial Prostatitis: An acute prostate infection usually affects younger men. The common causative agents of this condition are E. coli, Gonorrhoea, and Chlamydia.
- Erythroplasia of Queyrat: It is a carcinoma that occurs in situ on the glans. It is velvet red in appearance.
- Penile Fracture: This condition occurs with an erect penis during sex. A snapping sound, with rapid detumescence, and severe pain are some of the common symptoms of this disorder.
- Bowen Disease: It is a carcinoma in situ that is present on the penile shaft epithelium. It appears like a single red plaque with crust and oozing.
- Peyronie's Disease: When plaque, or scar tissue, builds up inside the penis, Peyronie's disease results in a painful, bent erection of the penis. However, when it hurts or the bend is considerable, it can cause erectile dysfunction and even prevent coitus.
- Decreased Libido: It is the condition develop in which the urge of sex reduces.
- Anorgasmia: In this condition, the male is not able to conceive orgasm despite multiple attempts at stimulation.
- S.T.D: These are the most common U.T.I in the urethra. Gonorrhoea and Chlamydia are the most common U.T.I in younger men.If this condition remains untreated, the infection may damage the kidney, which could lead to kidney failure.
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: It is caused by E. coli. In which you find that there is acute inflammation of the prostate associated with U.T.I.
Penis Tests
- Urethral Swab: It is the process by which soft tissue is inserted inside the male copulatory organ. This technique is used in the diagnosis of inflammation of the urethra and other infections.
- Urinalysis: It is the analysis of urine which helps in the diagnosis of infection, bleeding, and renal problems.
- Nocturnal Penile Tumescence Testing ( Erection Testing): It is used to determine the reason behind erectile dysfunction. In this, a muscular device is worn overnight to see the erection of the penis.
- Urine Culture: It is the process in which urine is collected and culture in the laboratory to identify the infective cause that affects penis.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (P.C.R): It is a method to identify the microbes that affect the male copulatory organ, such as Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea, etc. PCR is used to identify many other diseases too.
- Microscopic Examination: It is used to identify microbes such as bacterial prostatitis.
- USG: It is used to identify prostate calculi.
Penis Treatments
- Penis surgery: This method is very useful for penis cancer, and it is used to cure various disorders such as hypospadias.MAGPI (Metal Advancement & Glanuloplasty Integrated): For Hypospadias,. In order to correct this issue, a treatment known as MAGPI (Metal advancement and Glanuloplasty Integrated) is performed. This operation is carried out by both urologists and plastic surgeons.
- Preputioplasty: In addition, circumcision is performed, but it is often avoided in individuals who are younger. Regarding Phimosis When treating in adults, circumcision or preputioplasty are the two surgical options that are often used.
- Suprapubic Cystotomy: It is the broad word for the surgical development of an opening into the bladder; it may be a deliberate component of urologic surgery, or it may be an iatrogenic event that occurs as a result of medical intervention. On the other hand, the term may also be used in a narrower meaning to refer to operations that are performed suprapubically, such as suprapubic cystostomy or suprapubic catheterization.
- Circumcision: It refers to the process of surgically removing the foreskin, which is the tissue that covers the head (glans) of the penis. It is a time-honored custom that may be traced back to religious origins.
- Corporal Shunts: In order to stop fibrotic activity and make sure the patient can still have erections, an aspiration of blood and irrigation of the cavernosal bodies are also procedures that are done.
- Testosterone Therapy: The lower amount of testosterone is the major cause of erectile dysfunction. can be cured by testosterone supplements like Ashwagandha and Silajit.
- By Vaccination: It includes getting vaccinated against viruses like HPV, which prevents carcinoma.
Penis Medicines
- Phosphodiesterase (Pde) Inhibitors: The medications sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, and avanafil are the most popular ones prescribed to patients suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED).
- Collagenase: Oral treatments for Peyronie's disease have not shown substantial improvement in patient outcomes. On the other hand, drugs that are injected into the penis have shown to have very positive benefits. Injections of a considerable dose may be given to the penis on many occasions in order to treat Peyronie's disease. Collagenase, interferon protein, xiaflex, and a number of other medications are utilised for the therapy of the condition.
- Antifungal Medications: Clotrimazole, metronidazole, and miconazole are the drugs that are often used for the treatment of balanoposthitis. Miconazole is also sometimes used.
- Analgesics: Analgesics are a kind of drug used to treat priapism. This medicine often contains phenylephrine and acetaminophen. However, aspiration and surgery are currently the most effective therapies for this condition.
- Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs: for Penile Fracture, If this disease is treated with ibuprofen, the patient may see a reduction in both the swelling and the discomfort. On the other hand, the most effective treatments for this ailment are surgery and care received at home.
- Antibiotics: When treating urethritis, a patient is often prescribed a mixture of antibiotics and pain relievers. Antibiotic treatment for this illness is often administered in the form of azithromycin (Zithromax), doxycycline combined with ceftriaxone (Rocephin), or cefixime (Suprax).
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics: To treat acute bacterial prostatitis, medications such as TMP-SMX and ciprofloxacin are often prescribed.
- Steroidal Drugs: Regarding Phimosis Conservative treatment is recommended for youngsters, which consists of using steroidal cream for between four and six weeks.
- Enzymes: Regarding the Paraphimosis Hyaluronidase injections, physical compression, and the administration of cold bags are all components of the therapy for this condition. In the first stages of treatment for priapism, patients get injections of ketamine. In addition, hyaluronidase is administered through injection.
Table of content
Find Sexologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors