Pericarditis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
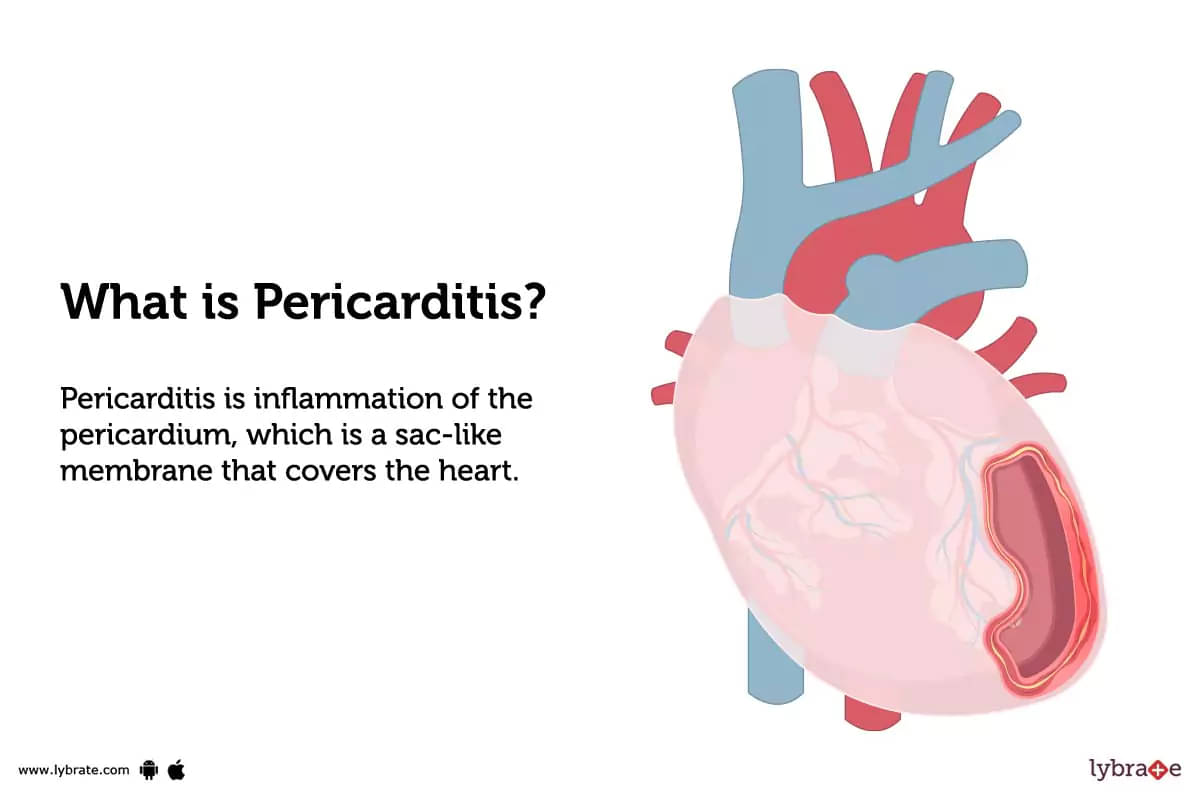
What is Pericarditis?
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, which is a sac-like membrane that covers the heart. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever. It can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, injury, or certain medical conditions such as lupus or kidney failure.
Types of Pericarditis
Depending on the cause, there are several types of pericarditis:
- Viral Pericarditis: This type of pericarditis is caused by a virus and is usually milder than other forms. Treatment typically involves rest and medications to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Bacterial Pericarditis: This type of pericarditis is caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species. Treatment often involves antibiotics to eliminate the infection along with other medications to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Fungal Pericarditis: This type of pericarditis is caused by a fungal infection such as Candida species or Aspergillus species. Antifungal drugs are often used in combination with other medications to minimise inflammation and discomfort.
- Autoimmune Pericarditis: This particular kind of pericarditis develops when the immune system of the body erroneously targets its own tissues in the region of the heart instead of attacking outside substances.
What causes Pericarditis?
It is caused by a variety of factors, including the following:
- Viral infections
- Bacterial infections
- Autoimmune diseases
- trauma to the chest area radiation therapy,
- kidney failure
- other medical conditions.
- It's possible that there is no identified reason in certain circumstances.
What are the symptoms of Pericarditis?
The primary sign of pericarditis is pain in the chest. Other warning signs and symptoms might be:
- Breathing problem
- Coughing
- Palpitations (irregular heartbeat)
- Low grade fever
- Weakness or fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
How can you prevent Pericarditis?
- The best way to prevent pericarditis is to practice good hygiene, exercise regularly, and manage any underlying health conditions.
- Additionally, getting vaccinated for illnesses such as measles, mumps, and rubella can help reduce the risk of developing pericarditis.
- Finally, avoiding contact with people who have an infection can also help reduce the chance of contracting pericarditis.
Pericarditis - Diagnosis and Tests
The diagnosis of pericarditis involves:
- Physical Examination: During a physical examination for pericarditis, the doctor may listen to your heart and lungs with a stethoscope. They may also feel your abdomen for any swelling or tenderness.
- Medical History: Your doctor will inquire about your medical records, including any recent infections or illnesses, in order to determine if you have pericarditis. They can also inquire as to whether you've ever had chest pain or cardiac issues.
Additional tests to verify or rule out the problem may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Pericarditis may often be diagnosed using the ECG. Changes in the electrical activity of the heart can be observed, including ST segment elevation, T wave inversion and P-wave changes.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray may be used to diagnose pericarditis by looking for signs of fluid in the space between the lungs and heart (the pericardial space).
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Any structural defects or indications of pericardial inflammation are found using MRI. It can also be used to monitor the progression of the disease and determine if any treatment has been effective.
- Blood Tests: C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, serum electrolytes, and a complete blood count (CBC) are blood tests used to identify pericarditis. These tests help to determine whether there is inflammation present in the body, as well as the cause of the inflammation.
What are possible complications of Pericarditis?
- Pericardial Effusion: This is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac and can be a complication of pericarditis. It can lead to decreased cardiac output, increased intra-abdominal pressure, and compression of other organs in the chest cavity.
- Constrictive Pericarditis: This is a serious complication that occurs when inflammation causes the layers of the pericardium to stick together, resulting in decreased heart function due to a decrease in the heart's ability to fill with blood properly.
- Heart Failure: If left untreated or if not treated properly, pericarditis can lead to heart failure due to accumulation of fluid in the pericardium or constriction of the heart muscle by scar tissue from healing inflammation.
- Cardiac Tamponade: This is a medical emergency where there is an excessive amount of fluid around the heart that squeezes it and impairs its ability to pump blood normally. It can be caused by severe cases of pericarditis or trauma that injures the pericardium causing it to leak fluid into this space around the heart.
- Arrhythmias: Inflammation caused by Pericarditis can cause disruption and scarring within cardiac tissue leading to abnormal electrical signals traveling through your heart muscle that can cause arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat).
Home Remedies for Pericarditis?
There are various home treatments that may be useful in controlling pericarditis symptoms:
- Ginger: Ginger possesses anti-inflammatory qualities that aid in the reduction of inflammation and discomfort. Ginger may be consumed in the form of ginger tea or by chewing on a piece of ginger root.
- Turmeric: Turmeric is another herb with potent anti-inflammatory effects. You may consume turmeric as a supplement or as a spice in your food.
- Triphala: Ayurvedic medicine often uses triphala, a combination of three fruits (amalaki, bibhitaki, and haritaki), to enhance digestion and lessen inflammation. You can take triphala as a supplement or drink it as tea.
- Ashwagandha: Ashwagandha is an ancient herb that is used to reduce stress and improve overall health. It may be taken as a supplement or in the form of a tea.
What not to eat in Pericarditis?
Foods to avoid when you have pericarditis include:
- Fried, greasy, and spicy meals, as well as processed meats, dairy products, and alcohol, are all forbidden.
- Salt-rich foods should also be minimized.
- Caffeine and high-sugar meals should also be limited or avoided.
Pericarditis Treatment
Pericarditis is treated according to the condition's aetiology and severity. Possible treatments include:
- Pericardiectomy: This operation includes the removal of the pericardium in whole or in part. This may help minimise pericarditis-related discomfort and inflammation.
- Pericardial Window: A small opening is created in the pericardium to allow fluid and air to escape from around the heart and reduce pressure on it.
- Percutaneous Balloon Pericardiotomy: This procedure involves inserting a balloon into the chest cavity and inflating it to break up scar tissue that has formed around the heart due to pericarditis.
- Surgical Repair of Damaged Heart Tissue: In cases where there is damage to heart muscle or valves due to pericarditis, surgery may be needed to repair this damage and improve symptoms.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): PCI refers to a class of minimally invasive techniques intended to clear coronary artery blockages (those which transport blood to the heart). By normalizing blood flow, the procedure may alleviate symptoms associated with clogged arteries, such as chest discomfort and shortness of breath.
Which doctor to consult for Pericarditis?
When it comes to treatment for pericarditis, seeing a cardiologist is the best choice.
Which are the best medicines for Pericarditis?
The best medicines for pericarditis include:
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressants, which may be prescribed if the cause of pericarditis is an autoimmune disorder or inflammatory condition. For example, Azathioprine.
- ACE inhibitors: ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) may be used to decrease inflammation and relieve high blood pressure associated with pericarditis. Examples include Captopril, Enalapri, Lisinopril ,Ramipril.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs help minimise pericarditis-related inflammation and discomfort. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), indomethacin (Indocin), and aspirin are some examples.
- Corticosteroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation, which in turn can reduce pain associated with pericarditis: Corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, may be administered for this problem.
- Antibiotics: If your pericarditis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be necessary for treatment. Amoxicillin (Amoxil) and cephalexin (Keflex) are two examples of antibiotics that can be used.
- Colchicine: This medication helps reduce inflammation and pain associated with some forms of pericarditis, including those caused by certain types of arthritis such as gout or pseudogout.
How long does it take to recover from Pericarditis?
- Pericarditis recovery duration might vary substantially depending on the underlying cause and severity of the ailment.
- In most cases, rest and anti-inflammatory medications are sufficient for a full recovery, which usually occurs within a few weeks.
- In more severe cases, treatment may involve antibiotics or even surgery to remove excess fluid from the pericardial sac.
- With adequate treatment and relaxation, the majority of individuals recover from Pericarditis within two to four weeks.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
- No, the effects of pericarditis treatment are not permanent. The purpose of therapy is to reduce inflammation and pain, although recurrence is likely.
- It is important to follow the treatment plan prescribed by your doctor, which may include lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking or reducing alcohol consumption, taking medications such as anti-inflammatories and/or steroids, and in some cases undergoing surgery.
- It is essential to maintain regular contact with your physician to ensure that any recurring symptoms are appropriately treated.
What are the post treatment guidelines?
Here are some general guidelines for post treatment of pericarditis:
- Take medications as prescribed: Your healthcare provider will likely prescribe medications to help reduce inflammation and pain. Ensure that you take these medications precisely as prescribed.
- Rest: During recovery following surgery, it is essential to relax and avoid intense activity. This will support in the healing process and reduce the likelihood of complications.
- Follow up with your healthcare professional: They will track your progress and alter your treatment strategy accordingly.
- Watch for signs of infection: If you develop fever, chills, or other signs of infection, be sure to notify your healthcare provider immediately.
- Avoid contact sports: If you have had surgery to repair a tear in the pericardium, you will need to avoid contact sports for at least six weeks to allow the repair to heal properly.
What is the cost of Pericarditis treatments in India?
- The cost of pericarditis treatment in India might vary significantly based on the severity of the disease, the kind of treatment needed, and other variables.
- In compared to other countries, most of the pericarditis treatments in India are fairly affordable. Medication might cost anything from a few hundred rupees to several thousand rupees.
- In addition, a hospital stay and related costs could add up to several thousand rupees as well. Other diagnostic tests may be necessary, increasing the entire cost.
What are side-effects of Pericarditis treatments?
The most common side effects of pericarditis treatments are:
- Fatigue,
- Dizziness,
- Nausea, and
- Abdominal pain.
Other potential side effects include headaches:
- Shortness of breath,
- Joint pain,
- Chest pain,
- Low blood pressure.
Pericarditis - Outlook / Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to pericarditis then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like constrictive pericarditis, heart failure, cardiac Tamponade, etc. in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors