Pineal Gland (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
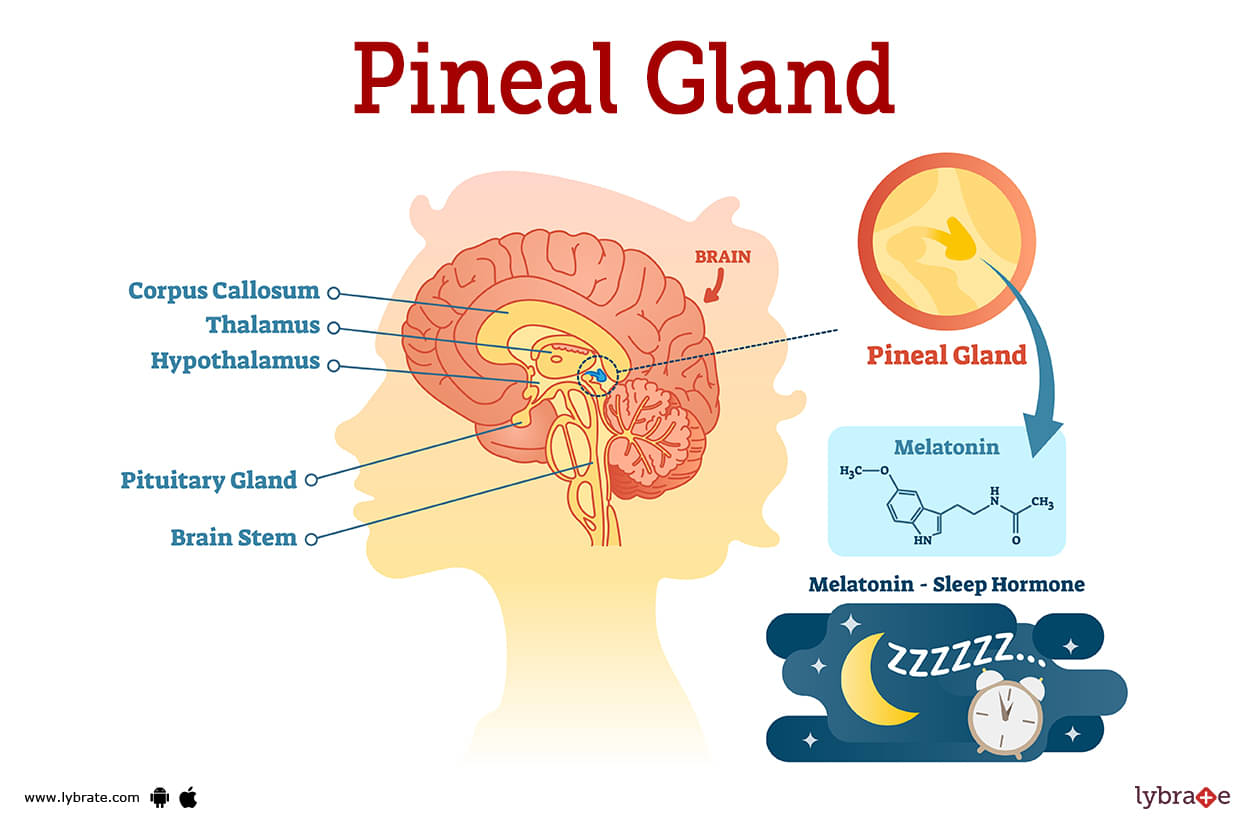
Pineal Gland Image
The pineal body, also known as the epiphysis cerebri, is a small gland in your brain located beneath the back half of the corpus callosum. The pineal gland is an endocrine gland that produces the hormone melatonin. The primary function of your pineal gland is to assist govern the circadian cycle of sleep and waking by secreting melatonin.
The pineal gland is formed like a little pinecone, thus the name ('pine' -al gland). It is, however, pronounced 'pin-ee-Uhl.'. The pineal gland was the latest component of the endocrine system to be discovered, and it is also the least understood.You can find your pineal gland near your brain's midsection. It sits in a cleft immediately above the thalamus, a brain area responsible for coordinating a variety of sensory processes.
Pineal Gland Functions
The fundamental function of the pineal gland is to receive information about the daily light-dark (day-night) cycle from your eyes' retinas. In response to this information, it manufactures and secretes melatonin, with larger quantities at night (during the dark hours) and lower levels during the day. The retinas in your eyes are responsible for providing this information (during light hours).
Pineal Gland Conditions
- Pineal gland tumours: Pineal gland tumours are incredibly uncommon, and there are a few distinct subtypes of this form of cancer. Children and adults younger than 40 are more likely to be affected. Pineal tumours aren't necessarily cancerous, but even if they aren't, they can cause problems as they develop because they press against other parts of your brain, leading to various neurological issues.
- Injuries that affect the pineal gland: A dysfunctional pineal gland may result from damage to the gland itself. People who have had a traumatic brain injury (TBI) experience issues with at least one of their brain's endocrine glands. These glands include the pineal gland and the pituitary gland. People with these problems range from approximately 30 to 50 percent.
- Pineal gland calcification: Calcification of the pineal gland is a very common occurrence. The process of calcification occurs when calcium accumulates in body tissue, which causes the tissue to become more rigid. As you age, your pineal gland is more likely to become calcified. While a certain amount of calcification is considered acceptable, having an excessive amount can hinder your pineal gland's operation. In many studies, a higher degree of calcification of the pineal gland is associated with Alzheimer's disease.
- Obstruction of the Third Ventricle: Because it is a relatively narrow passageway, the third ventricle can be easily blocked by local brain tumors or congenital abnormalities. The obstruction causes an excessive accumulation of CSF within the brain, resulting in increased intracranial pressure in adults and in hydrocephalus in children. This condition can also cause headaches. Ventriculography allows for the localization of the obstruction to be determined.
- Depression: Melatonin secretion is aberrant in individuals with affective disorders such as major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD), according to hormonal data. This aberrant melatonin output might be contributing to the circadian rhythm dysfunctions seen in these individuals.
- Mood Swings: The pineal gland is responsible for producing several hormones. Melatonin is one of these, and it plays a role in helping to regulate the body clock, which includes the patterns of sleep. Additionally, the pineal gland may play a role in regulating levels of female hormones and contributing to cardiovascular health and emotional stability.
- Peptic or Stomach Ulcers.: The results of our earlier research on the pineal gland's protective role against stress are presented, along with a brief overview of those findings. The neuroendocrine aspect of ulcers, as well as the neuroendocrine part of chronic auditory stress
- Disruption in Sleep Patterns: If you have a problem with your pineal gland, it may cause an imbalance in your hormones, affecting other bodily systems. For instance, sleep patterns are frequently thrown off when there is an issue with the pineal gland. It can manifest itself clinically in conditions such as sleeplessness and jet lag.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Anxiety, inadequate thyroid hormone production, menopause symptoms, and other health issues can all be caused by low melatonin output. An overabundance of melatonin in the body can result in low blood pressure as well as a disruption in the normal functioning of the thyroid and adrenal glands. Pineal gland abnormalities might involve a kind of depression known as seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Pineal Cysts: Ten percent of patients who have received MRI or CT scans have been found to have pineal cysts. However, the vast majority of persons who have pineal cysts do not exhibit any apparent symptoms. Some individuals occasionally report experiencing headaches and eye movements that are not usual.
- Alzheimer's Disease: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition that affects a large number of people all over the world. AD is accompanied by changes in various lifestyle patterns, including sleep disturbances. The pineal gland is the major endocrine organ, and it is responsible for the production of hormones like melatonin as well as the regulation of circadian rhythms. Melatonin synthesis is reduced because of a shrinking pineal gland and increased pineal calcification, both of which are associated with ageing.
Pineal Gland Test
- X-ray: The form of radiation known as electromagnetic waves is what makes up X-rays. Imaging with X-rays allows for creating photographs that show the inside of your body. A variety of dark and light greys depict the various components of your body in the pictures. It is because multiple types of tissue absorb varying levels of radiation. Calcium's X-rays are most effectively absorbed by calcium, giving bones their characteristic white appearance. Because they drink less water, fatty tissue and other soft tissues appear grey. Since air is the medium that absorbs the least, the lungs seem dark.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic method that creates high-quality images of inside organs and structures. MRI combines a strong magnet, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed pictures. It's X-ray-free (radiation).
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: CT scans can identify injuries and infections. A computer combines x-rays to produce a 3D representation of a patient's bones and soft tissues. Your doctor can identify disorders using CT without pain or infection.
- Eeg: An EEG monitors brain electrical activity by connecting electrodes to the scalp. Even while we sleep, brain cells exchange electrical impulses. When they occur, EEG recordings show wavy lines.
Pineal Gland Treatments
- Ventriculostomy: During this surgery, a drain is surgically implanted into one of the naturally occurring cavities inside the brain (ventricles). The ventriculostomy procedure is often carried out to lower excessive pressures inside the brain.
- Craniotomy: this is a surgical procedure in which a hole is drilled into the side of the skull by a surgeon to release pressure within the skull.
- Lumbar Drain: Drainage of the lumbar region occurs when a drain is inserted into the fluid that surrounds the spinal cord. This may reduce the pressure applied to the brain and spinal cord.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are utilised in the process of chemotherapy to kill cancer cells and stop their growth.
Pineal Gland Medicines
- Medicine for the treatment of Hormonal imbalance: Artificial hormones are given for the treatment of hormonal imbalance, including medroxy progesterone and estrogen derivatives.
- Use of Cholinesterase inhibitors: Several drugs have demonstrated some potential for improving patients' cognitive abilities, ranging from moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. They do not impact preventing Alzheimer's disease or delaying its course.
- Antibiotics for infection in the Pineal gland: Antibiotics are a drug used to treat bacterial disorders affecting the brain and pineal gland. Some medicines include Vancomycin, Cephalosporin (or Cefepime if concerned for Pseudomonas), and azithromycin or doxycycline.
- Antidepressants for the maintenance of the daily cycle: Antidepressants are prescribed for fatigue, sleep and appetite disturbances. Antidepressants like SSRIs and SNRIs can raise mood- and pain-regulating neurotransmitter levels. Duloxetine and amitriptyline are commonly given.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are some disorders of the pineal gland?
What are the symptoms of a malfunctioning pineal gland?
What happens when the pineal gland is impaired?
How do I know if my pineal gland is damaged?
What happens when the pineal gland is damaged?
Which disease is caused by the pineal gland?
What does the pineal gland really do?
Can humans live without pineals?
Table of content
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors