Pulmonary Embolism: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
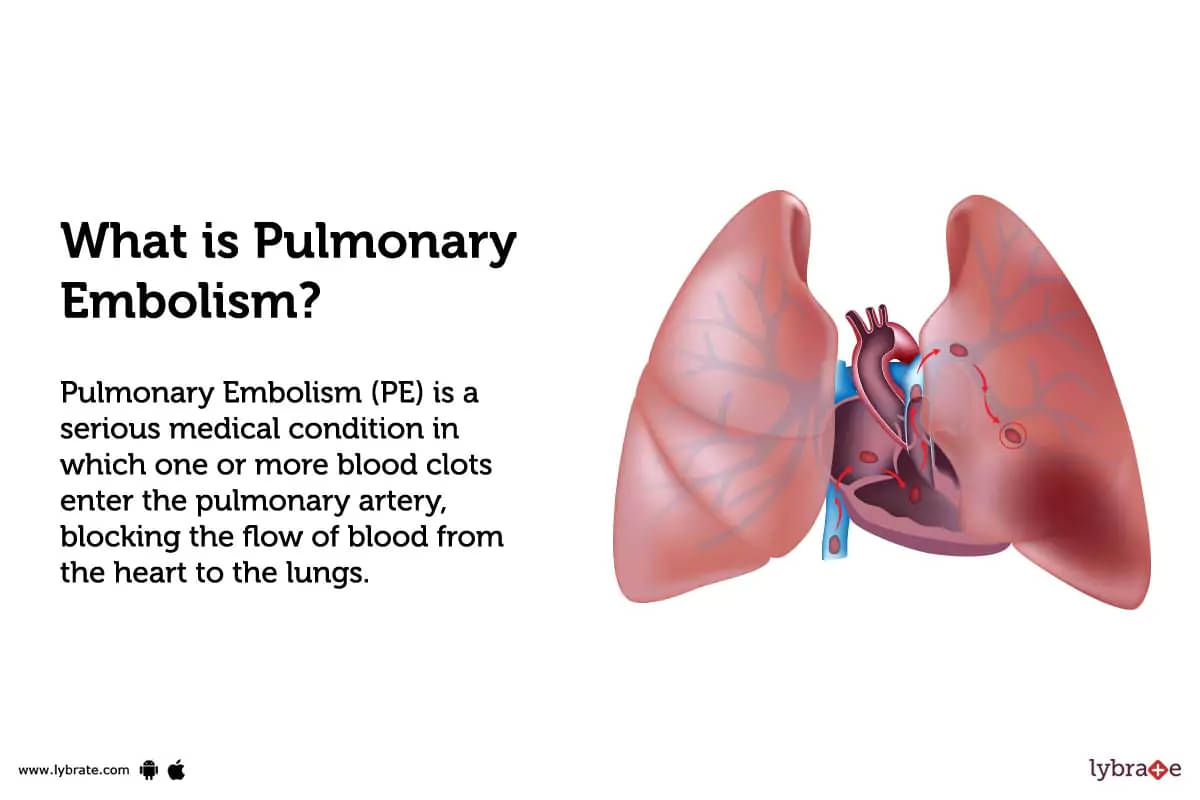
What is Pulmonary Embolism?
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) is a serious medical condition in which one or more blood clots enter the pulmonary artery, blocking the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs. It is estimated that between 300 000 and 600 000 people suffer from PE each year in America alone.
Types of Pulmonary Embolism
- Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): This kind of pulmonary embolism is the result of a blood clot that originates in a vein deep inside the body and reaches the lungs.
- Arterial Embolism: An arterial embolism occurs when a clot in an artery, usually from the heart, blocks blood flow to the lungs. This type of pulmonary embolism is more serious than VTE and can lead to death if not treated quickly.
- Fat Emboli: Fat emboli are clumps of fat particles that travel through the bloodstream and lodge in small arteries and capillaries in the lungs, blocking blood flow and leading to pulmonary embolism. This type of embolism is most common after long bone fractures or other traumatic injuries where fat can break away from surrounding tissue and enter into circulation.
- Air Emboli: Air emboli occur when air enters into circulation, usually due to a puncture wound or surgery on a major airway such as the trachea or bronchus; this type of pulmonary embolism can be deadly if not treated quickly enough.
What causes Pulmonary Embolism?
- A blood clot that develops in a vein, generally deep inside the leg or pelvis, and goes to the lungs is the most frequent cause of pulmonary embolism.
- Other causes include air bubbles, fat from broken bones or tumors, or foreign objects such as pieces of clothing or gauze pads that become lodged in the arteries of the lungs.
What are the symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism?
These are frequent signs of pulmonary embolism:
- Shortness of breath: A sudden and significant increase in the difficulty of breathing.
- Chest pain: Sharp and stabbing pain in the chest that worsens with a deep breath.
- Coughing up blood: Blood-tinged sputum may appear.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: Feeling faint or passing out when standing up.
- Rapid heartbeat: Heart rate increases to over 100 beats per minute.
- Sweating or sweating profusely: Excessive perspiration, even at rest.
How can you prevent Pulmonary Embolism?
- Maintaining a healthy weight and consistent exercise routines are essential.
- Staying seated for extended periods of time should be avoided wherever possible, particularly on long flights or road journeys.
- It is recommended to use compression stockings to help prevent blood clots from developing in the legs.
- Take preventive medications, such as anticoagulants, if you are at high risk for pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Quit smoking to reduce your risk of developing blood clots and PE.
- Talk to your doctor about any existing medical conditions that may increase your risk for PE, such as deep vein thrombosis or heart valve replacement surgery.
Pulmonary Embolism - Diagnosis and Tests
Pulmonary embolism is diagnosed based on:
- Physical examination: It generally includes looking for signs and symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, coughing up blood, rapid heart rate, and low oxygen levels.
- CT Scans: This kind of imaging scan makes use of X-rays to obtain precise photographs of the lungs. It may assist in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (PE) by locating blockages in the blood arteries.
- Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram is a non-invasive ultrasound test used to evaluate the structure and function of the heart. The echocardiogram can detect changes in blood flow, such as decreased oxygen levels or blockages in the pulmonary arteries, which may indicate an embolism.
- Ventilation-perfusion scans (V/Q scans): Ventilation-perfusion scans are a type of imaging test used to diagnose pulmonary embolism. This scan is done by placing a radioactive tracer in the bloodstream and then using a special camera to take pictures of the lungs while they are being ventilated. The tracer highlights any areas of decreased ventilation or perfusion, which can indicate the presence of a pulmonary embolism.
- D-dimer tests: A D-dimer test is a blood test that is used to help diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). This test examines the concentration of fibrin degradation products (FDPs) in the blood. FDPs are created when a clot breaks down. High levels of FDPs may indicate that a clot has formed, such as in PE.
- Prothrombin time: The Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures how long it takes for a clot to develop in a blood sample. It is used to determine if the patient has a clotting disorder, such as pulmonary embolism.
What are possible complications of Pulmonary Embolism?
The following are potential complications of pulmonary embolism:
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Right-sided heart failure
- Hypoxia
- Shock
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)
Home Remedies for Pulmonary Embolism?
- Garlic: Lung inflammation brought on by pulmonary embolism may be lessened with the use of garlic. To use garlic as a home remedy, crush two cloves of garlic into a paste and mix with one teaspoon of honey or lemon juice. Consume this mixture twice daily to get relief from symptoms of pulmonary embolism.
- Eucalyptus Oil: Due to its anti-inflammatory characteristics, eucalyptus oil may help decrease lung inflammation carried by pulmonary embolism. To use eucalyptus oil as a home remedy, add five drops of eucalyptus oil to hot water or tea and inhale the steam for 10 minutes twice daily to get relief from symptoms of pulmonary embolism
- Drink ginger tea: Ginger is a natural anticoagulant and can help reduce the risk of blood clots, including pulmonary embolisms. Boil some fresh ginger root slices in water for 15 minutes to prepare ginger tea.
- Take ginkgo biloba: Ginkgo biloba is an herb used to treat many conditions, including blood vessel diseases and circulation problems. It may help reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism by thinning the blood and improving circulation.
What to eat in Pulmonary Embolism?
- Foods with anti-inflammatory properties should be prioritized, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish.
- Foods high in fiber can help to reduce the risk of blood clots, such as legumes, oats, and nuts.
- Low-fat dairy products are beneficial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
What not to eat in Pulmonary Embolism?
Foods to avoid in pulmonary embolism:
- Fatty, salty, and sugary foods.
- Luncheon meats, hot dogs, sausage, and other processed meats.
- Refined carbs, including white bread, spaghetti, and pastries.
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
- Medications: Treatment for PE typically involves medications to help dissolve the clot, reduce inflammation, and prevent further blood clots from forming.
- Thrombolytic therapy: This involves the use of clot-dissolving drugs to dissolve the clot and improve blood flow in the lungs.
- Clot removal: Clot removal can be done surgically or with a catheter-based procedure called an embolectomy.
- Symptomatic treatments: Patients may receive oxygen therapy, diuretics, or other medications to reduce symptoms caused by pulmonary embolism, such as difficulty breathing or chest pain.
- Vena cava filter placement: A device is inserted into the inferior vena cava during this surgery to stop more blood clots from reaching the lungs.
- Pulmonary embolectomy: This is a surgical procedure in which the clot is physically removed from the lungs through an incision in the chest wall.
Which doctor to consult for Pulmonary Embolism?
The most appropriate doctor to consult for this condition is a pulmonologist, who specializes in diseases of the lungs and respiratory system. A pulmonologist can diagnose, treat, and monitor the progress of an individual with PE, as well as advise them on ways to reduce their risk of future clots. Depending on the intensity of the PE, other experts including cardiologists or hematologists may also be contacted.
Which are the best medicines for Pulmonary Embolism?
- Anticoagulant medicines: Anticoagulant medications such as heparin, enoxaparin, and warfarin are the most common medications used to treat pulmonary embolism.
- Thrombolytic drugs: Thrombolytic drugs such as alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase can be used to dissolve large clots quickly.
- Anti platelet drugs: Antiplatelet medications including aspirin, clopidogrel, and ticagrelor are often used for pulmonary embolism to stop the development of new blood clots.
How long does it take to recover from Pulmonary Embolism?
Depending on the extent of the clot and any existing illnesses, the time it takes to recover from a pulmonary embolism might vary. Generally, it takes around 6 to 12 weeks for the body to naturally dissolve and break down the clot. With proper care and attention, most people will make a full recovery from a pulmonary embolism.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The treatment for pulmonary embolism (PE) is usually effective in preventing further complications, such as long-term disability or death. However, it cannot reverse any existing damage caused by the clot.
In most cases, the effects of treatment are permanent and the patient can expect to make a full recovery. Depending on the severity of the PE and any underlying medical conditions, some individuals may have residual effects that may require additional treatment or lifestyle modifications.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- After a patient is treated for a pulmonary embolism, it is important to follow up with their doctor regularly to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
- Patients should continue taking prescribed anticoagulant medications such as warfarin or heparin for the duration of treatment and possibly beyond, depending on the severity of their condition.
- It is important for patients to maintain an active lifestyle that includes regular exercise and physical activity to help keep blood vessels open and reduce the risk of further clotting.
- Patients should also monitor their diet, avoiding foods high in fat and cholesterol while increasing intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to maintain a healthy weight.
- In addition, patients should seek medical advice before starting any new medication or supplement as these can interfere with anticoagulants.
What is the cost of Pulmonary Embolism treatments in India?
The cost of treating Pulmonary Embolism in India depends on the severity of the condition, location and the type of treatment required. Generally, conservative treatments such as anticoagulant medications can cost anywhere between Rs.1,000 to Rs.20,000 per month.
For more invasive treatments such as thrombolytic therapy and surgical removal of the clot, costs can range from Rs.50,000 to Rs.5 lakhs or even more depending on complexity and hospital charges.
What are side-effects of Pulmonary Embolism treatments?
The side effects of pulmonary embolism treatments depend on the specific treatment used. Common side effects of anticoagulant medications include: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding.
Other possible side effects can include headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and skin rashes.
Surgery to remove a blood clot from the lung may cause pain or discomfort at the site of the surgery and an increased risk of infection. In rare cases, lung surgery may also cause a pneumothorax (collapsed lung).
Pulmonary Embolism -Summarize
If you are suffering from any complications relating to pulmonary embolism then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like pulmonary hypertension, right-sided heart failure, shock, etc. in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors