Renin (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 02, 2023
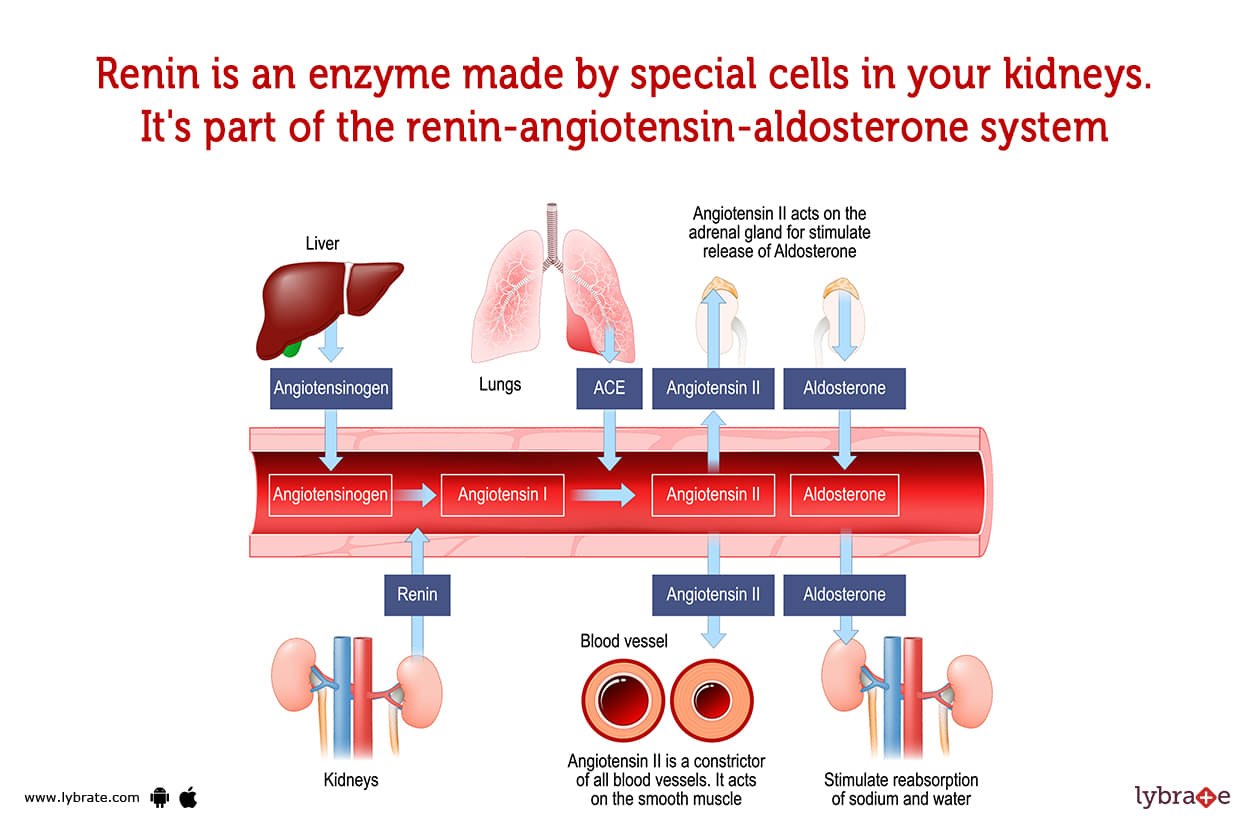
Renin Image
Renin is an enzyme that supports healthy sodium and potassium levels in the body as well as blood pressure regulation. Renin is a chemical that is produced by specific kidney cells and released into the bloodstream when blood pressure falls too low.
Renin is an enzyme produced by particular kidney cells. It is a component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, a series of events that control blood pressure. Renin specifically regulates the adrenal gland's production of the hormone aldosterone.
Where is renin produced?
Your kidneys are where renin is made. Your kidneys release renin into your bloodstream when your systolic blood pressure drops or they detect that you are volume-depleted.
What is renin made of?
There are 340 residues of amino acids in renin. (Water is eliminated during the process in which two or more amino acids combine to form a peptide. The residue of amino acids is what's left.)
How is renin measured?
Plasma renin activity is the most commonly used renin measurement (PRA). It measures how well renin generates angiotensin I. (the precursor of angiotensin II). It can also be measured by direct renin
Renin Functions
Renin's primary role is the control of blood pressure. It controls the levels of potassium and sodium in your body along with angiotensin and aldosterone.The steps involved in the process are as follows:
- Your liver produces angiotensinogen, a precursor to angiotensin, which renin then transforms into angiotensin I. (The hormone angiotensin causes your blood vessels to constrict.)
- To create angiotensin II, angiotensin I is converted.
- Your blood vessels are constricted by angiotensin II, which also causes the production of aldosterone.
- Your body's water content rises as a result of aldosterone's role in salt and water retention by the kidneys. Your blood pressure will rise as a result.
How is renin released?
- Once your blood pressure falls too low or when your body doesn't have enough sodium, renin is released in and out of your bloodstream. Renin secretion specifically takes place when:
- The baroreceptors, or pressure-sensitive receptors, throughout your arterial vessels can detect low blood pressure.
- Low salt (sodium) levels are detected by your kidneys.
- Beta 1 adrenergic receptors, which control your heart rate, notice sympathetic nervous system activity.
Does renin increase blood pressure?
Not quite. Renin doesn't affect your blood pressure on its own. Instead, it collaborates with aldosterone and angiotensin to achieve this. Aldosterone makes your kidneys retain water and salt, while angiotensin makes your blood vessels narrow. Your body retains more fluid as a result, which raises your blood pressure.
Renin Conditions and Disorders
- Reninoma: Reninomas are benign tumours of the cells of the kidney that produce renin (juxtaglomerular cell tumors). They create excessive amounts of renin, which results in severe hypertension, high aldosterone, and low potassium levels in the blood.
- Low renin hypertension: A significant and frequently undiagnosed cause of hypertension is low renin hypertension. It may also be linked to syndromes of apparent mineralocorticoid excess, glucocorticoid-remediable hypertension, high aldosterone levels (as in Conn's syndrome), low aldosterone levels (as in Liddle syndrome), and these other conditions.
- Renin over production: Lack of aldosterone in Addison disease causes increased sodium excretion, which lowers blood sodium levels and, as a result, blood volume and pressure. This decrease in blood salt levels prompts the kidneys to produce renin.
- Renin diabetic nephropathy: Chronic renal disease has it as its main cause. Numerous cases of morbidity and mortality in the diabetic community have been attributed to diabetic nephropathy. Most of the degenerative processes that lead to diabetic nephropathy are thought to be mediated by the renin-angiotensin system (RAS).
- Heart Disease: In persons with mild to moderate hypertension, higher plasma renin activity levels were linked to a higher risk of heart attacks (independent of blood pressure).
- Electrolyte imbalance: The activation of the renin-angiotensin system is a clinical marker of potassium depletion, which is manifested by a decrease both in total body potassium and serum potassium concentration. Ventricular arrhythmias may develop as a result of these electrolyte abnormalities.
- Inflammation of renin angiotensin systems: This renin-angiotensin system also may cause potassium depletion, which is clinically manifested by a drop both in total body potassium and serum potassium concentration. These electrolyte imbalances may help the development for ventricular arrhythmias.
Renin Tests
- Kidney function test (KFT): A kidney function test includes multiple measurements. When you experience symptoms that could be explained by a kidney disease, a kidney function test is most commonly utilised as a diagnostic test.
- Renin test: A renin test (or renin and aldosterone test) measures how much aldosterone the adrenal glands produce. The test helps diagnose primary aldosteronism, a disorder caused by too much aldosterone. PA causes excessive blood pressure, also called Conn syndrome.
- Computed tomographic angiography: It is widely regarded as the gold standard in the imaging assessment of renin-mediated hypertension. When compared to MRI, CT has higher spatial and temporal resolution and is easier to access and conduct.
- Renal angiography: Although not required in all cases of reninoma, it is commonly done in those where RAS is suspected or where further radiological intervention, such as balloon angioplasty or pre-operative tumour embolization, is likely to be necessary.
Renin Treatments
- Surgical resection of reninoma: It is indeed curative and causes most people's blood pressure to return to normal after treatment. After a reninoma has been removed, there are some instances of persistently elevated blood pressure.
- Laproscopy for reninoma: A reninoma tumour is removed using a minimally invasive, nephron-sparing surgical method. It is a surgical procedure that gives a surgeon access to the pelvis and abdomen's interior.
- kidney transplant For renin: When a person's kidneys can no longer function effectively, surgery is utilised to replace them with a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor.
- Nephrectomy for renin: Nephrectomy, also known as kidney removal surgery, is done to treat various kidney conditions, including kidney cancer.
- Dialysis for renin: This therapy employs machines to remove waste from your body when your kidneys are unable to do it naturally. It happens three times a week, takes three to four hours to complete, and takes place at a clinic, hospital, or dialysis centre.
- Chemotherapy for reninoma: Chemotherapy is a medical procedure that uses strong chemicals to destroy the body's rapidly dividing cells. Chemotherapy is the main form of treatment for cancer because cancer develops and multiply far more quickly than the majority of normal cells in the body.
Renin Medicines
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors for renin: Ace inhibitors are medications that lower blood pressure and alleviate blood vessel tension. a some of the instances Take Captopril, Enalapril, Quinapril, and Ramipril as examples.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): It works against the effects of angiotensin. This protein constricts blood vessels, resulting in high blood pressure. ARBs are also used to treat heart failure, kidney illness, and to lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The medicine relaxes blood vessels, making it easier for blood to circulate. Examples include Azilsartan, Candesartan, Eprosartan, Irbesartan, and Telmisartan.
- Alpha and beta dual receptor blockers: They belong to a subclass of beta blockers, which are medications that are typically prescribed for the treatment of hypertension (BP). Eg- Carvedilol, Labetalol, Dilevalol.
- Chemotherapeutic Agent: Chemotherapeutic medications are a type of medical treatment that eliminates quickly dividing cells within the body by using powerful chemicals. Chemotherapy is commonly used to treat cancer. Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), and gemcitabine are the drugs that were used.
- Calcium channel blockers: People take calcium channel blockers, which are a type of drug, in order to speed up the circulation of their blood. some of the examples include Amlodipine, Diltiazem, Felodipine
- Diuretic for renin: A popular treatment for hypertension is the use of diuretics, which are sometimes sometimes referred to as 'water pills.' Eg-Thiazide , Spironolactone, Amiloride.
- Nutritional supplements for renin angiotensin aldosterone: It aids in correcting the renin-angiotensin system's imbalance. some of the examples are vitamin D, calcium, etc.
How can I keep my renin levels in a healthy range?
Your healthcare provider will create a treatment strategy for you if your renin levels are unusually high or low based on the underlying cause. For instance, your doctor might recommend beta-blockers, clonidine, or other drugs to lower your blood pressure if you have high renin levels and high blood pressure.
Table of content
Find Nephrologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors