Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Respiratory System (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
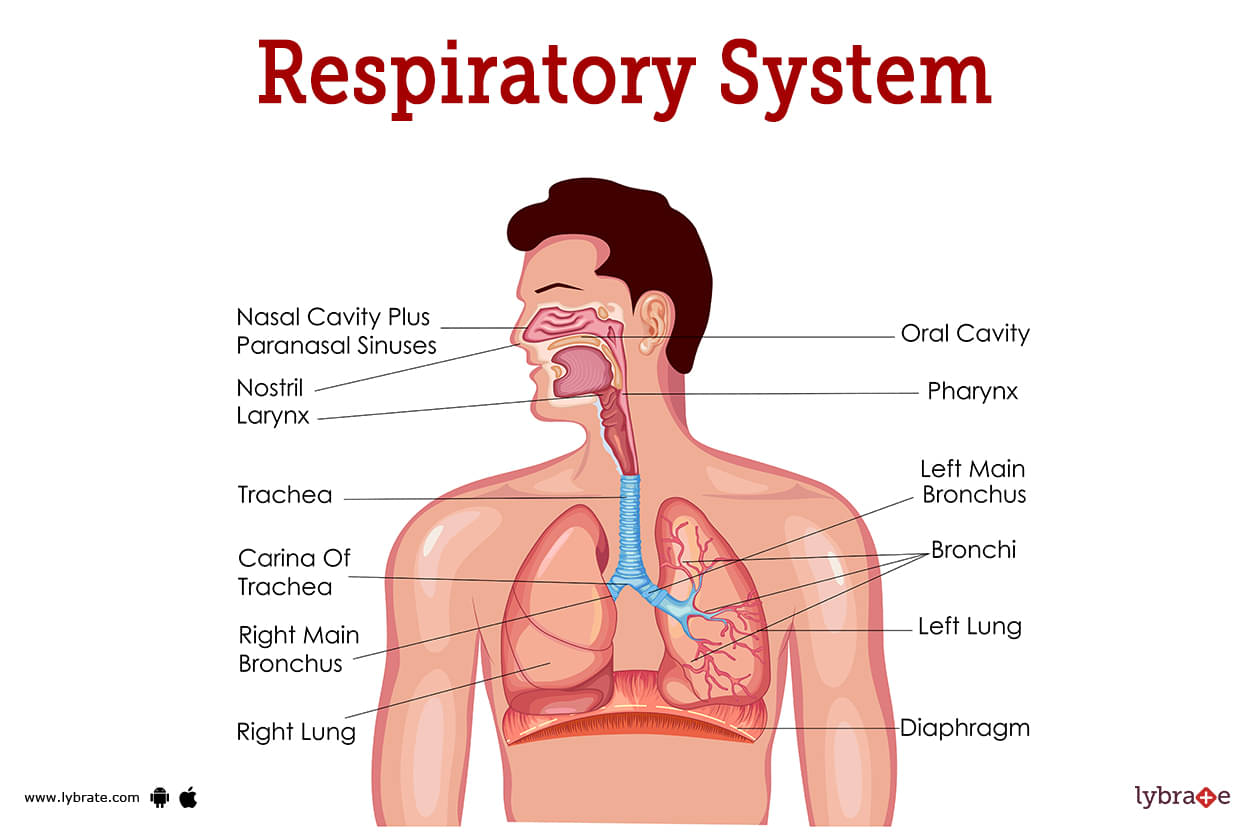
Respiratory System Image
- The respiratory system permits the body to expel waste and take in oxygen. This process also contributes to the disposal of metabolic waste and the maintenance of a healthy pH level.
- The upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract are the two primary components of the respiratory system.
- Upper respiratory tract
- The sinuses and nasal cavity located behind the nose represent the start of the upper respiratory system.
- In order for air to enter the body from the atmosphere, it must first pass via the nasal cavity, which is the space just behind the nose. A passageway through the nasal cavity is lined with cilia that interact with air as it passes through. A person's cilia can aid in the removal of any unwanted debris by trapping it.
- The sinuses are a series of air sacs behind the front of your skull that go from either side of your nose to your forehead. The sinuses play a role in tempering the air you breathe in and out. The pharynx and larynx make up the lowest part of the upper respiratory system and are the first to receive air after it has entered the body.
- The pharynx, sometimes known as the throat, is the opening between the nasal cavity or mouth and the larynx and trachea.
- The vocal folds, which are required for making sounds, are housed in the larynx, also known as the voice box.
- Lower respiratory tract
- The trachea, often known as the windpipe, is the airway that transports air to the lungs. Due to the presence of many tracheal rings, this tube is very durable. When the trachea gets inflamed or clogged, the amount of oxygen that reaches the lungs decreases.
- The primary function of the lungs is to inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. Each time we inhale, we exhale carbon dioxide and inhale oxygen.
- As it reaches the lungs, the trachea separates into two distinct bronchial tubes. Eventually, the bronchi would divide into even smaller tubes known as bronchioles. The alveoli of each bronchiole facilitate gaseous exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out).
Respiratory System Functions
- The upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract make up the two components of the respiratory system. The upper respiratory system includes everything above the vocal folds, as suggested by the names, whereas the lower respiratory tract includes everything below the vocal folds.
- Together, these two tracts perform respiration, which is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with the outside world.
- The numerous components of the respiratory system, which extend from the nose to the lungs, each play a unique but essential role in the act of breathing.
- The stages which are known for the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood are:
- The heart pumps blood depleted of oxygen to the lungs. This deoxygenated blood contains carbon dioxide, a byproduct of our cells' normal metabolic processes.
- At the alveoli, deoxygenated blood transforms carbon dioxide to oxygen. The blood has now acquired oxygen.
- The blood mixed with oxygen is transported from the heart to all the parts of the body by pumping.
- The exchange of minerals in the kidneys and carbon dioxide in the lungs are crucial for maintaining the blood's pH equilibrium.
Respiratory System Conditions
- Allergies: There are several forms of allergies that can impact the upper respiratory system, including food allergies, seasonal allergies, and even skin allergies. Mild symptoms of allergies include a runny nose, congestion, and an itchy throat. More severe allergies can cause anaphylaxis and airway closure.
- Common cold: It is a well known and highly spreading infected illness caused by more than 200 to 250 types of or families of viruses. Common cold symptoms include runny or stuffy nose, congestion, sinus pressure, sore throat, and more.
- Laryngitis: When the larynx or voice chords become inflamed, the illness is known as laryngitis. Irritation, illness, or misuse can all contribute to this syndrome. The most frequent symptoms are loss of voice and discomfort of the throat.
- Pharyngitis: Inflammation of the pharynx from bacteria or viruses causes pharyngitis, sometimes known as a sore throat. The major symptom of pharyngitis is a painful, scratchy, and dry throat.
- Sinusitis: Acute and chronic sinusitis are also possible. Swollen, inflammatory membranes in the nasal cavity and sinuses define this illness. Congestion, sinus pressure, mucus leakage, and other symptoms may occur.Lower respiratory tract conditions
- Asthma: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory illness of the respiratory tract. This inflammation constricts the airways, making breathing harder. Difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing are all signs of asthma. An allergy may develop if these symptoms worsen.
- Bronchitis: The respiratory disorder in which there is inflammation of the bronchial region. Symptoms of this ailment typically begin as cold symptoms and progress to a mucus-producing cough. There could be two different forms of infection which are acute and chronic.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Associated with both bronchitis and emphysema as a combined disease. These conditions may lead to the deterioration of the airways and lungs over time. If left untreated, they might lead to other chronic respiratory disorders. Breathing difficulties, chest tightness, wheezing, coughing, and recurrent respiratory infections are all symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Emphysema: Emphysema is a lung disease that destroys the alveoli and reduces the quantity of oxygen in the blood. Emphysema is a persistent, incurable disease. Exhaustion, weight loss, and an elevated heart rate are the most prevalent symptoms.
- Lung cancer: Lung cancer is a kind of cancer that affects the lungs. Lung cancer is classified differently based on where it is found, such as in the alveoli or airways. Lung cancer symptoms include difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest pain, a persistent cough with blood, and unexpected weight loss.
- Pneumonia: Pneumonia inflames the alveoli with pus and fluid. SARS and COVID-19 are coronaviruses that induce pneumonia-like symptoms. This viral family causes respiratory illnesses. Untreated pneumonia is lethal. Breathlessness, chest discomfort, and mucous coughing are symptoms.
Respiratory System Test
- Chest X-ray: This is the gold standard for diagnosing pneumonia and other chest-related fluid issues.
- Computed Tomography (CT scan): By combining X-rays and a computer, this examination can reveal more nuanced details about a patient's lungs.
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): Lung capacity problems and breathing difficulties during inspiration and expiration might be uncovered by doing this test.
- Spirometry: The purpose of this test is to measure both our respiratory rate and our lung capacity.
- Sputum Culture: Cough sputum culture is a test that helps identify the bacteria that cause diseases like pneumonia and bronchitis from the mucus that is produced during a cough.
- Sputum Cytology: Lung cancer detection relies on this procedure. This examination involves examining sputum under a microscope for the presence of abnormal cells.
- Lung Biopsy: The health of one's lungs is evaluated using this procedure. Lung tissue biopsies are utilised for analysis in this test.
- Flexible Bronchoscopy: As the name implies, this is an endoscopic examination. The physician can diagnose lung issues by inserting an endoscope into the patient's airways all the way to the bronchi.
- Rigid Bronchoscopy: In this procedure, a hard metal tube is introduced into the airways via the mouth. When compared to flexible bronchoscopy, it is superior. Anaesthesia is essential for this procedure.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI Scan): Highly specific images of the lungs may be captured with the use of radio waves. It is essential to use an MRI scanner for this analysis.
Respiratory System Treatments
- Thoracotomy: It's a kind of operation performed on the thorax (the chest area). It is performed to treat life-threatening lung conditions identified by a lung biopsy.
- Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): Several lung conditions may be remedied with the help of this operation on the chest wall. The purpose of this preliminary endoscopy is to maximise the quality of the final image.
- Chest Tube (Thoracostomy): An incision is created in the patient's chest, and any excess fluid is evacuated.
- Pleurocentesis: It involves inserting a needle into the chest wall in order to remove fluid from the space surrounding the lung. In order to decide whether or not pleurocentesis is necessary, a tissue sample is first analysed in great detail.
- Lung Transplant: Lung transplantation is a medical procedure in which a person's unhealthy lungs are exchanged with a donor's healthy ones. In certain cases, such as with COPD, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis, etc., a new set of lungs must be transplanted into the patient.
- Chemotherapy And Radiation Therapy: Advanced lung cancer cannot be treated surgically. Lung cancer pain may be successfully treated with chemotherapy and radiation. Also, patients' life expectancies may improve as a consequence.
- Mechanical Ventilation: A ventilator bed, which assists patients with breathing, is necessary for those suffering from several ailments, including Covid -19. Patients receive breathing assistance by having ventilator bed pump tubes placed in their mouths or around their necks.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): When used for conditions such as sleep apnea and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, this method involves applying air pressure through a mask in order to keep the airways open and avoid collapse.
- Lung Resection: This procedure involves cutting and surgically removing the diseased tissue. Used mostly for benign tumours.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: The goal of treating dyspnea is to relieve the underlying condition(s) that are causing the patient's breathing difficulties. You could require more oxygen if your oxygen levels decrease dramatically when you're sleeping, relaxing, or working out. Changes in exercise capacity as a result of pulmonary rehabilitation for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (C.O.P.D).
Respiratory System Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Respiratory System: Drugs that have anti-inflammatory characteristics, such as the corticosteroids methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, and dexamethasone, reduce inflammation by blocking the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to sites of cellular and tissue damage.
- Analgesics for pain in the Respiratory System: Some drugs, such as analgesics like aspirin, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen, can alleviate the pain associated with respiratory inflammation. Paracetamol and naproxen are two more examples of analgesic combinations.
- Muscle relaxants for stiffness in Respiratory System: A specialist may prescribe a muscle relaxant such as orphenadrine, metaxalone, methocarbamol, orphenadrine, tizanidine, or carisoprodol.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in the Respiratory System: These drugs are used for the treatment of bacterial lung infections like pneumonia. These drugs, however, do not work against viral lung illness. Amoxicillin is a typical antibiotic.
- Supplements for promotion of growth at the time of fracture of Respiratory System: Vitamin B complex, cyanocobalamin, and lycopene are all examples of nutritional supplements that can also be used medicinally.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Respiratory System: It is normal practice to treat rhinitis and other rhinovirus infections using antiviral drugs like oseltamivir or inhaled zanamivir. When treating laryngeal congestion, it is standard practice to give these drugs for a full five days.
- Decongestants for respiratory system: Use of oxymetazoline nasal spray can reduce inflammation and itching in the nose and throat caused by the common cold, allergies, and hay fever.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the top 3 most common respiratory diseases?
Bronchitis, asthma, and pulmonary disease are the most prevalent respiratory illnesses.
What is the major disorder of the respiratory system?
The major disorder of the respiratory system is asthma.
What is the most common treatment prescribed for respiratory diseases?
The most commonly prescribed treatment for respiratory diseases is therapy.
What are 5 ways to care for your respiratory system?
The five ways to care for the respiratory system are: doing exercises, quitting cigarettes, keeping yourself hydrated, avoiding infections and taking fresh air.
What are the symptoms of the respiratory system?
Symptoms of the respiratory system are: fever, breathing problems, coughing, wheezing, sore throat and headache.
What are the 8 causes of respiratory?
The causes of respiratory issues are smoking, infections, air pollution, passive smoking, pneumonia, injury, asbestos and inhalation of infectious substances.
How do you heal your respiratory system?
The respiratory system can be healed by doing breathing exercises, avoiding smoking and taking a healthy diet.
Can respiratory disease be cured?
No, respiratory diseases can not be cured.
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Pulmonologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously