Shoulder (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Parts, and More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
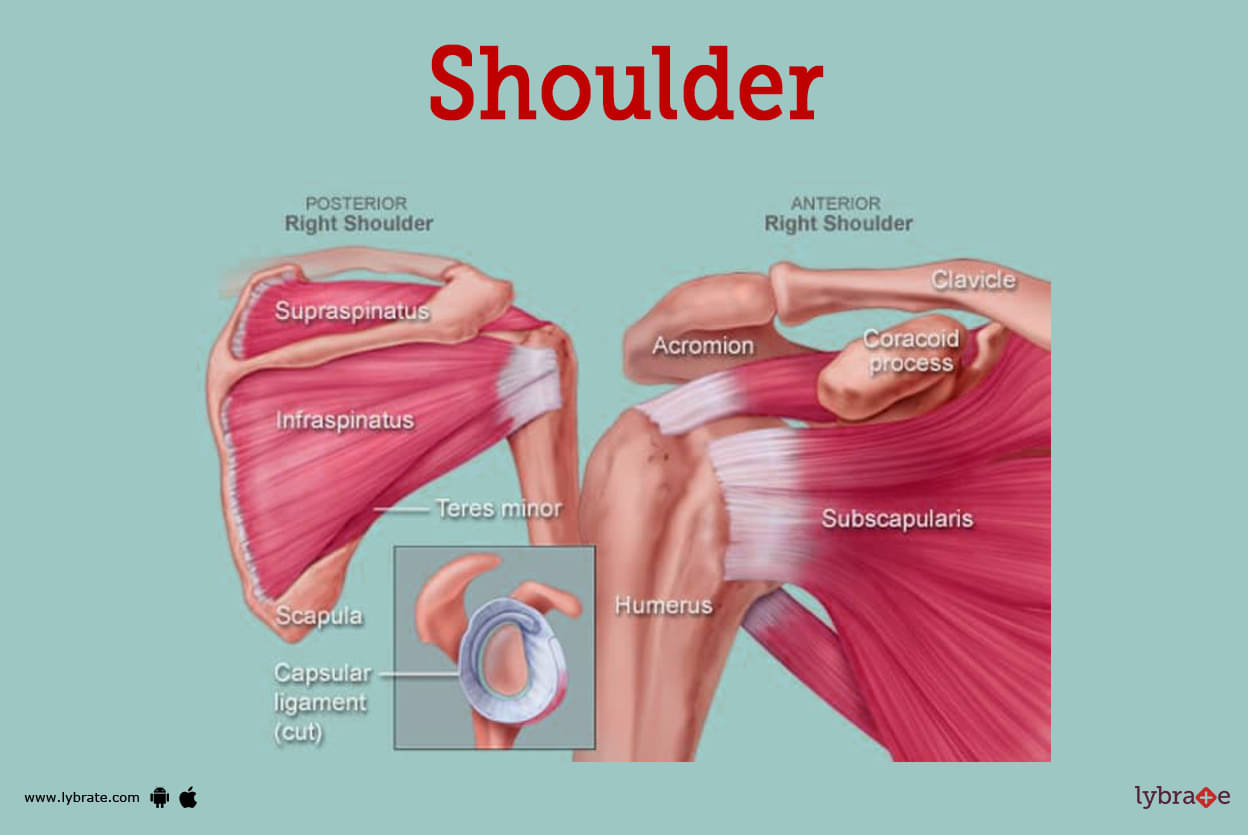
Shoulder Image
The shoulder is a complex joint that allows a wide range of motion, including flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, and rotation. It is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone). These bones are held together by a network of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, which work together to provide stability and support to the joint.
The shoulder bone is one of the biggest bones in the body containing some of the most complicated joints. The shoulder is really made up of two joints. One of them is the glenohumeral joint, in which the humerus bone (the upper bone of the arm) forms a ball and socket joint with the scapula (the blade of the shoulder), which is the other bone in the shoulder.
The second joint is known as the acromioclavicular joint, and it is located where the acromion, a portion of the shoulder blade known as the scapula, and the collarbone or clavicle meet.
Anatomy of the Shoulder
Following are the different parts that make the shoulder
- Humerus: The humerus is only held in place by a loose fit inside the shoulder joint. This allows the shoulder to have a large range of motion, but it also leaves it open to injury.
- Acromion: An outgrowth of the scapula in the form of a bony protrusion, the acromion. In men, the clavicle is known as the collarbone, while in females, it is known as the beauty bones. The acromioclavicular joint is where these two bones come together. A bony extension from the scapula that looks like a hook is known as a coracoid process.
- Rotator cuff: A group of tendons and muscles that surround the shoulder make up what is known as the rotator cuff. They allow for a large range of motion while still providing support to the shoulder. When the arm is elevated, the acromion, which is the edge of the scapula, places strain on the rotator cuff.
- Bursa: A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion for the tendons that make up the rotator cuff and also serves to safeguard those tendons from injury.
- Labrum: Labrum is the name given to the cuff of cartilage that creates a cup for the head of the humerus, which is shaped like a ball, to fit into.
Shoulder Functions
The main functions of shoulder are as follows:-
- Supporting the upper limb: The shoulder joint allows the upper limb to move in a wide range of directions, which is essential for activities such as reaching, lifting, and throwing.
- Providing stability: The muscles and tendons around the shoulder joint work together to provide stability and support to the joint, helping to prevent dislocation and other injuries.
- Facilitating movement: The shoulder joint is capable of a wide range of movements, including flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, and rotation. This allows the upper limb to move in a variety of directions, which is essential for activities such as reaching, lifting, and throwing.
- Protecting vital organs: The shoulder joint is located near several important organs, including the heart, lungs, and brain. It helps to protect these organs by providing a barrier between them and the rest of the body.
Shoulder Diseases
- Shoulder stiffness: It is a symptom of frozen shoulder, which is also known as a frozen shoulder. The inflammation that develops in the shoulder region is the root cause of the pain and stiffness that results from it. Shoulder motion may become extremely restricted as the disease progresses in patients with frozen shoulders.
- Osteoarthritis: from the Greek word for bones, osteo. Arthritis is known as 'wear and tear,' which is typically associated with ageing. The knee is the joint that is affected by osteoarthritis more frequently than the shoulder.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a form of arthritis that is caused by an autoimmune disorder. This type of arthritis is characterised by an attack on the joints by the immune system, which results in inflammation and pain. Rheumatoid arthritis can impact more than just the shoulder joint; it can also impact other joints.
- Gout: gout is a form of arthritis that is characterised by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, which leads to joint inflammation and pain. Despite the fact that gout in the shoulder region is an extremely unusual occurrence, it can happen.
- Rotator cuff tear: A tear in the rotator cuff occurs when one of the muscles or tendons that surround the top of the humerus becomes torn. A tear in the rotator cuff can be the result of a sudden injury, or it can be brought on by the consistent overuse of the shoulder brought on by things like work or exercise.
- Shoulder impingement: Impingement of the shoulder is a term that refers to inflammation in the rotator cuff or an injury to the rotator cuff itself. As a result of such an injury, there will be pain.
- Shoulder dislocation: shoulder dislocation is the term used to describe when one of the bones of the shoulder, most commonly the humerus but sometimes one of the other bones as well, moves out of its normal position. In the event that the patient raises his or her arm, it results in a painful feeling and a 'popping' sound since the shoulder may be dislocated.
- Shoulder tendonitis: It is an inflammation that affects one of the tendons that are found in the rotator cuff of the shoulder.
- Bursitis: bursitis of the shoulder refers to inflammation of the bursa, a tiny sac filled with fluid that sits on top of the rotator cuff tendons. Shoulder bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa that is located in the shoulder. A typical symptom is pain that occurs while conducting too strenuous activities or when there is pressure placed on the upper arm or the outside arm.
- Labrum tear: A rip in the labrum occurs when the cartilage cuff that covers the head of the humerus becomes detached. A tear in the labrum may be caused by an injury sustained in an accident or by misuse of the joint, both of which can lead to wear and tear. The majority of labral rips may be healed without the need for surgical intervention.
- Hill-Sachs lesion: A Hill-Sachs lesion is a fracture that occurs in the long bone area of the humerus in the upper arm. The humerus is the bone that joins the arm to the body at the shoulder. In this particular instance, the arm bone has dislodged itself from its socket and is pressing up against the rim of the socket.
- luxio erecta: The term 'luxio erecta' refers to the inferior dislocation of the glenohumeral joint that occurs when the joint becomes stuck below the coracoid and the glenoid. Injuries to the neurovascular joints are a typical cause of this condition. The vast majority of them involve traumatic events, such as the rider losing control of the motorcycle and falling to the ground.
- Osteoarthritis1: A lesion of the front portion of the glenoid labrum of the shoulder, a Bankart lesion is one kind of shoulder lesion. This injury is a result of many anterior shoulder subluxations that occurred over time. Should the shoulder joint become dislocated, this might cause injury to the connective tissue ring that surrounds the glenoid labrum.
Shoulder Tests
- SERUM calcium test for osteoarthritis of shoulder: A calcium blood test measures the amount of calcium in your blood. If there is too much or too little calcium in the blood, it may be a sign of a wide range of medical conditions, such as bone disease, thyroid disease, parathyroid disorders, kidney disease, and other conditions.
- Serum Urea and creatinine for Gout of shoulder: They are useful in determining the nitrogenous compounds that are the final result of metabolism. Urea is the major metabolite that is formed from the turnover of protein in tissue and in the body's food. It accumulates in the bone in the form of crystals and reduces bone mineral density.
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody for arthritis of shoulder: Despite the fact that the levels can be high in other rheumatologic disorders linked with inflammatory arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, the levels are generally elevated in rheumatoid arthritis.
- RA factor for arthritis of shoulder: The presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) can be determined using a blood test. The immune system creates an autoantibody called rheumatoid factor. Autoantibodies like RF target healthy cells and tissues rather than their intended targets, such as germs and viruses.
- CRP LEVELS for myositis and arthritis of shoulder: Higher levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammatory marker, are associated with increased fracture risk, although previous studies on CRP and bone mineral density (BMD) have yielded conflicting results.
- SERUM VIT D3 for shoulder fractures: To ensure adequate levels for optimal health, a blood test can determine the concentration of vitamin D in your system. Strong bones and teeth can only be maintained with enough vitamin D. In addition to its health benefits, regular exercise helps maintain your muscles, nerves, and immune system functioning regularly.
- DEXA SCAN for osteomyelitis of shoulder: The most common and accurate way is with a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. DEXA uses low-dose x-rays.
- bone mineral density (BMD) for checking grouth of shoulder bones: IT IS A test measures how much calcium and other types of minerals are in an area of your bone. This test helps your health care provider.
Shoulder Treatments
- Shoulder surgery: Surgery is generally performed to help make the shoulder joint more stable. Shoulder surgery may be arthroscopic (several small incisions) or open (large incision).
- Arthroscopic surgery: A surgeon makes small incisions in the shoulder and performs surgery through an endoscope (a flexible tube with a camera and tools on its end). Arthroscopic surgery requires less recovery time than open surgery.
- Physical therapy: An exercise program can strengthen shoulder muscles and improve flexibility in the shoulder. Physical therapy is an effective, nonsurgical treatment for many shoulder conditions.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) can relieve most shoulder pain. More severe shoulder pain may require prescription medications.
- RICE therapy: RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression (not usually necessary), and Elevation. RICE can improve pain and swelling of many shoulder injuries.
- Corticosteroid (cortisone) injection: A doctor injects cortisone into the shoulder, reducing the inflammation and pain caused by bursitis or arthritis. The effects of a cortisone injection can last several weeks.
- Sling support: Wearing a shoulder sling may be key to helping your arm or shoulder heal after an upper-body injury or surgery. This hemi-arm sling is manufactured to support a patient's shoulder after a stroke or another injury
- Acromioplasty: An acromioplasty aims to remove the impingement by increasing the sliding space for the shoulder tendons. This procedure is performed arthroscopically and involves shaving of the undersurface of the acromion.
- Arthroscopic repair: most common forms of arthroscopic repairs includes Rotator cuff repair; Removal or repair of the labrum; Repair of ligaments; Removal of inflamed tissue of the shoulder reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: The reverse total shoulder replacement relies on the deltoid muscle, instead of the rotator cuff, to power and position the arm. enables experienced shoulder surgeons to treat patients with conditions that previously had no solution.
- Figure of 8 bandage: A bandage applied alternately to two parts, usually two segments of a limb above and below the joint, in such a way that the turns describe the figure 8. It is used for shoulder support and also to prevent gliding or tilting of the shoulders.
Shoulder Medicines
- NSAIDs: As well as being used to treat aches and pains in other parts of the body, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are a family of medications that are used to address discomfort in the knee. Feverish conditions can also be brought under control with its application within the human body. Examples of usual drugs that fit within this group are ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen sodium. Naproxen Indomethacin with ibuprofen Ketorolac Diclofenac Meloxicam Celecoxib.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Platelet-rich plasma, often known as PRP, is a mixture of several growth factors that is injected into a joint, most commonly the knee. This not only assists in reducing inflammation but also has a positive impact on the healing process of injured tissue. Platelet-rich plasma, also known as PRP, is a mixture of several different growth factors. Osteoarthritis, according to some reports, is another condition that can benefit from PRP treatment.
- DMARDs: DMARDs are medications that affect the course of disease and are used to treat rheumatic conditions. Patients who are suffering from autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis are often prescribed this class of drug in order to alleviate the pain that they are experiencing. Methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib are some of the disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines (DMARDs) that are now available on the market. Sulfasalazine
- Nutritional supplements: Physicians provide nutritional supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin to decrease the pain of a person and boosten the healing process in joints.Vitamin D and Calcium supplements are given as per age and deficiency of the requred elements for normal bone growth and metabolism.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): they are a class of drug used to treat depression, OCD, bedwetting, migraines, tension headaches, and multiple pain disorders for example Amitriptyline
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI): they are drugs placed in class of antidepressants that help treat depression, anxiety etc Milnacipran/Duloxetine
- Pregabalin: it is an anticonvulsant used to treat neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. It's also used to treat partial onset seizures when taken with other seizure.
- Cortisone injections: When treating some types of ankle arthritis, cortisone injected into the ankle joint might be helpful. The inflammation in the ankle joint may be reduced and the associated pain alleviated with the use of cortisone.
- Bisphosphonates: They belong to a class of drugs that can either stop or decrease the process of bone loss, making for stronger bones. Inhibiting osteoclasts, which are responsible for the removal and reabsorption of minerals such as calcium from bone, is the primary function of bisphosphonates (the process is known as bone resorption). zoledronic acid. Both alendronate and risedronate were used.
- Hyperuricemia treatment drugs: Allopurinol, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, Febuxostat, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, Probenecid, which inhibits tubular resorption of uric acid in PCT Pegloticase, and Rasburicase, which is a Recombinant uricase that catalyses uric acid to water soluble, are all effective medications for the treatment of Gout as well as Tumor
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are a type of drug that is used to treat bacterial disorders that affect the calf muscles, such as myosotis. One of the most common conditions that antibiotics are used to treat is cellulitis. Gram-positive staining bacteria: Vancomycin and bacteria that do not stain with the Gram stain: 3rd Gen Cephalosporin (or Cefepime if concern for Pseudomonas) when Gram stain does not appear to be disclosing Vancomycin Ceftriaxone in combination with either azithromycin or doxycycline
- Corticosteroids: Patients who suffer from specific kinds of myositis that present in the calf muscle may be given prescriptions for cortisone-like medications such as prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone, as well as other pharmaceuticals that are comparable to cortisone. These drugs work by reducing the amount of activity that is produced by the immune system.
- Antiviral medicine: Amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, oseltamivir, ribavirin, acyclovir, ganciclovir, and foscarnet are just some of the medications that belong to this class that are frequently prescribed. In the field of calf medicine, medicines belonging to this category are the ones that are utilised for the treatment of viral infections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are 2 warning signs of a rotator cuff tear?
What is the most common reason for shoulder pain?
How do I relieve shoulder pain?
What are 3 common shoulder injuries?
How do your self check for shoulder injury?
How do I know what type of shoulder injury I have?
What are shoulder diseases?
What is the most common shoulder condition?
What diseases cause shoulder pain?
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors