Spleen (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases and More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
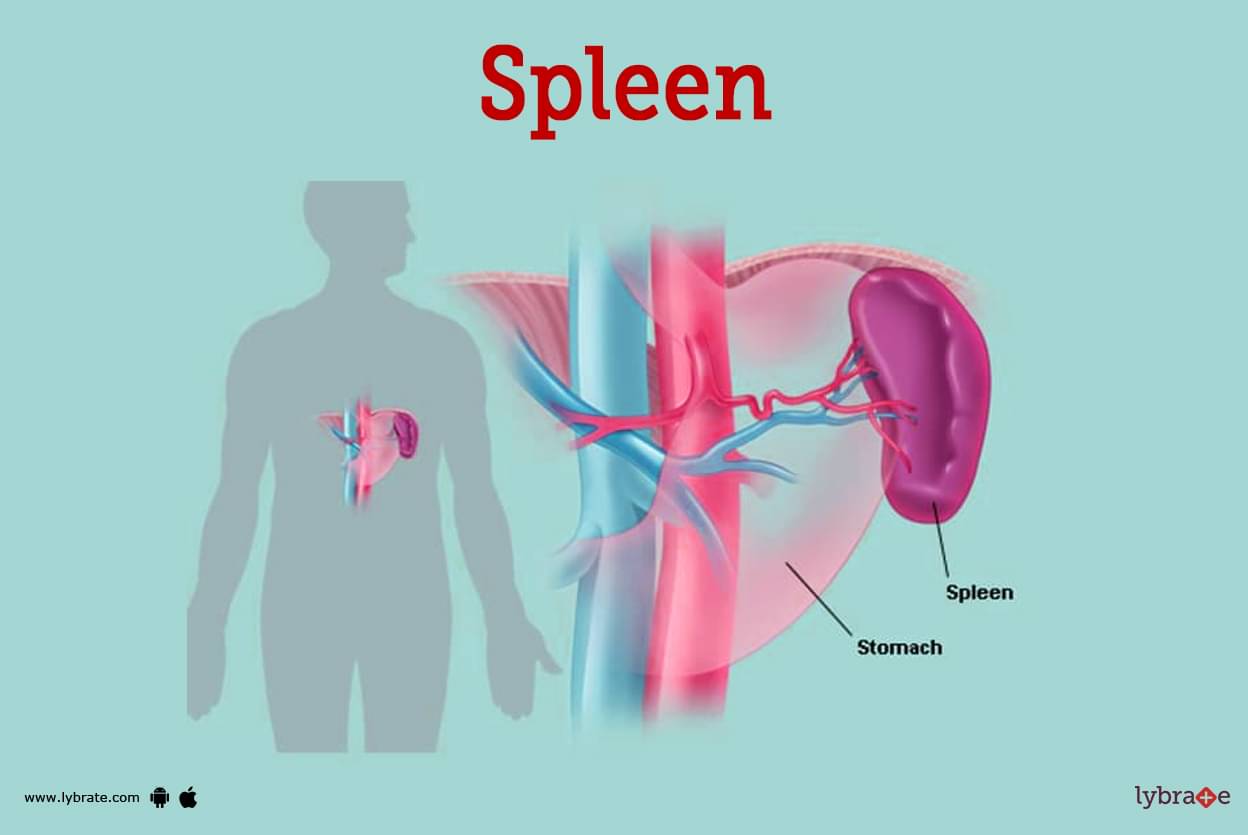
Spleen Image
The spleen is an organ that may be found in the upper left quadrant of the abdominal cavity and to the left of the stomach in normal conditions.
Although the size and form of a person's spleen might vary, the organ often has the appearance of a purple color, is around 4 inches in length and has a shape like that of a clenched fist.
The spleen is made up of two main types of tissue: red pulp and white pulp. The red pulp is responsible for filtering the blood and removing old or damaged red blood cells, as well as foreign substances and abnormal cells. The white pulp is responsible for producing immune cells, such as T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, which help to fight infection and disease. The spleen also assists in the battle against certain types of bacteria that may lead to pneumonia and meningitis.
In addition to these functions, the spleen also stores red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, and it can release these cells into the bloodstream when needed, such as during injury or infection. It also helps to regulate the volume of blood in the body by removing excess red blood cells and storing them when needed. The spleen is often referred to as the 'graveyard of RBCs.
Overall, the spleen plays a vital role in maintaining the health of the body by filtering the blood, storing blood cells, producing immune cells, and regulating blood volume.
Spleen Functions
The main functions of the spleen include:
- Filtering the blood: The spleen filters the blood and removes old or damaged red blood cells, as well as foreign substances and abnormal cells.
- Storing blood cells: The spleen stores red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It can release these cells into the bloodstream when needed, such as during injury or infection.
- Producing immune cells: The spleen produces immune cells, such as T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, which help to fight infection and disease.
- Regulating blood volume: The spleen helps to regulate the volume of blood in the body by removing excess red blood cells and storing them when needed.
Spleen Diseases
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: It is a disorder in which antibodies are formed automatically against the platelets due to which platelets get destroyed in the spleen and decreased platelets cause petechial haemorrhages and purpura. It commonly evolves more in girls than in boys.
- Splenic tumors: Tumours can develop in the spleen which can be benign or can also be malignant. They can cause haemangioma or angiosarcoma.
- Splenic Abscess: It is a rare condition in which a unilocular abscess develops in the spleen as a result of streptococcus salmonella and gramme negative enteric bacilli infections.
- Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly): Splenomegaly is the medical term for when the spleen becomes enlarged. In most cases, the illness is the result of viral mononucleosis, liver problems, blood malignancies such as lymphoma and leukaemia, or some other potentially dangerous ailment.
- Ruptured spleen: A ruptured spleen can produce severe internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening, and should be treated as an emergency condition. In the event that it sustains an injury, it may even burst soon after the damage, however in other instances, this may not take place until a few days or weeks after the injury.
- Sickle cell disease: There is a production of red blood cells with an irregular shape in patients who have this genetic condition, which may also manifest as a kind of anaemia.People who have sickle cell disease need vaccines to protect themselves from sickness since their spleens are unable to function normally and help them fight off infections caused by the dangerous environment.
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count): In certain cases, thrombocytopenia is caused by an expanded spleen because it accumulates an abnormally high quantity of the body's platelets. Splenomegaly may cause unusually low levels of platelets to circulate in the circulation, which is not how they should behave.
- Accessory spleen: Even though the likelihood of it happening is very low, around 10% of individuals have a spleen that is somewhat enlarged. It is not going to result in any issues and is deemed to be typical.
- Splenic infarction: This is a situation in which the spleen doesn't get enough blood, which can give rise to a partial or total infarction and tissue death due to a lack of oxygen in the organ.
- Obstruction of the spleen: When the splenic artery or one of its branches is blocked like by a blood clot, this is called a splenic infarction.
- Hypersplenism: When the spleen is in a hyperactive state, it sometimes works too hard and kills more blood cells than it should. The symptoms depend on what part of the blood is missing. Most cases of hypersplenism are caused by problems in other parts of the body, like liver cirrhosis.
- Extravascular hemolysis: This happens when red blood cells are broken down in the liver or the spleen. It may cause abnormally large amounts of yellow pigment known as bilirubin. Bilirubin is normally broken down by the liver, but extravascular hemolysis may result in levels of bilirubin that are abnormally high in the blood.
Spleen Tests
- Physical examination of spleen: By pressing the right flank below the thoracic region of the body or below the rib cage spleen can be palpated tenderness in the region can be a marker of spleen splenomegaly and also if there is some sort of rash or redness in this region it can also be a marker of injury to spleen or splenic haemorrhage.
- Thromboelastography: In this test, a blood sample is collected by venipuncture, and then it is capped in a solution of 3.2 percent sodium citrate, which binds with calcium and prevents blood from clotting. The primary goal of this test is to evaluate visco elastic changes in clotting whole blood under conditions of low shear.
- Serum ferritin: It is done for the purpose of determining the amount of ferritin compound that is in the blood and is responsible for the presence of iron or the binding of iron. A decrease in the quantity of serum ferritin can be connected with hemolysis, splenomegaly, and a variety of spleen and liver problems.
- Serum iron: It is for the purpose of determining the quantity of iron that is present in the blood, which is very relevant to conditions such as anaemia, hemolysis, and blood loss, and is also taken into consideration as a marker for nutritional deficiencies.
- Bleeding time: The test is a routine diagnostic technique that is used to determine both the number of platelets in the body as well as the functionality of the platelets that are currently present in the body. When there are more platelets, there is less time spent bleeding, and there are also more clotting factors.
- Clotting time: It is a significant diagnostic method that can, without making use of any chemicals or laboratory equipment, determine the presence of platelets and clotting factors in the body. This makes it a very useful diagnostic tool.
- Platelet count: It is the evaluation of the amount of platelets which are present in the blood that can correlate with conditions like hemolysis, splenomegaly, splenic abscess etc.Prothrombin time: it is the marker for checking amount of platelet factor prothrombin present in the blood which is responsible for clotting of blood and functioning of platelets which can be directly or indirectly considered a sign of infection in kidney liver or spleen
- Serum vitamin K: it is considered an evaluation for finding out the capability of liver and spleen and whether it is functioning properly or not as vitamin K is also a marker for clotting factor formation as it involves information of different clotting factors. It's deficiency can lead to bleeding disorders like petechial hemorrhages.
- PTiNR: It is a test for partially measuring and evaluating the international normalised ratio after PT and prothromboplastin. It is known to be used for patients who take anticoagulant drugs like warfarin, aspirin, etc. and also for patients who are having symptoms of hemolysis and other infective etiology, which includes damage to the spleen, liver, or circulatory system.
- Serum ferritin1: It is also known as complete blood count. It is for the evaluation of platelet count, RBC count, MCHC values, and MCV values.
- Cect: It stands for contrast enhanced computed tomography, in which high resolution images are produced using a 3 dimensional flow of X-rays around the organs. It is a gold standard diagnostic technique for many of the disorders of the liver, spleen, brain, kidneys and other vital organs.
- Serum ferritin3: It stands for magnetic resonance imaging, for which high resolution imaging is done by using a super magnetic conductor and a central processing unit, which involves resizing and impartial diagnosis of disorders of bones, heart, spleen, kidney and other vital organs.
Spleen Treatments
- Splenic drainage ; it is done at the time of pus or Abscess formation in the spleen. drainage is done through left upper quadrant and antibiotics are also given after splitting drainage
- Laparoscopic splenectomy: When the spleen is removed through a laparoscopic procedure, it is called a 'laparoscopic splenectomy.' It can be a total laparoscopic splenectomy or a partial laparoscopic splenectomy. It is done after the ligation of the splenic artery.
- Vaccination after splenectomy: Because a person becomes immunodeficient after having their spleen removed, vaccination is a must as it prevents infections like influenza and pneumonia, which can be caused recurrently and create a condition of sepsis and can lead to death.
- Chemotherapy for spleen carcinoma: it is done after like you should not linick artery and removal of spleen which can be a open procedure or a closed one depends on the size of spleen if there is a symptom of splenomegaly then open splenectomy is done and if there is a normal size of spleen then laparoscopic splenectomy is done but after both of these chemotherapy is done.
- Vaccine for meningitis: it has to be taken after splenectomy to prevent overwhelming post splenectomy infection which can cause sepsis.
Spleen Medicines
- Platelet transfusion after splenectomy: Platelets from donors of blood are separated from the rest of the blood and placed in a plastic bag. Platelets can then be used in medical treatments. It is utilised in situations where the platelet count is exceedingly low. Which can be at the time of spleen injury or any sort of splenic infection or after play next to me
- Fresh frozen plasma after splenic hemorrhage: Plasma is extracted from the donor's blood, then preserved for future use after being separated from the blood. It has an important role in the prevention of coagulation-related haemorrhage as well as the decrease of blood clotting.
- Prothrombin Complex for splenomegaly: It is a recombinant four factor concentrate that contains factors II, VII, IX, and X. This concentrate is used for indications that are comparable to those for which fresh frozen plasma is prescribed, and it is rapidly becoming the option of choice.
- Cryoprecipitate for splenomegaly: After being extracted from the circulation, proteins are concentrated and stored in a liquid state. When one's levels of proteins that are important for controlling blood coagulation drop drastically, as is the situation with thalassemia, it is possible for this treatment to restore those proteins.
- Cilostazol for thrombocytosis: When administered at the time of claudication, this strong phosphodiesterase inhibitor causes a reduction in the inhibition of platelets, as well as a vasodilation of the coronary arteries. Among the side effects are: Symptoms include as a headache, flushing, sensitivity to heat, and palpitations
- Heparin for thrombocytosis: Thrombin and platelet factor 10 both have their levels of activity lowered as a result. Both pulmonary embolisms and deep vein thrombosis can be remedied with its application. During periods of active bleeding, its use is strictly prohibited.
- Apixaban for thrombocytosis: It is a Factor Xa inhibitor that is prescribed for the treatment of pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis. Additionally, it lowers the risk of developing atrial fibrillation.
- Bivalirudin for thrombocytosis: It is a direct thrombin inhibitor, which is a medication that is not only dangerous during pregnancy but also dangerous for those who have chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Cyclosporine before splenectomy: It is one of the most important calcineurin inhibitors vastly used at the time of transplant procedures. It has various side effects which include nephrotoxicity, hypertension, alopecia, gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, hyperlipidemia, etc.
- Romiplostim for thrombocytopenia: It is a medication that can boost the number of platelets present in the body during times of thrombocytopenia or when the spleen is bleeding excessively.
- Eltrombopag for thrombocytopenia: It is a medication that is prescribed to patients in order to treat idiopathic thrombocytopenia and raise the platelet count in their blood.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes a spleen problem?
Why spleen is called blood bank?
How does spleen pain feel?
How do you know if your spleen is not working properly?
How do I know if I have damaged my spleen?
How big is a spleen?
What attacks the spleen?
Table of content
Find General Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors