Subdural Hematoma: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
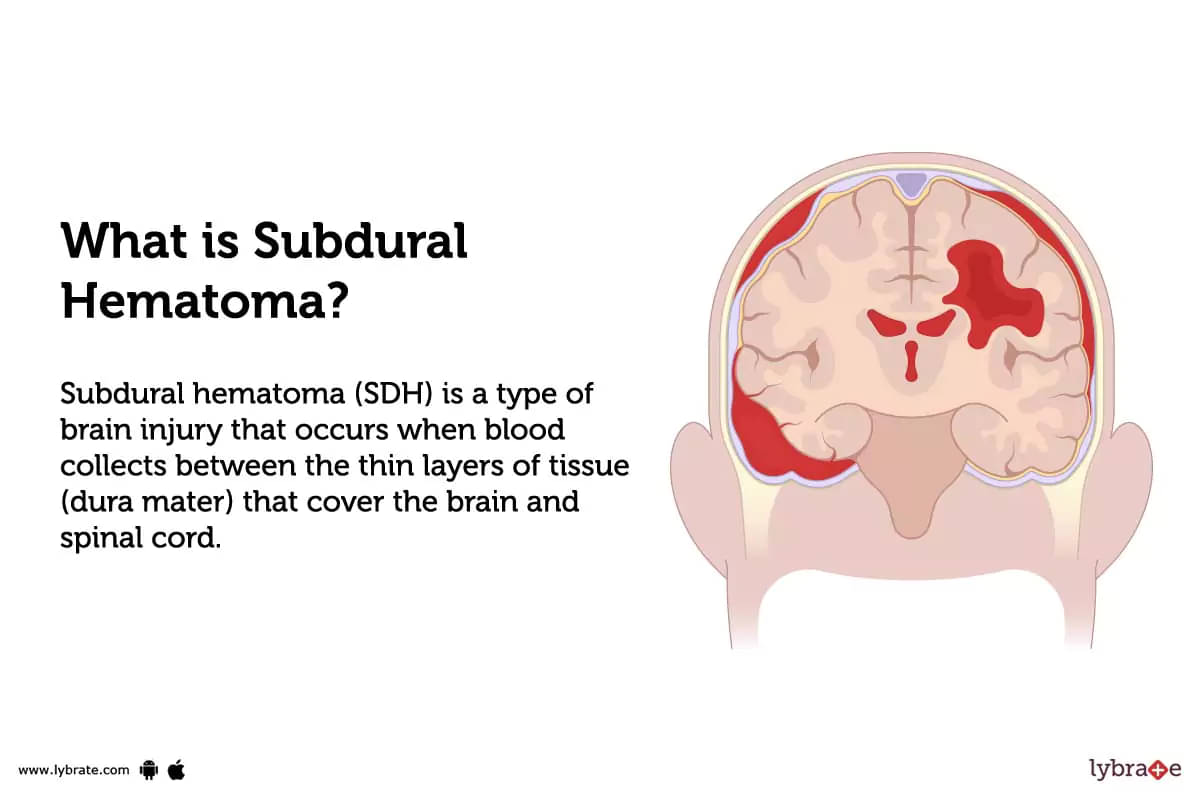
What is Subdural Hematoma?
Subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of brain injury that occurs when blood collects between the thin layers of tissue (dura mater) that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Types of Subdural Hematoma
- Acute Subdural Hematoma: After suffering a severe brain injury, the patient may suddenly develop a condition known as acute subdural hematoma. It is marked by significant accumulation of blood between the dura mater and the underlying brain tissue.
- Subacute Subdural Hematoma: A subacute subdural hematoma is less severe than an acute one but still requires medical attention. It develops over days or weeks after a traumatic injury and usually has less severe symptoms than an acute SDH.
- Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A chronic subdural hematoma is one that has been present for weeks to months before being diagnosed and treated medically.
What causes Subdural Hematoma?
It is most commonly caused by a head injury due to a fall, car accident, or sports-related incident.
Additional factors include medical disorders such as hypertension, brain tumours, or aneurysms.
What are the symptoms of Subdural Hematoma?
- Common symptoms include headache, confusion, nausea and vomiting, drowsiness or decreased level of consciousness, difficulty walking or speaking, seizures and changes in vision.
- In more severe cases there may be signs of increased intracranial pressure such as dilated pupils, decreased reflexes and coma.
- Subdural hematomas may also cause paralysis on one side of the body due to pressure on the brainstem or cranial nerves.
How can you prevent Subdural Hematoma?
- When engaging in sports that involve physical contact, it is important to wear protective equipment.
- Use safety equipment when operating machinery, such as helmets and seat belts.
- Avoid falls from heights, especially in older adults, by using handrails and avoiding slippery surfaces.
Subdural Hematoma - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical examination: A physical examination is conducted to assess the person's overall health and to check for any signs of head trauma, such as cuts, bruises, or swelling.
- Neurological examination: A neurological examination is conducted to evaluate the person's level of consciousness, motor and sensory function, and reflexes. This examination helps to determine the extent of brain injury and the specific areas of the brain that are affected.
- Imaging studies: Imaging studies such as CT or MRI scans are used to confirm the diagnosis of a subdural hematoma and to determine the size and location of the hematoma. These studies provide detailed images of the brain and can help to identify the presence of any bleeding or other abnormalities.
- Lumbar puncture: In some cases, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) may be performed to check for signs of increased pressure on the brain. A needle is inserted into the lower back to obtain cerebrospinal fluid. If the pressure of the fluid is found to be elevated, it may indicate the presence of a subdural hematoma.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be done to check for signs of anemia, infection, or other underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the brain injury.
- Angiography: In some cases, an angiography may be performed to check for bleeding in the brain. This test involves injecting a dye into the blood vessels and then taking X-ray images to visualize the blood vessels.
- EEG (Electroencephalogram): An EEG may be performed to check for any abnormal electrical activity in the brain. This test involves attaching electrodes to the scalp to measure the brain's electrical activity.
What are possible complications of Subdural Hematoma?
- Increased intracranial pressure: Subdural hematomas can cause pressure on the brain, leading to headaches, confusion, drowsiness, and other neurological symptoms.
- Seizures: In some cases, a subdural hematoma can cause seizures due to increased pressure in the brain.
- Stroke: Due to reduced blood supply to the brain, a subdural hematoma may cause a stroke.
- Cognitive deficits: Loss of memory and other cognitive abilities may occur if the subdural hematoma is not treated promptly or if it affects a large area of the brain.
- Paralysis: In rare cases, paralysis of one side of the body can occur if a subdural hematoma compresses certain nerves within the brain stem or spinal cord.
- Death: If left untreated, a large subdural hematoma can cause death due to increased intracranial pressure or stroke-related complications
Home Remedies for Subdural Hematoma?
- Take a mix of equal parts of Ashwagandha and Brahmi. Both of these herbs are known to possess anti-inflammatory qualities, which may help to relieve the swelling and inflammation related to a subdural hematoma.
- Make a paste using turmeric powder and water, and then apply it directly to the troubled region. Turmeric has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and analgesic properties that can reduce pain and swelling in the head due to a subdural hematoma.
- The herb Shankhapushpi helps to promote natural healing by improving blood circulation in the brain, which is beneficial in treating a subdural hematoma. You can take this herb as an herbal supplement or make an infusion from its leaves to drink twice daily for best results.
- Brahmi is another herb that helps improve blood circulation, thus helping with the healing process of subdural hematomas. You can take it as an herbal supplement or make an infusion from its leaves to drink twice daily for best results.
- Amalaki is an Ayurvedic herb known for its antioxidant properties which are beneficial in reducing inflammation caused by a subdural hematoma while promoting natural healing at the same time. You can take it as an herbal supplement or make an infusion from its berries to drink twice daily for best results
What to eat in Subdural Hematoma?
Lean meats, fruits and veggies, whole grains, and low-fat milk products should all be included into the diet.
Important to the healing from a subdural hematoma is the consumption of generous amounts of fluids, such as water.
What not to eat in Subdural Hematoma?
- Avoid alcohol and drugs, as they can increase the risk of brain bleeds.
- Reduce your salt consumption, since it might induce fluid retention in the brain.
- Avoid fatty and cholesterol-rich foods, including fried food, red meats, and whole-milk dairy products.
- Stay away from processed and junk foods, which are full of sugar, salt, and fats that are bad for you.
- Limit caffeine intake to avoid dehydration that can worsen brain swelling associated with a subdural hematoma
Subdural Hematoma Treatment
- Medications: Depending on the severity of symptoms, medications such as diuretics and anticonvulsants may be prescribed to help manage pain and reduce swelling in the brain.
- Rehabilitative therapies: Rehabilitative therapies like physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help improve function in affected areas of the body.
- Burr Hole Surgery: This is an open surgical procedure that involves drilling two small holes into the skull and using a suction device to remove the hematoma.
- Craniotomy: During this procedure, a surgeon will open the skull and remove the hematoma.
- Endoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive technique involves inserting an endoscope into a small incision in the skull to locate and remove the hematoma.
- Stereotactic Surgery: This is an advanced form of endoscopic surgery that uses imaging technology to guide surgeons to precise locations within the brain for precise removal of the hematoma.
Which doctor to consult for Subdural Hematoma?
- The best doctor to consult for a subdural hematoma is a neurologist.
- Neurologists are doctors who are trained to find and treat problems with the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and muscles, which are all part of the nervous system.
- They have extensive training in detecting neurological problems such as subdural hematomas.
Which are the best medicines for Subdural Hematoma?
- Blood thinner: Blood thinners, such as heparin or warfarin, may be necessary to prevent further bleeding or clots from forming in the brain and causing further damage.
- Anticonvulsant: Anticonvulsant medications may be prescribed to manage seizures associated with a subdural hematoma.
- Analgesic: Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, can be used to reduce brain swelling.
- Diuretic: Diuretics such as furosemide can also be used to reduce brain swelling by increasing the amount of fluid removed from the brain.
- Steroids: Steroids such as dexamethasone can be used to reduce inflammation.
How long does it take to recover from Subdural Hematoma?
Most of the time, it takes anywhere from a few weeks to a few months to make a full recovery.
The first step is typically rest and avoiding activities that could worsen symptoms.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
Generally, if the hematoma is treated promptly and appropriately, the prognosis is good and there can be permanent resolution of symptoms.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- After treatment for a subdural hematoma, the patient should be monitored closely for any signs of increased intracranial pressure (ICP).
- The patient should also avoid any activities that may increase ICP, including bending and lifting heavy objects.
- Also, you might be given medicine to help reduce the swelling in the brain and stop more bleeding.
- Physical therapy may also be suggested in order to enhance muscle ability and coordination.
- Regular follow-up visits with a doctor should also be scheduled in order to monitor progress and ensure that any complications are addressed promptly.
What is the cost of Subdural Hematoma treatments in India?
- Generally, treatment costs can range from around INR 20,000 to INR 3 lakhs or more.
- This includes hospitalization charges, doctor's fees, laboratory tests, imaging studies and medications.
- Additional expenses may arise if surgical intervention is necessary.
What are side-effects of Subdural Hematoma treatments?
- Headache, confusion and drowsiness are common side effects of treatment for subdural hematoma.
- Nausea, vomiting, and seizures may also occur.
- Long-term effects may include memory problems, personality changes and depression.
Subdural Hematoma - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to a subdural hematoma then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'brain damage, seizures, coma' in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors