Tooth Decay: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Cost
Last Updated: Jan 20, 2025
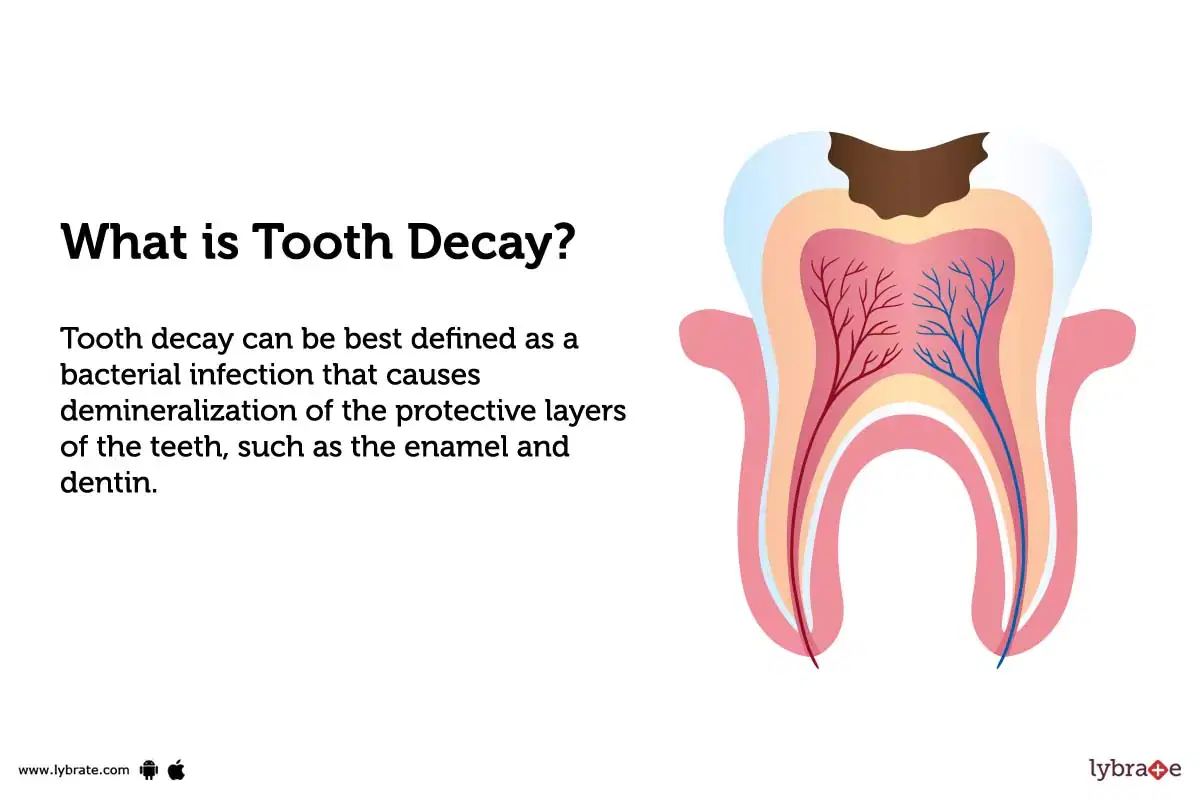
What is tooth decay?
Tooth decay can be best defined as a bacterial infection that causes demineralization of the protective layers of the teeth, such as the enamel and dentin. This condition is more commonly known as dental caries, or cavities.
It is a serious problem that can lead to a number of chronic oral health problems in both children and adults. The decay essentially arises from a bacterial process that begins when harmful bacteria in the mouth produce acids that attack the tooth surface.
Bacteria feed on the sugars and carbohydrates present in the food we eat, converting them into acids that erode the protective coating of the teeth. The bacteria then penetrate the enamel and dentin, creating tiny cavities in the enamel and softening the dentin, which can eventually lead to the formation of a cavity. If the bacterial infection progresses to more advanced stages, it can get to the nerve and cause severe toothache.
If a dental condition like tooth decay is left untreated for a long time, it can cause severe pain, infection, and even the loss of a tooth (or teeth) in many cases. To prevent tooth decay, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing twice a day, limiting sugary and acidic foods, and visiting the dentist regularly.
Summary: Tooth decay is the process of a tooth decaying owing to the buildup of bacteria on the surface of the tooth. This bacteria feeds on sugars and starches in the mouth to produce acid, which erodes the enamel and causes cavities and other dental decay. Therefore, it is important to seek dental treatment as soon as possible if you suspect that you have a cavity or tooth decay.
What are the stages of tooth decay?
Dental pain can be a sign of tooth decay, which may take place in five stages. The stage of decay will determine the treatment required to resolve the issue. Keep reading to learn more about dental decay stages and what to expect from your dentist.
Chalky white spots:
The first stage of tooth decay is typically marked by the appearance of chalky white spots on the tooth's surface. These spots are caused by the demineralization of the tooth enamel, which is caused by acids produced by bacteria in the mouth.
The bacteria feed on sugars and starches present in food, and the acid they produce is able to dissolve the enamel. The demineralization process is reversible at this stage and can be prevented by brushing and flossing regularly, as well as reducing the intake of sugary foods.
Decay of the Dental Enamel:
The second stage of tooth decay is marked by the decay of the dental enamel. The enamel is the hard outer layer of the tooth and is responsible for protecting the underlying layers of tooth structure from damage.
Once the enamel has been weakened by acid, it will begin to erode. At this stage, the decay can still be reversible with early intervention, such as professional dental cleanings and proper oral hygiene.
Decay of the Dentin:
The third stage of tooth decay is marked by the decay of the dentin, which is the layer of the tooth located beneath the enamel. Dentin can be even more vulnerable to decay because it's softer than enamel. At this stage, the decay is irreversible and will require more aggressive treatment to restore the tooth.
The decay has reached the point of no return (or pulp):
The fourth stage of tooth decay is marked by the decay reaching the pulp, which is the innermost layer of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. At this stage, the decay is more advanced and can cause severe sensitivity or pain.
A root canal is a treatment that is used to save a tooth from infection or decay. This procedure typically involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth and replacing it with an artificial rubber-like material.
Abscess:
The fifth and final stage of tooth decay is marked by the formation of an abscess. An abscess is a throbbing, red lump that is full of pus or an accumulation of pus. If left untreated, an abscess can cause severe pain and possibly lead to systemic illness.
Treatment for an abscess typically involves antibiotics and drainage of the abscess. If the infection is severe or irreversible, a tooth extraction may be the best option to prevent further damage from occurring. In other words, this is the final stage of tooth decay, where the tooth has become so damaged and decayed that it can no longer be saved and must be removed.
Summary: Tooth decay is a progressive condition occurring in five stages (as described above), and it is important to take steps to prevent it from developing. Good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly and reducing the intake of sugary foods, can help prevent the onset of tooth decay. Additionally, regular visits to the dentist are important to detect and treat any signs and symptoms of decay in their early stages.
What causes tooth decay?
- Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common dental health problem that affects millions of people around the world. Tooth decay occurs when the enamel of the teeth breaks down due to bacteria that feed on the sugar and carbohydrates in the mouth. This bacteria produces acid, which erodes the enamel and causes cavities.
- This acid then begins to break down the enamel, leading to cavities. One of the major (or primary) causes of tooth decay is poor oral hygiene, which means bacteria buildup and tooth decay can be prevented by regularly brushing and flossing your teeth. Eating an inadequate or unbalanced diet can be a major cause of tooth decay, or dental caries.
- Foods and drinks high in sugar and carbohydrates are especially problematic, as they provide the fuel for the bacteria to produce the acid. Other factors can also contribute to tooth decay, such as certain medications that reduce saliva production, dry mouth, and the use of certain types of mouthwash. Saliva helps to rinse away food particles and bacteria, so a decrease in saliva can increase the chances of bacteria building up and causing decay.
- Genetics can also be a predisposing factor when it comes to tooth decay. This is because some people are born with softer tooth enamel, which makes it easier for bacteria to break it down and enter the inner layers of the tooth. Apart from that, some people may be more susceptible to cavities due to the shape of their teeth or the way they bite down.
- Tooth decay is a widespread issue, but with proper oral hygiene, it can be avoided. Practicing proper oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing your teeth on a regular basis, is essential to keeping your teeth healthy and preventing decay.
- In addition, reducing your intake of sugary foods and drinks helps decrease the amount of harmful bacteria in the mouth. Additionally, seeing a dentist on a regular basis for cleanings and routine checkups can also help to catch any early signs of tooth decay before it becomes a major problem.
Summary: Tooth decay is caused by bacteria in the mouth breaking down sugars and starches in food, resulting in the production of acids that can erode the enamel on teeth. Poor oral hygiene, inadequate fluoride, and consuming sugary and starchy foods can also contribute to the development of tooth decay.
What are the symptoms of tooth decay?
- Tooth decay is a common dental problem that can cause pain, discoloration, and other damage to teeth if left untreated. Bacteria that thrive on sugars and starches in food are the primary cause of tooth decay. These bacteria in our mouths tend to produce acids that can potentially break down (or cause damage to) tooth enamel, which can lead to cavities.
- The most common symptom associated with this dental health condition is increased tooth sensitivity. This occurs when the enamel of the tooth is weakened and the inner layers of the tooth become exposed. This can cause pain and discomfort while consuming hot or cold foods and beverages.
- Other symptoms can include discoloration of the teeth, pain when biting down, or the development of holes in the tooth. Tooth decay can also cause bad breath, or halitosis. This is due to the bacteria that are feeding on food particles and producing acids that can create an unpleasant odor.
- If the decay is left untreated, it can also lead to infection, which can cause a fever and swelling of the face, neck, and gums. To prevent tooth decay, it is crucial to uphold good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing daily and making regular visits to the dentist for check-ups and cleanings. In addition to these preventive measures, limiting sugary and starchy foods and drinks can also help reduce the amount of bacteria in the mouth.
- If you already have tooth decay, it is crucial that you seek medical intervention or the appropriate treatment immediately to prevent further damage. This condition can progress quickly and cause extensive damage if not treated promptly, so it's important to take action as soon as possible. The consequences of untreated tooth decay can lead to extensive damage to your teeth, gums, and other parts of your mouth.
- A dentist can assess the severity of the problem and recommend treatments such as fillings, crowns, or root canals. In some cases, it may be indispensable to extract the tooth.
- Depending on the extent of the decay, a dentist may also recommend a fluoride treatment to help protect the teeth from further damage. In summary, tooth decay can cause pain, discoloration, bad breath, and other damage to teeth if left untreated. The most common symptom is tooth sensitivity, but other signs can include discoloration, pain when biting down, and the development of holes in the tooth.
- To keep tooth decay at bay, it is necessary that you maintain good oral hygiene and, at the same time, limit sugary and starchy foods and beverages. Moreover, if you suspect that you may have tooth decay, it is important to seek medical help or treatment promptly.
Summary: The first indication of tooth decay is pain or discomfort in the tooth. Gum swelling around the tooth may also happen. You may also be able to see the areas of tooth decay due to a brown or black discoloration. If you have frequent mouth pain or toothache, or if a tooth starts to turn brown or black, then you should see your dentist as soon as possible.
Who might get a cavity?
A cavity is a type of tooth decay caused by the accumulation of bacteria in the mouth. Anyone can get a cavity, but it is most common in children and young adults. People who do not practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly, are more likely to develop cavities.
People who eat a lot of sugary and starchy foods are also at risk of developing cavities. People with a dry mouth or certain medical conditions may be more prone to cavities as well. Finally, people who do not visit their dentist regularly may be more likely to get cavities, as a dentist can diagnose cavities early and provide treatment to prevent further damage.
Summary: Cavities can affect anyone, regardless of age or diet. They are not just something that affects people who eat lots of sugar. Everyone is at risk for cavities, and how often and how bad they can be depends on different factors.
What are the risk factors for tooth decay?
Risk factors for tooth decay may include:
- Diet: Eating a diet high in sugar, carbohydrates, and starches can increase the risk for tooth decay. This is because these foods can lead to the formation of plaque on the teeth, which can result in cavities.
- Lack of proper oral hygiene: If teeth are not brushed and flossed on a regular basis, plaque and bacteria can gather, raising the possibility of developing cavities.
- Age: Tooth decay is more prevalent in young children and seniors (over the age of 40) than any other age demographic. Because their teeth are still developing, young children can be at risk of oral health complications, while elderly individuals may find it difficult to sustain proper dental hygiene.
- Medical conditions: The presence of diabetes (and some other medical conditions) can heighten the odds of tooth decay due to a decrease in saliva production, leading to a proliferation of bacteria and plaque.
- Medications: Some medications, such as steroids and anti-seizure medications, can cause a decrease in saliva production. Saliva helps to wash away food particles and bacteria, and a decrease in saliva can increase the risk for tooth decay.
- Smoking: Smoking not only leads to an increase in bacteria in the mouth, but it can also cause an increase in plaque formation and tooth decay.
- Genetics: Tooth decay can be significantly influenced by genetics, like a number of other medical conditions. If a parent has a history of tooth decay, their children may be at increased risk.
- Poor Access to Care: People who have poor access to dental care may be at increased risk for tooth decay. This is because they may not receive preventive care or treatment for cavities, which can lead to more serious tooth decay.
Summary: There are several risk factors for tooth decay, including a poor diet, a lack of oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, and a lack of fluoride in the drinking water. Other contributing factors can include acid reflux, dry mouth, and certain drugs or medications. To help maintain oral hygiene and prevent tooth decay, it is essential to brush and floss teeth on an everyday basis, cut down on sugary and acidic foods, and regularly visit the dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups.
How can you prevent tooth decay?
- Tooth decay is a very common problem that can have an overall negative impact on one's health if not taken care of properly. In order to avoid tooth decay, it is essential to have good oral hygiene habits and to maintain a balanced diet.
- Brushing your teeth twice a day for two minutes using a good-quality toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush is a key factor in preventing cavities. Make sure to cover the front, back, and top of each tooth.
- Furthermore, flossing daily removes plaque buildup and food particles from between teeth.
- In addition to brushing and flossing, a balanced diet is key to keeping teeth healthy. Eating foods high in calcium and phosphorus, such as dairy products, can help strengthen tooth enamel and reduce the risk of tooth decay. Avoiding sugary and acidic foods, such as candy, soda, and processed snacks, is also important because they can erode tooth enamel and contribute to the formation of cavities.
- You should also consider visiting your dental health provider on a regular basis for checkups and cleanings. During these appointments, your dentist will be able to monitor the health of your teeth and detect signs of decay early on. Your dentist may also suggest additional treatments, such as fluoride treatments or sealants, to help protect your teeth from decay.
- By following these steps, you can help prevent the onset of tooth decay and keep your teeth healthy and strong.
Summary: The best way to keep your teeth healthy and prevent tooth decay is to brush them twice a day and floss at least once. You can even use an antibacterial mouthwash a few times a day to keep your mouth clean. Avoid sugary foods and drinks, and if you have decayed teeth, you should get them fixed as soon as possible.
Do
To keep your smile healthy and sparkling, be sure to brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day, floss every day, and see your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. You can also help prevent tooth decay by limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks, and replacing your toothbrush every three to four months.
Don't
- To prevent tooth decay, you should not:
- Skip brushing your teeth
- Eat or drink acidic or sugary drinks and foods
- Smoke or consume any tobacco product
- Neglect regular dental check-ups
- Forget to floss on a daily basis
- Ignore any dental problems that arise
Tooth Decay: Diagnosis and Tests
- Tooth decay is a serious oral health issue that, if left untreated, can lead to extensive damage to teeth, including tooth loss. The diagnosis and testing for tooth decay involve assessing the condition of the teeth and gums, as well as examining the teeth for signs of cavities or other damage.
- A dentist or dental hygienist may also use an x-ray or other imaging technology to examine the teeth and surrounding structures. The dentist may then perform a dental exam to look for signs of decay, such as chalky white spots, brown or black stains, and other discolorations.
- If necessary, the dentist may take a sample of the affected area to test for bacteria that can cause tooth decay. Depending on the severity of the decay, the dentist or dental care provider may recommend a specific treatment plan such as fillings, crowns, or other procedures.
Summary: The diagnosis of tooth decay requires a physical examination of the mouth and teeth and may involve dental x-rays. A dentist may also use a dental explorer to check for signs of cavities, such as soft spots, discoloration, or texture changes on the surfaces of the teeth. Dental imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, can also help to identify and diagnose any cavities that may be present.
What are the possible complications of tooth decay?
- Tooth decay is a common dental (or oral health) issue that can lead to a variety of complications if left untreated. Complications of tooth decay may range from mild to severe and can include damage to the enamel of the tooth, gum disease, abscesses, and even tooth loss. Among the most common complications associated with tooth decay is enamel erosion.
- The tooth enamel is the outer layer of your tooth, made up of minerals like calcium and phosphate. When tooth decay forms, these minerals are broken down, resulting in holes or pits in the enamel. This damage to the enamel can cause pain and sensitivity to temperature, and it can also make the teeth look discolored.
- Another common complication of tooth decay is gum disease. When the enamel of the tooth is compromised, it leaves the underlying dentin layer exposed. This can cause bacteria to accumulate and lead to gum disease.
- Gum disease, which may also be referred to as periodontitis, is an inflammatory infection of the gum tissue that can lead to swelling, redness, and bleeding. If not treated for a long period of time, gum disease can be a reason for tooth loss as well as the formation of abscesses. These abscesses are another serious complication that can arise from tooth decay.
- An abscess is basically an accumulation of pus that tends to form around the tooth in response to an infection. This type of infection can be extremely painful and can lead to further damage to the tooth or even spread to other parts of the body, resulting in more serious health issues. It's important to seek professional medical treatment if an abscess is found to be present.
- Finally, tooth loss is a major complication of tooth decay. When the tooth decay is severe enough, the tooth may become so damaged that it can no longer be saved. In such cases, the affected tooth may need to be extracted or removed, resulting in tooth loss.
- All in all, practicing good oral hygiene and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings help prevent tooth decay and its complications. This may help ensure that you continue to have healthy gums and teeth that are free from decay.
What are the home remedies for tooth decay?
Although there are many home remedies for tooth decay, it's always best to consult with a dental care specialist before trying any of them. Some of them include:
- Saltwater rinse: A simple solution of warm water and a teaspoon of salt can help reduce inflammation and pain caused by tooth decay. Swish it around the mouth for at least 30 seconds before you eventually spit it out.
- Garlic: Garlic is a natural antibiotic that may help fight off the infection that can cause tooth decay. Simply crush up a garlic clove and place it on the affected area for a few minutes.
- Clove oil: Clove oil has antiseptic and anesthetic properties, making it a great remedy for tooth decay. Put a few drops of this medicinal oil on a cotton ball. Then, gently place the cotton ball on your affected tooth.
- Turmeric: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Make a paste with turmeric powder and water, and apply it directly to the affected tooth.
- Hydrogen peroxide: It is an effective disinfectant that can aid in the prevention of bacterial growth. To clean your mouth with hydrogen peroxide, mix a cup of water with a teaspoon of the solution. Swish this mixture around in your mouth for at least 30 seconds before spitting it out.
- Baking soda: Baking soda is a great remedy for tooth decay as it helps to neutralize acids and remove plaque from the teeth. Make a paste with baking soda and water. Apply this paste directly to the affected tooth.
Summary: There are several remedies that can help prevent or treat tooth decay. These include brushing your teeth at least two times a day, flossing every day, and avoiding any sugary or acidic snacks or beverages. Additionally, rinsing your mouth with a saltwater solution can help reduce inflammation in the gums and help remove bacteria, while swishing with hydrogen peroxide can help kill bacteria and reduce plaque. Finally, using baking soda, lemon juice, and clove oil can help reduce pain and remove bacteria.
What should I eat if I have tooth decay?
If you have tooth decay, it is important to be aware of what you eat, as certain foods can worsen your condition. In other words, when you are dealing with tooth decay, it is very important to make healthy food choices. Here are some excellent tips to help:
- Opt for low-acid foods, as foods with a high acid content can erode enamel and make it easier for decay to occur.
- Avoid acidic foods such as citrus fruits, pickles, and vinegar-based dressings and sauces.
- Choose crunchy and fibrous foods. Eating crunchy and fibrous foods, such as apples, carrots, and celery, can help clean food particles from between teeth and stimulate saliva production. Saliva's ability to help stop tooth decay is an important factor in preventing tooth decay—it's not just there to keep your mouth wet! When you produce saliva, it actually helps to remove or wash away the bacteria that cause tooth decay.
- Drinking ample water is also essential for good oral health. Water helps rinse away any bacteria and food particles from the mouth, and it's recommended to drink water after meals in order to keep the mouth free from bacteria and clean. Drinking water also helps keep your teeth and gums hydrated, which prevents dryness and irritation. By staying hydrated, you can help reduce the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Opt for dairy products. Dairy products, such as yogurt, cheese, and milk, help to protect teeth by providing a source of calcium and phosphorus. These two nutrients help to remineralize teeth, making them stronger and less vulnerable to decay.
- You can easily safeguard your teeth from further damage by following the above-given simple suggestions. If you are concerned about your dental health, it is important to speak to your dentist to determine the best course of action for your particular situation.
Summary: Eating soft, nutritious foods is the best way to protect teeth when suffering from tooth decay. Foods such as yogurt, applesauce, and soft-cooked vegetables are easy to digest and can help limit the damage caused by decay.
What should I not eat if I have tooth decay?
If you have tooth decay, it is best to avoid sugary and acidic foods and drinks, such as candy, soda, and citrus juices, as these can cause further damage to your teeth. Additionally, it is important to avoid sticky snacks, such as dried fruit and chewy granola bars, as these can get stuck in the crevices of your teeth and cause further decay.
It is also important to avoid hard foods, such as nuts or raw vegetables, as these can put extra pressure on your teeth and cause further damage. Finally, it is important to avoid foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as white breads and pastas, as these can increase the amount of plaque on your teeth and cause further decay.
Summary: Avoid foods that are high in sugar and acid, such as candy and soda, as these can worsen tooth decay. Additionally, avoid sticky and hard foods, such as nuts and hard candy, as these can cause further damage to the teeth.
Tooth decay treatments
The treatment for tooth decay depends on the severity of the decay and may include one or more of the following:
- Dental Fillings: Dental fillings are predominantly used to fill in cavities resulting from tooth decay. The dentist will first remove any decayed tooth structure and, thereafter, fill the empty area with a special material to restore the tooth. Materials used for this purpose include amalgam, composite resin, or glass ionomer. Fillings are important because they help restore the function and integrity of the tooth, as well as prevent further decay.
- Root canal: In more severe cases where a tooth is decaying, a root canal may be the only way in which the tooth can be saved. During a root canal, the dental care specialist or dentist removes the infected pulp, cleans the inside of the tooth, and fills the area with a special material. This procedure is necessary in order to save the tooth from rotting away and eventually falling out.
- Crowns: When a large portion of a tooth is affected by decay, a crown may be used to cover the tooth and protect it from further damage. A 'crown' can be best defined as a 'tooth-shaped cap.' It is placed over a damaged tooth to improve its appearance and strength.
- Extractions: If the tooth decay is too severe and cannot be treated, the tooth may need to be extracted.
- Fluoride Treatments: Fluoride treatments can help prevent further decay and can help rebuild enamel that has been weakened by decay. The most common forms of fluoride treatments include foams, gels, and varnishes that are applied directly to the teeth.
Summary: In most cases, tooth decay can be treated with a filling, which involves removing the decayed area and replacing it with a material such as composite resin. In cases where the tooth is more seriously damaged, a dental crown might be the best option to restore it. And in extreme cases, root canal therapy may be indispensable for removing the infection and saving the damaged or affected tooth.
Which doctor should I consult for tooth decay?
If you suspect tooth decay, it is important that you see an oral health specialist or dentist as soon as possible. Your dentist can assess the decay and provide treatment options to restore the health of your tooth and put a stop to any further damage.
A general dentist can diagnose and treat most tooth decay, but you may also wish to consult with an endodontist for more advanced cases. An endodontist specializes in root canals and other complex dental procedures and can provide additional expertise in the treatment of tooth decay and other oral health issues.
Which are the best medicines for tooth decay?
The most effective medicines for treating tooth decay may include fluoride treatments, such as fluoride gels, rinses, and varnishes. Fluoride helps to strengthen and repair the tooth enamel. This essentially makes the tooth enamel much more resistant to decay and cavities.
Other treatments for tooth decay include sealants, which help to protect the tooth from further damage, and antibiotics, which are used to treat any infection caused by the decay. Regular brushing and flossing are also part of a good oral hygiene routine and help keep tooth decay and other oral health issues at bay.
How long does it take to recover from tooth decay?
The length of time it takes to recover from tooth decay generally corresponds with the severity of the damage done to your teeth. You can recover quickly from mild tooth decay with a few treatments if you do your part as required. Having said that, if the decay is severe, you will most likely need a crown to fix it, which may take longer.
All in all, it may take several weeks for your bone to start growing and fill in the damaged area. Also, your dentist may apply a temporary cementing material in the damaged area, which will protect the tooth from further damage. It's imperative for a speedy recovery that you follow all of your dental care specialist's recommendations and instructions.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The results of tooth decay treatment can be lasting (and even permanent), depending on the intensity of the decay and the kind of treatment received. Standard upkeep and proper oral care are essential to make sure that the decay does not come back. Frequent dental check-ups and routine brushing and flossing can also assist in keeping the treated area unharmed and free from additional decay.
Who is eligible for the treatment?
Tooth decay treatment is generally available to anyone who is suffering from decay or damage to their teeth. This can include adults, children, and seniors. Typically, dentists will recommend a combination of treatments, such as fluoride treatments, fillings, sealants, and dental crowns.
If you have a lot of decay in your tooth (or teeth), your dental care provider may recommend a root canal as the best option to treat the condition in order to save your teeth. In this procedure, the affected tissue will be carefully taken out, and the area will be closed off to prevent any further harm. Your dentist may help you decide if this treatment option is necessary for you or not and explain the process in detail.
Who is not eligible for the treatment?
Anyone who does not have tooth decay is not eligible for the tooth decay treatment. Tooth decay is an oral health condition that involves the breakdown of tooth enamel due to the acid produced by bacteria. As such, individuals who do not have any signs or symptoms of tooth decay, such as cavities, do not require treatment.
What are the post-treatment guidelines?
- After the dentist removes a tooth, you may have some pain in the empty socket for a few days. You can control this with pain relievers. After a few days, you will notice a soft bump where the tooth used to be.
- This is the tissue called the gum margin that is filling in the space where the tooth was removed. This is normal; it will take 6–12 months for this gum tissue to heal into a firm, healthy gum.
- Furthermore, the most important post-treatment guidelines are:
- Brush and floss your teeth regularly
- Visit your dentist for a professional cleaning
- If you have had root canal treatment, take good care of the tooth to prevent infection
- Take good care of your mouth
- Do not eat too much hard food, and consult your dentist if you have any issues
- Consume fewer sugary and starchy foods and more fresh fruits
What is the price of tooth decay treatments in India?
The cost of tooth decay treatment in India can vary depending on the severity of the decay and the type of treatment required. Generally, a simple filling may cost anywhere from Rs. 500 to Rs. 2,000, while more complex procedures like root canals and crowns may cost up to Rs. 5,000 or more. The cost may also vary based on the type of material used and the dentist's experience.
That said, it is always advisable to consult a dental care professional to learn the exact cost of treatment based on your specific needs. This way, you can make an informed decision that best suits your situation.
Summary: The cost of tooth decay treatments in India can vary depending on the severity of the decay, the type of treatment needed, and the location of the dental practice. However, on average, a filling for a cavity can cost anywhere between Rs. 500 and Rs. 2,000. Root canal treatments can cost between Rs. 1,500 and Rs. 4,000.
What are side effects of Tooth Decay treatments?
The most common side effects of tooth decay treatments can include tooth sensitivity, gum irritation, and inflammation. When a dentist performs a filling, crown, or root canal procedure on a decayed tooth, it can cause sensitivity that may manifest as discomfort when consuming hot or cold items. Also, gum irritation and inflammation can occur from the use of antibiotics to treat the decay or from other treatments such as laser therapy.
Other minor side effects can include swelling and bleeding of the gums and a bad taste in the mouth. Sometimes, an allergic reaction may also take place. It is important to contact your dentist if you experience any of these side effects, as they can provide additional treatment or advice as needed.
Summary: The most common side effects of tooth decay treatments include pain, sensitivity, irritation, and gum inflammation. In some (rare) cases, there can be an allergic reaction to the particular medication that has been used to treat the decay. In rare cases, infection may occur if the decay is not treated promptly or if the treatment is not effective.
Tooth Decay: Outlook / Prognosis
Tooth decay is a common problem that can be treated with proper oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and professional dental treatments. While it may seem intimidating, the process of treating tooth decay can be conveniently performed with the help of a qualified dental professional who can provide the necessary services and advice to prevent further damage.
Taking the necessary steps to maintain proper oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing on a regular basis, can help reduce the risk of tooth decay and other dental health issues. All in all, tooth decay can be managed with the right treatment plan. In fact, regular checkups and professional interventions can ensure healthy teeth and gums for years to come.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Dentist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors