Top 12 Tips for Diabetic Retinopathy Prevention
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a form of eye damage caused by complications of diabetes. It is the most common cause of vision loss among people with diabetes and a leading cause of blindness in adults. This condition occurs when diabetes affects the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the part of the eye responsible for capturing light and images.
Diabetes-related changes in blood sugar, cholesterol levels and blood pressure can cause these vessels to swell, leak fluid, or close off entirely. Without proper treatment and management, diabetic retinopathy can lead to significant vision impairment or permanent blindness over time.
What are the signs and symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
The most common signs and symptoms associated with Diabetic Retinopathy can be broadly grouped into three categories:
- Blurred Vision: This is the most common symptom of Diabetic Retinopathy. People with diabetic retinopathy can experience blurred vision, hazy vision, or difficulty seeing fine details.
- Fluctuations in Vision: People with diabetic retinopathy can also experience sudden changes in their vision, such as dark spots that come and go, flashes of light, or completely blurred out vision.
- Eye Pain or Pressure: Diabetic retinopathy can cause eye pain or pressure due to swelling and fluid build-up in the retina.
What are possible complications of Diabetic Retinopathy?
- Vision Loss: Diabetic Retinopathy is the leading cause of vision loss, which can range from mild to severe cases. It can damage blood vessels in the retina, limit oxygen supply and cause swelling in the macula which leads to blurred or distorted vision.
- Advanced Retinopathy: People with advanced Diabetic Retinopathy may experience severe vision problems, including blind spots or total blindness. The condition can also increase the risk of developing glaucoma and cataracts, as well as permanent retinal detachment which could eventually lead to total blindness.
- Secondary Conditions: Other serious conditions that may develop as a result of Diabetic Retinopathy include vitreous hemorrhage (bleeding into the eye), neovascularization (abnormal new blood vessel formation), and neovascular glaucoma (increased pressure on the optic nerve). These secondary conditions can often lead to delayed visual impairment or even complete loss of sight if not treated promptly and effectively.
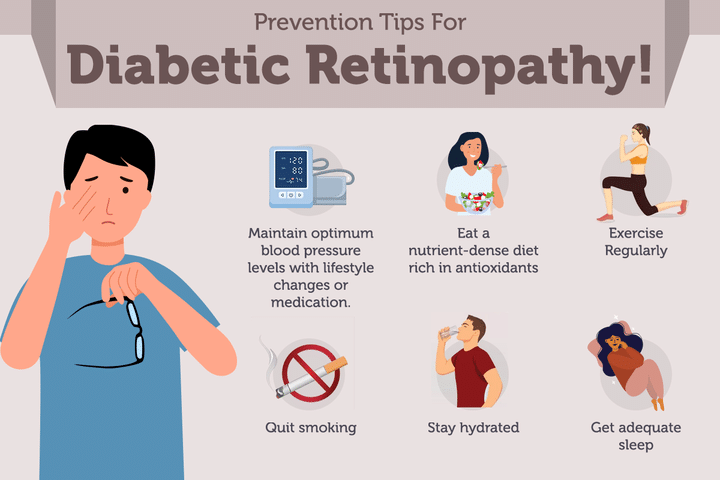
Top 12 Tips for Diabetic Retinopathy Prevention
- Maintain Healthy Blood Glucose Levels: Elevated blood glucose levels are one of the main risk factors for developing diabetic retinopathy, making it extremely important that you monitor and maintain your blood glucose levels. Aim to keep your numbers above 80 mg/dL with the help of medication and lifestyle changes.
- Monitor Blood Pressure Levels: Hypertension can worsen symptoms of diabetic retinopathy, thus making it important to regularly check and manage your blood pressure levels. High blood pressure can damage delicate structures in the eye, so take measures to prevent this!
- Eat A Nutrient-Dense Diet Rich in Antioxidants: A nutrient-dense diet is essential for preventing worsening diabetic retinopathy symptoms. Eat plenty of foods containing antioxidants such as dark leafy greens, berries, colorful vegetables, fatty fish, nuts and seeds which help reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health in those with diabetes.
- Exercise Regularly: It is important to stay physically active when living with diabetes– forming a regular exercise routine may help lower your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy by improving blood glucose control or preventing obesity– two huge risk factors for developing serious eye complications from diabetes. Consider going for regular walks or adding light cardio into your daily routine.
- Quit Smoking And Limit Alcohol Intake: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress are all factors thought to increase your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Therefore, quitting smoking or limiting your alcohol consumption may reduce your risk significantly.
- Wear Proper Eye Protection During Activities That Might Result In Trauma To The Eyes: Activities such as driving long distances, working around hazardous machinery or participating in contact sports may increase risks for sustaining trauma that could lead to vision impairment. Thus wearing proper protective eyewear is key for avoiding any form of eye injury and therapeutic contact lenses can aid prevention against infection related vision problems as well. Additionally ensure you wear sunglasses whenever outdoors during sunny days since exposure to UV radiation has been tied to increasing risks for macular degeneration. Wearing tinted glasses while using digital screens may also be beneficial.
- Take Your Diabetes Medications As Prescribed By Your Healthcare Provider: It is important to take your insulin, anti-diabetic medications, and other prescribed drugs as instructed by your doctor. These medications can help you lower your blood sugar levels and reduce the risks of complications from diabetes including diabetic retinopathy.
- Visit your eye doctor: Schedule regular eye exams with an eyecare professional every year (or more often if recommended). This will allow them to identify any signs of diabetic retinopathy early on so that treatment can be started as soon as possible and visual loss may be prevented or minimized.
- Avoid Stress & Get Enough Sleep Intermittently Allowing Mind & Body To Recuperate: Stress is one of the most common risk factors associated with diabetes. High levels of stress can worsen your blood sugar levels and make it harder to manage your diabetes. Additionally, lack of sleep can have a negative effect on your health, making it harder to control your blood sugars and increasing the risk for diabetic retinopathy.
- Reach and Maintain a Healthy Weight: Carrying excess weight is linked to diabetes and also increases the risk for diabetic retinopathy. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can prevent and/or effectively treat type 2 diabetes.
- Take breaks: Whenever engaging in activities that require focusing on details, such as reading, crafts or urgent paperwork. Take periodic breaks to rest your eyes as this will reduce strain on them which could lead to further excessive swelling in the back of the eye.
- Stay hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water daily because dehydration increases the risk of developing blood vessel problems linked to DR.
If the above methods don't work, you may be required to undergo surgery.
What are the surgical treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy?
- Macular Grid Laser Photocoagulation: It aims to destroy abnormal blood vessels and stop them from regrowing around the macula (the area of the retina responsible for central vision). This treatment also helps block leaking fluid or hemorrhages around the macula which can cause scarring or retinal detachment.
- Panretinal Photocoagulation: This method uses a laser beam to shrink abnormal blood vessels or eliminate any new blood vessel growth that has affected other parts of the retina outside the macula.
- Vitrectomy: This treatment involves removing some parts of the jelly-like substance in your eye known as vitreous humor from behind the retina which can help remove scar tissue creating traction on your retina that may have caused it to detach from its base.
- Asymmetric Reflective Panning Technique and Implantable Device Insertion: These are two types of device/stent inserted into either side of your eye over areas with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy which works by pressing against certain areas narrowed by high intraocular pressure (IOP).
- Membrane Peeling: It removes fibrovascular membranes from inside sclera while simultaneously repairing retinal tears or holes with laser or freezing technique known as cryopexy which helps reduce chances of detached retina due to contraction of these fibrous membranes on your retinas surface.
Best doctors to consult for Diabetic Retinopathy
- The best doctor to consult for diabetic retinopathy is an ophthalmologist or retina specialist.
- It is important to find a doctor who specializes in diabetes and its effects on vision, as well as one with experience in treating diabetic retinopathy.
- For those with advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, a vitreoretinal surgeon is recommended for laser treatment and surgery.


+1.svg)
