High Uric Acid Level: Causes, Risks, Treatment, Prevention
Last Updated: Apr 11, 2023
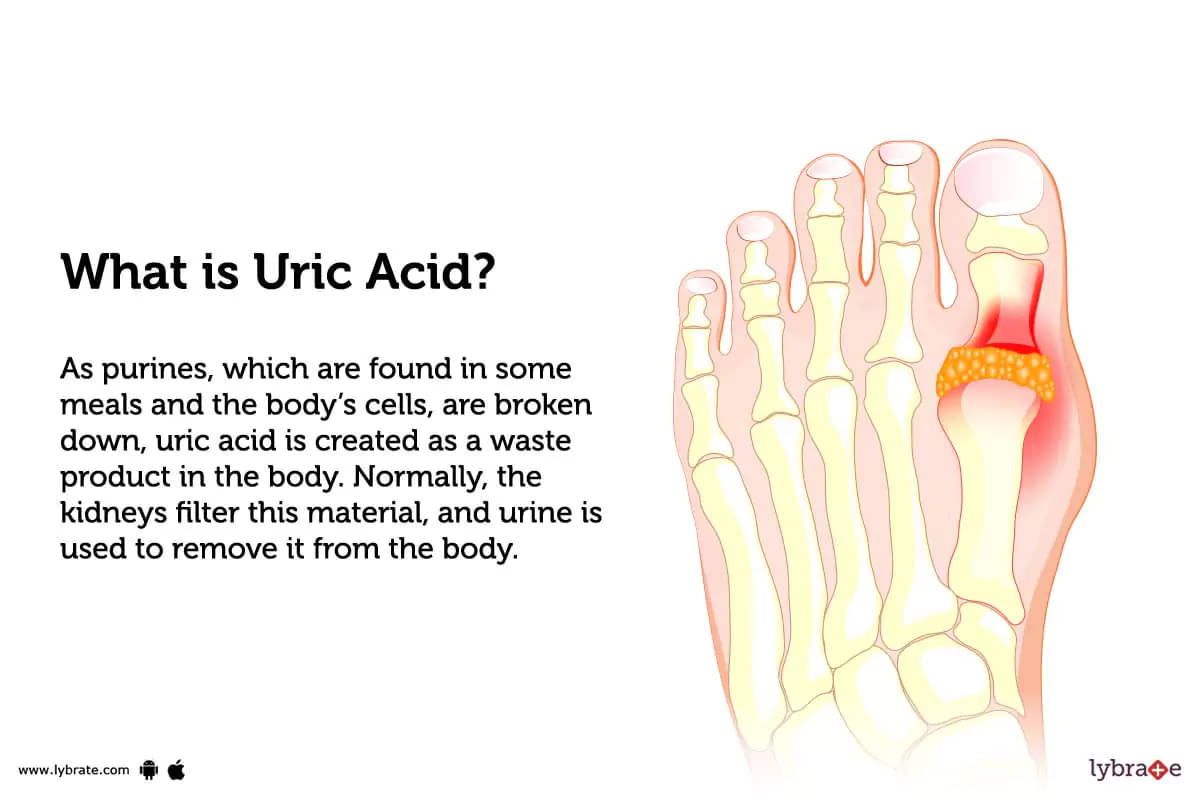
What is Uric Acid?
As purines, which are found in some meals and the body's cells, are broken down, uric acid is created as a waste product in the body. Normally, the kidneys filter this material, and urine is used to remove it from the body. A condition known as hyperuricemia can result from an excessive amount of uric acid in the blood, which is something that is generally found in the blood in modest amounts.
What is high uric acid level?
Hyperuricemia, often known as a high uric acid level, is a disorder when there is too much uric acid in the blood. This may happen if the body creates too much uric acid or has trouble getting rid of it properly. Elevated uric acid levels can result in the production of urate crystals, which can build up in the joints and cause discomfort and inflammation, a condition known as gout.
Genetics, some drugs, and a diet heavy in purine-rich foods are among additional variables that might cause elevated uric acid levels. Treatment options for high uric acid levels may include medications to reduce uric acid production or increase its excretion, lifestyle modifications such as changes in diet and exercise, and in severe cases, joint aspiration or surgery.
Uric acid levels in males and females
Both males and females can have uric acid in their blood, but studies suggest that males tend to have higher levels of uric acid than females. This is because estrogen, which is found in higher levels in females, can help to lower uric acid levels by increasing its excretion. In contrast, testosterone, which is found in higher levels in males, has been shown to increase uric acid production.
However, it is important to note that the normal range for uric acid levels in the blood is the same for both males and females.
In general, a high uric acid level, or hyperuricemia, is characterized as a level that is higher than 6.0 mg/dL for women and 7.2 mg/dL for men. Genetics, nutrition, some drugs, and underlying medical disorders including metabolic syndrome or kidney disease can all contribute to high uric acid levels.
How uric acid can build up in the body
Purines, which are contained in some meals and the body's cells, are broken down in the body to form uric acid, a waste product. Urinary excretion of uric acid from the body is typically filtered by the kidneys. However, uric acid can accumulate in the blood and cause a disease called hyperuricemia if the body creates too much of it or is unable to get rid of it effectively.
Here are some typical causes and elements that may have an impact on the body's uric acid buildup;
- Diet: Eating foods high in purines, like red meat, organ meat, shellfish, and particular kinds of fish, can make the body produce more uric acid.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to having excessive uric acid production or ineffective uric acid elimination.
- Medical conditions: The body's ability to remove uric acid can be compromised by disorders like kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, and hypothyroidism, which can cause uric acid to accumulate in the blood.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, aspirin, and certain chemotherapy drugs, can interfere with uric acid excretion and lead to hyperuricemia.
- Alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol, especially beer and hard liquor, can increase uric acid production and reduce its excretion.
Causes of high uric acid levels
High uric acid levels, or hyperuricemia, can have various causes, including genetics, diet, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions such as kidney disease or metabolic syndrome. The following are some typical causes and factors that may lead to elevated uric acid levels;
- Diet: The body can produce more uric acid when purine-rich meals like red meat, organ meat, shellfish, and particular certain kinds of fish are consumed.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to having excessive uric acid production or ineffective uric acid elimination.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, and hypothyroidism, can impair the body's ability to eliminate uric acid, leading to its buildup in the blood.
- Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, aspirin, and certain chemotherapy drugs, can interfere with uric acid excretion and lead to hyperuricemia.
- Alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol, especially beer and hard liquor, can increase uric acid production and reduce its excretion.
- Dehydration: Drinking insufficient amounts of water can cause urine to become concentrated, which may raise uric acid levels.
- Obesity: Having excess body fat can result in insulin resistance and increased uric acid production, which increases the chance of having hyperuricemia.
Symptoms of high and low levels
Any ailment that affects the heart or blood vessels falls under the umbrella term of 'cardiovascular disease.' Depending on the particular condition and the degree of the disease, cardiovascular disease symptoms can change. Here are some of the common symptoms associated with cardiovascular disease;
- Chest pain: Chest pain or discomfort is one of the most common symptoms of cardiovascular disease. It can range from a mild ache or pressure to severe, crushing pain.
- Shortness of breath: Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing can occur with cardiovascular disease, particularly during physical activity or exertion.
- Fatigue: When coupled with additional symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain, fatigue or weakness might be a sign of cardiovascular disease.
- Swelling: Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet can be a symptom of cardiovascular disease, particularly if it's accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath or fatigue.
- Palpitations: Palpitations, or a rapid or irregular heartbeat, can occur with cardiovascular disease, particularly if it's accompanied by other symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath.
Diagnosis
Lab testing, a physical exam, and a medical history are frequently used to diagnose excessive uric acid levels. Here are some of the common methods used to diagnose high uric acid levels;
- Medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history, including any family history of gout or kidney disease, as well as any medications you're taking that may affect uric acid levels.
- Physical examination: Your healthcare professional may do a physical exam to look for symptoms of gout, such as joint swelling, redness, or pain.
- Blood tests: A blood test can help diagnose elevated uric acid levels by measuring your amount of uric acid. It's crucial to remember that uric acid concentrations can change throughout the day and may be influenced by things like diet and drugs.
- Urine tests: A urine test can measure the amount of uric acid in your urine and help diagnose conditions like kidney stones or kidney disease, which can cause high uric acid levels.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests like X-rays or ultrasound to check for signs of joint damage or kidney stones.
It's important to note that a high uric acid level alone doesn't necessarily mean you have gout or another related condition, and many people with high uric acid levels never experience symptoms.
Treatment of high and low levels
The underlying cause and seriousness of the problem will determine the best course of treatment for high or low uric acid levels. These are a few typical approaches for treating both high and low uric acid levels:
Treatment for high uric acid levels
- Medications: To lower uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks, medications such allopurinol, febuxostat, and probenecid may be used. Gout attacks can be treated with colchicine or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs).
- Lifestyle changes: Implementing dietary adjustments, such as consuming fewer foods high in purines and drinking more water, can help lower uric acid levels. Alcohol consumption restrictions and weight loss can both be beneficial.
- Treating underlying conditions: Treating an underlying medical condition that is causing high uric acid levels, such as kidney disease, may help lower uric acid levels.Treatment for low uric acid levels
- Medications: In some cases, medications like probenecid or sulfinpyrazone may be used to increase uric acid levels.
- Treating underlying conditions: If an underlying medical condition, such as Fanconi syndrome or Wilson's disease, is causing low uric acid levels, treating that condition may help increase uric acid levels.
- Dietary changes: Eating foods rich in purines may help increase uric acid levels. Before making any dietary adjustments, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional or certified dietician.
Conclusion
When purines in the body are broken down, uric acid is created as a natural waste product. While it is necessary to maintain a healthy balance of uric acid in the body, high levels can lead to various health problems, including gout, kidney stones, and cardiovascular disease. Low levels of uric acid are uncommon and are generally not considered a significant health concern.
Consuming a lot of foods high in purines, such as organ meats, seafood, and alcohol, might raise your blood levels of uric acid. Nonetheless, a healthy diet and consistent exercise can help to control and avoid elevated uric acid levels. In cases of high uric acid levels, treatment options include lifestyle modifications, medications, and dietary changes. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to properly diagnose and manage high uric acid levels to prevent potential health complications.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Urologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors