Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Uterus (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
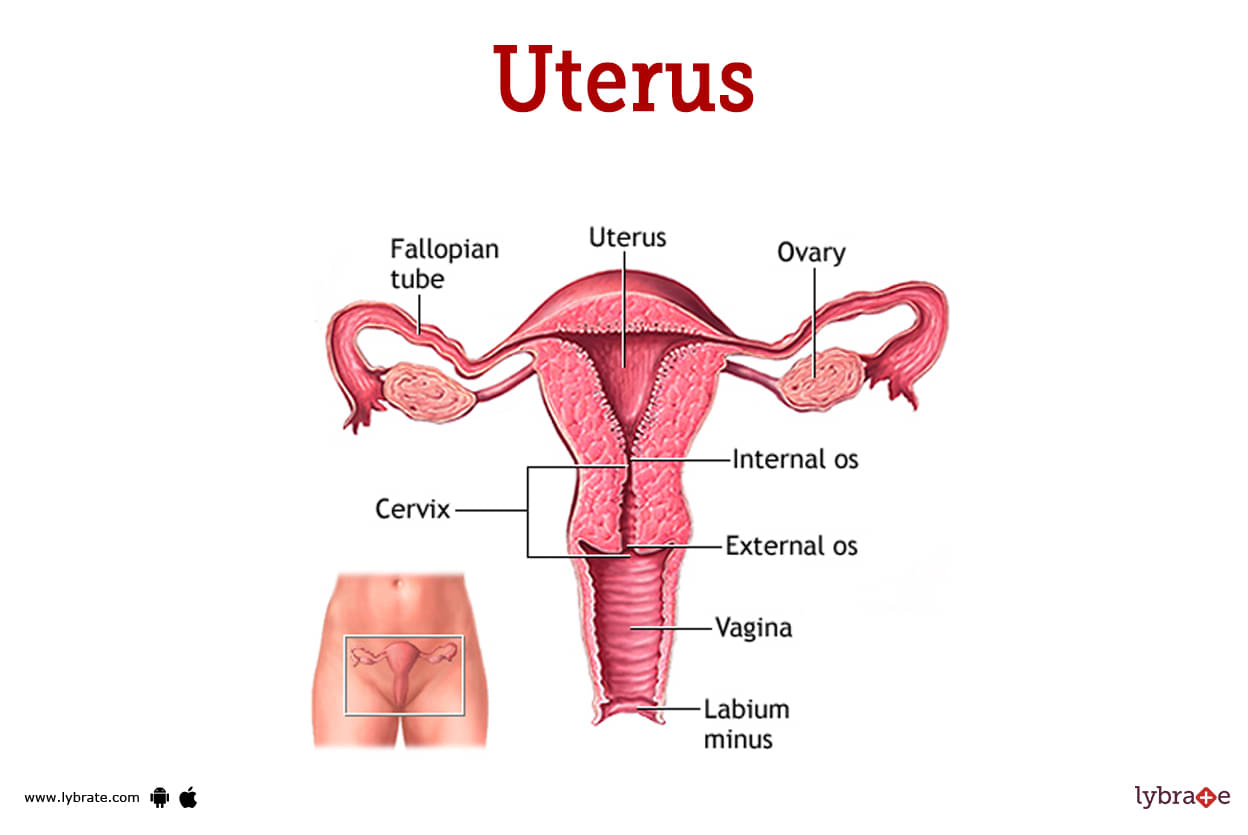
Uterus Image
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ placed between the bladder and the rectum in the female pelvis. The ovaries are responsible for producing the eggs that are transported through the fallopian tubes After the egg has been released from the ovary, it is ready to be fertilised and implanted in the lining of the uterus
Uterus Function
- Endometrium: This is the layer that is the deepest within. It has been proven to be the layer that possesses the highest level of activity The thickness of the endometrium increases just before the onset of menstruation. This thicker layer breaks down as a result of the cyclical hormonal shifts that occur during menstruation. As a consequence of this breakdown, blood is expelled from the uterus via the vagina. It is highly specialised and plays an extremely significant role in the reproductive and menstrual processes.
- Myometrium: The majority of the uterine volume is contained within this middle section. It refers to a layer of muscle that is composed of smooth muscles for the most part During the process of partition, this is the layer that assists in the contraction of the uterus and assists in the expulsion of the baby out of the uterus via the birth canal.
- Perimetrium: The serosa is the name given to the most superficial layer of the uterus, which is termed the serosa. It is a very thin layer that is composed of epithelial tissue that surrounds the uterus on its exterior side.
- Development of the foetus: for the continuity of the human race it is essential to reproduce and maintain the human species and this is possible due to the presence of the uterus which helps the implantation of the blastocyst in the uterine wall and leads to pregnancy.
- Mechanical support: The provision of mechanical protection to the foetus contributes to the prevention of any physical injury to the developing child and is done because of the uterus.
- Nutritional support: The foetus receives the nourishment it needs to grow and develop normally as a result of this. In the event that they are not provided with it, it may result in an ectopic pregnancy or other health-related illnesses.
- Removal of waste: It regulates the elimination of waste from the foetal body and, as a result, maintains a sanitary and healthy environment for the developing foetus.
- Implantation site of the blastocyst: The development of a pregnancy requires the blastocyst to get implanted in the endometrium.
- Menstruation: The falling of the endometrium, which occurs during menstruation, causes blood to be expelled via the vagina. Menstruation is the result of a malfunction in the organ known as the uterus
Uterus Disorders
Abnormal uterine bleeding: Symptoms like Irregular bleeding, Pelvic pain, irregular vaginal discharge, unable to reproduce and dysuria/painful urination can be seen if there is any abnormality present in the uterus.
- Anteverted uterus: The normal position of the uterus has it leaning forward at the cervix and pointing towards the abdominal cavity This is the most common type of uterus women usually have.
- Retroverted uterus: Alternately referred to as a tipped or tilted uterus, this condition occurs when the uterus is positioned in such a way that it bends toward the spine rather than forward into the belly
- Anteflexed uterus: When the uterus is anteflexed, it’s bent forward. Because of the severity of the tilt, there is a risk of unpleasant symptoms being caused by pressure being applied to the abdominal region or the urine bladder
- Retroflexed uterus: When the uterus is positioned in a retrograde position. Because of the angle, pressure is applied to the lower back
- Uterine fibroids: A condition in which there are small, noncancerous tumours in the uterus.
- Uterine polyps: unnatural growths in the layer of the endometrial of the uterus.
- Uterine cancer: Cancer of the uterus also called uterine sarcomas.
- Endometriosis: In this condition, the lining of the uterus develops in sites other than the uterus itself
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: An infection of the reproductive organs. It can either be due to unprotected sexual intercourse or due to bacterial/viral/fungal infections.
- Uterine prolapse: Uterine prolapse is the term given to the condition that occurs when the uterus moves out of its normal position
- Infertility: when a couple is unable to reproduce or give birth to a baby even after having unprotected sexual intercourse is called as infertility.
- Arcuate uterus: Comparable to a uterus with a bicornuate form but with less of a depression or heart shape
- Septate uterus: When your uterus is split in half by a membrane and placed in a position to accommodate pregnancy
- Unicornuate uterus: the existence of only one fallopian tube and a uterus that is not normal in form
- Didelphys uterus: presence of 2 uteruses at the time of birth.
- Adenomyosis: When the endometrial tissue that typically borders the uterus develops into the muscular wall of the uterus, this condition is referred to as endometriosis During each menstrual cycle, this tissue continues to carry out its normal duties, which include thickening, tearing apart, and bleeding
- Fibroids: The benign growths made up of muscle tissue in the uterus are called fibroids. Fibroids are not cancerous. They can develop at any stage of life and to any gender. If fibroids are small theh don’t cause issues during pregnancy, but when larger fibroids are present then it may cause complications.
- Uterus scars: These are scars in the uterus also called Asherman syndrome. Presence of these scars can damage the endometrium of the uterus. They can be caused due to an infection or condition like endometriosis.
Uterus Test
- Physical Examination Of Uterus: A pelvic examination is performed by a doctor, and it includes checking the uterus to see if there is a rash in the lower abdominal region or if there is any pain or abnormal fliud in or out of the vagina, any of which could be signs of a uterine infection. A medical professional is the one who will carry out this process, which entails an examination of the uterus
- Ultrasound Whole Abdomen: In the process of making a gynaecological diagnosis on a woman, an ultrasound is routinely utilised as a primary screening instrument for the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. This is common practise. The use of sound waves allows for images of the inside of the body to be obtained utilising ultrasonic technology
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: A transvaginal ultrasound, often known as a TVUS, is frequently the method of choice for examining the uterus. The transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) procedure includes inserting a probe into the vagina. This probe performs a function very similar to that of an ultrasound transducer. TVUS pictures can be analysed to determine whether or not the uterus has a mass (tumour) or whether or not there are symptoms of endometrial cancer, such as endometrium that is excessively thick.
- Sonohysterography: It is a medical treatment that allows for an examination of the lining of the uterus. The examination is risk-free and completely painless, as it relies on sound waves and a computer to produce pictures.
- Papanicolaou (Pap) Test: The sample is obtained by inserting a speculum, which is a metal or plastic instrument, into the vagina in order to spread apart the walls of the vagina and then using a plastic brush in order to remove some cells from the surface of the cervix and from the passageway through the cervix. This is how the doctors collect the sample (cervical canal). for the purpose of determining whether or not any kind of infection associated with a viral infection, such as human papilloma virus, exists.
- Colposcopy: After spreading the vaginal walls with a speculum, a binocular magnifying lens can be used to examine the cervix for abnormalities that could indicate the presence of cancer (akin to a microscope).
- Hysterosalpingography: During a procedure known as hysterosalpingography, both the uterus and the fallopian tubes are seen with the use of X-rays (HSG). Even while HSG is considered to have a low risk profile, there is no medical treatment that is entirely without danger. It is possible that you will have some discomfort if you have an allergy to the colour of the fluid.
- Endocervical Culture: A swab is used to collect cells and mucus from the endocervix in preparation for testing. The uterus is located within the cervix, which is a component of the pelvic. It is thus possible to see the future development of any microbes, mycelia, or yeast. It is possible that more testing will be required in order to identify the bacterium responsible for the infection and devise a treatment strategy.
Uterus Treatment
- Myomectomy: By utilising a hysteroscope or a laparoscope probe during the procedure, it is possible to remove fibroids without having to make a big incision in the abdominal region. At the moment of necessity, it is something that can be performed only by a gynaecologist who specialises in the field. It is a method that is less invasive for the excision of fibroids from the uterus.
- Uterine artery embolization: uterine fibroids can be treated using this method, which involves inserting an embolus into the uterine artery. This method reduces the amount of blood that flows through the uterus, which is beneficial for the destruction of ascending uterine fibroids.
- Hormone replacement therapy: The hormones progesterone, oestrogen, and hCG can be replaced by synthetic versions of the hormones through the use of medicines like diethylstilbestrol and progesteron depot. They are extremely beneficial in the treatment of growth-related illnesses of the uterus and are also useful in the treatment of uterine cancer.
- Hysterectomy: hysterectomy is a sort of surgical operation that refers to the process of removing a woman's uterus. This can be done either by an open surgical procedure or through a laparoscopic surgical procedure.
- Polypectomy: It is the removal of uterine polyps with the use of a hysteroscope. It is one of the most recommended ways to treat the disease of uterine polyps since it is less intrusive and does not require any post-operative stress related medicine.
- Endometrial ablation or resection: Abnormal uterine bleeding is treated by endometrial ablation, which involves inserting a probe called a hysteroscope into the uterus and destroying the uterine lining.
- Ovarian Cyst Removal: It is considered a minimally invasive therapy method when fluid-filled cysts in the ovaries are removed by uterine surgery. This procedure removes the cysts.
Uterus Medicine
- Antifungals medicines for uterine infection: Clotrimazole, miconazole and tioconazole are well known antifungal medicines known to be used for any form of fungal infection found in the uterus
- Antibiotics medicines for uterine infection: Some of the antibiotics known to be useful for any form of uterine infection includes amoxycillin, cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones
- Antibiotics for Fibroids: Some of the medications includes metronidazole, ofloxacin and norfloxacin etc.
- Analgesics for Uterine prolapse: Tramadol, diclofenac sodium, Mefanemic acid and dicycloamine are the pain relieving medicines for the conditions of uterine prolapse which are considered useful.
- Analgesics for Endometriosis: Medicines like naproxen sodium, diclofenac sodium add tramadol hydrochloride are useful when it comes to pain related problems of endometriosis.
- Artificial hormones for uterine fibroids: Synthetic hormones which have a specific similar function like progesterone and estrogen are called as Progestins which are useful when it comes to problems of polycystic ovarian disorders and uterine growth disorder.Artificial hormones for uterine growth: Diethylstilbesterol is known to be useful for promoting uterine growth and also maintaining proper environment of the uterus
- Artificial hormones for uterus carcinoma: Synthetic form of estrogen progesterone and HCG are useful for hormone replacement therapies when it comes to the disorders of uterus carcinoma.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is normal uterus size?
Normally, the uterus is 8 cm long and 4mm thick.
What are common uterus problems?
The most common uterus problems are heavy bleeding, abdominal pain, pain after intercourse and constipation.
What causes uterus disease?
Uterus diseases can be caused by some hormones, cancer and pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of uterus problems?
Symptoms of uterus problems are pelvic pain, frequent urge to urinate, abdominal pain and bleeding.
What is a uterine infection?
Uterine infection is an infection affecting the reproductive system.
Can uterus problems be cured?
Yes, uterus problems can be cured.
Which treatment is best for uterus fibroid?
The best treatment for uterus fibroid is a hysterectomy.
How do I know my uterus is healthy?
You may face symptoms like infertility, pain and bleeding if your uterus is not healthy.
What can damage the uterus?
The uterus can be damaged by uterus fibroid, infection and thyroid.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Urologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously