Variceal Bleeding: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
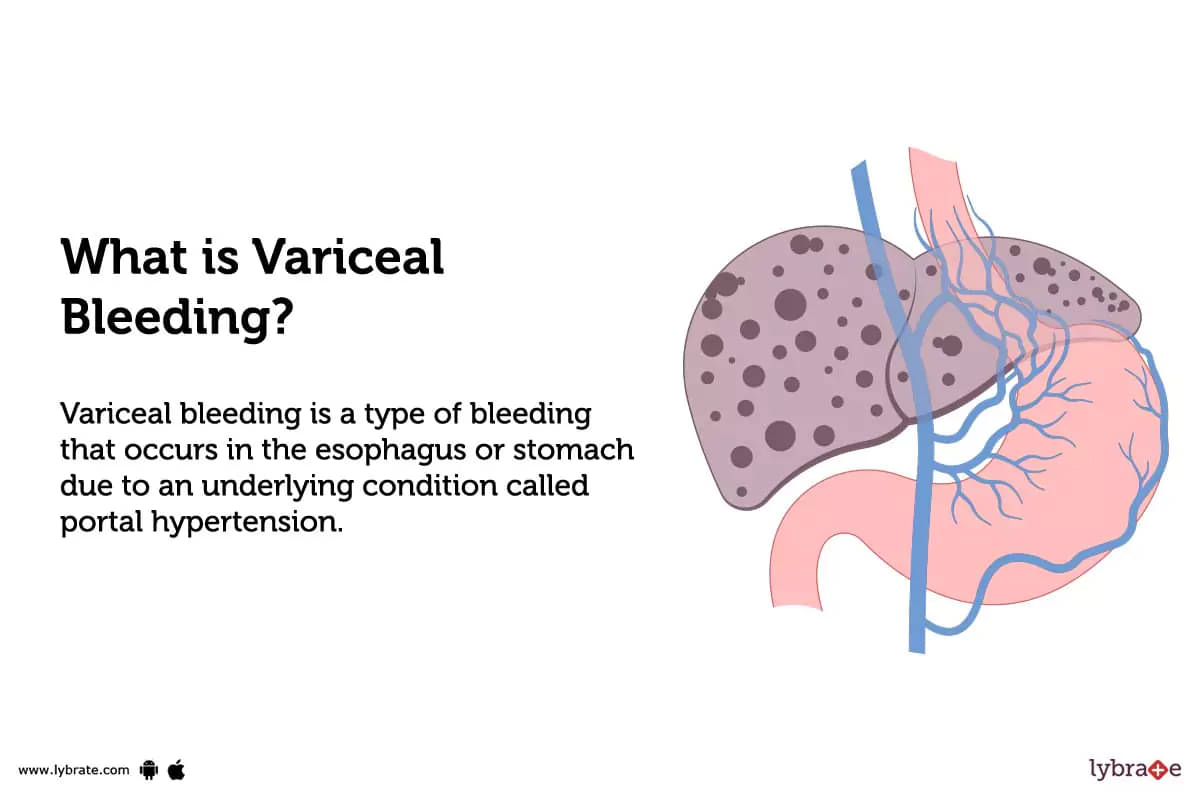
What is Variceal Bleeding?
Variceal bleeding is a type of bleeding that occurs in the esophagus or stomach due to an underlying condition called portal hypertension. Portal hypertension is caused due to blockage in the portal vein, which is the primary vein that help in transport of blood from the intestines to the liver.
When this obstruction occurs, blood pressure within the portal vein increases, causing veins in the esophagus and stomach to become swollen and fragile. These swollen veins are known as varices, and in case if they rupture, they have the powerl to cause significant bleeding.
Types of Variceal Bleeding
There are two types of variceal bleeding:
- Acute Variceal Bleeding: This type occurs suddenly and is often severe. It is caused by high pressure in the portal vein, which is located between the liver and small intestine, leading to rupture of varices in the stomach or esophagus.
- Chronic Variceal Bleeding: This type is a more insidious progression from discontinuous episodes of milder bleeding to more profuse but less frequent outbreaks, over time leading to large volumes of blood loss and potential life-threatening complications such as anemia or shock.
What causes Variceal Bleeding?
Variceal bleeding is caused by the dilated and weakened veins in the esophagus or stomach, known as varices. These varices can rupture and lead to bleeding.
Other potential causes of variceal bleeding include:
- Portal hypertension
- Cirrhosis
- Chronic alcohol abuse.
What are the symptoms of Variceal Bleeding?
Symptoms may include vomiting of blood, tarry and/or dark-colored stools, abdominal pain, dizziness and light-headedness due to loss of blood.
Other symptoms may include rapid heart rate, low blood pressure and chest pain or difficulty breathing due to accumulation of fluid in the lungs caused by pressure from increased veins around the stomach or esophagus.
How can you prevent Variceal Bleeding?
- Losing weight and avoiding obesity.
- Avoiding alcohol and certain medications that increase pressure in the veins.
- Taking medications that reduce the pressure in the veins (beta blockers or nitrates).
- Consuming a diet that is minimal in salt and beneficial to one's health.
- Exercising regularly.
- Avoiding straining during bowel movements or lifting heavy objects.
- Quitting smoking.
Variceal Bleeding - Diagnosis and Tests
- Endoscopy: An endoscopy is a procedure used to examine the digestive tract using a long, flexible, lighted tube with a camera at one end. The camera transmits images of the esophagus and stomach to a monitor, allowing the doctor to look for varices and other potential causes of bleeding.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging forms images of organs and structures within the body with the help of sound waves. It can be used to evaluate varices and check for any blockage in blood vessels that may be causing bleeding.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help diagnose variceal bleeding by looking for signs of anemia or infection that may indicate bleeding in the digestive tract. These tests can also help determine if there is active bleeding or if it has been stopped by endoscopic treatment or other means.
- X-Ray: X-rays help identify any foreign objects in the gastrointestinal tract that may be causing bleeding or any abnormalities in blood vessels that can lead to variceal bleeding.
- CT Scan: A CT scan is an imaging procedure that produces
- 3d images of organs and structures inside the body using X-rays and computer technology. It may be used to examine for varices, tumours, obstructions, or other digestive system abnormalities that might cause variceal bleeding.
What are possible complications of Variceal Bleeding?
- Shock: The rapid loss of blood can cause a severe drop in blood pressure, leading to shock.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Severe bleeding can lead to electrolyte imbalance caused by low sodium and potassium levels in the body.
- Hypoglycemia: Rapid blood loss can lower the amount of glucose in the body, a condition called hypoglycemia that can cause confusion and weakness.
- Respiratory Distress: If a large amount of blood is lost, respiratory distress can occur due to fluid overload or deficiency in oxygen or both due to inadequate delivery of oxygen from lungs.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: An increase or decrease in heart rate due to disruption of electrical currents within the heart, resulting from large amount of lost fluids and electrolytes, may potentially occur during variceal bleeding leading to cardiac arrhythmias which can be fatal if not treated timely with appropriate medical interventions escalating quickly into cardiac arrest.
- Death: Excessive and relentless bleed on varices could cause death if not treated timely or adequately.
Home Remedies for Variceal Bleeding
- Amalaki (Emblica officinalis): Amalaki is an excellent Ayurvedic remedy for treating variceal bleeding. It aids in reducing inflammation and improve blood flow, which in turn makes the bleeding less severe.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Ashwagandha is a popular Ayurvedic herb that has been used for centuries to treat a variety of ailments, including varicose veins and variceal bleeding. It reduces inflammation, improves blood flow, and strengthens the walls of the veins, all of which can make the bleeding less severe.
- Triphala: Triphala is a traditional Ayurvedic herbal medicine for a wide range of conditions, including variceal bleeding.
What to eat in Variceal Bleeding?
- You should focus on a balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables and antioxidants.
- To lessen the frequency of bleeding episodes, increase your fibre intake.
- Include sources of lean protein like eggs, poultry, fish and legumes.
- Choose complex carbohydrates, such those found in whole grains, beans, and lentils, over simple carbohydrates.
- Drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration caused by frequent vomiting or diarrhea.
What not to eat in Variceal Bleeding?
- Foods containing a high amount of salt, such as canned soups, canned vegetables, processed meats, and salty snacks.
- Spicy foods such as curries, chili peppers, and other spicy dishes.
- Dairy items like cheese and milk.
- Alcoholic beverages or caffeinated drinks.
- Fatty or fried foods like burgers and fries.
- Foods that may result in gas or bloating, such as beans and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower.
Variceal Bleeding Treatment
- Endoscopic Band Ligation: This is a minimally invasive procedure in which elastic bands are placed around the base of the varices to stop the bleeding.
- Sclerotherapy: During this process, a chemical solution is injected into the varices to promote inflammation and scarring, which ultimately closes up the veins and stops the bleeding.
- Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): It involves creating a shunt between two blood vessels in the liver to divert blood away from the varices, reducing pressure on them and preventing further bleeding.
- Splenectomy: This is a surgical procedure in which the spleen is removed, as it can sometimes contribute to portal hypertension and variceal bleeding.
- Balloon Obliteration: This is an endoscopic procedure in which a balloon catheter is used to block off a section of the vein, cutting off the blood supply to the varices and stopping further bleeding.
- Liver Transplantation: It is a radical treatment for refractory variceal bleeding.
- Mesocaval Shunt: It redirects the blood flow away from the esophageal veins and into the systemic circulation, relieving the pressure on the vessels and thus stops the bleeding.
Which doctor to consult for Variceal Bleeding?
A gastroenterologist or an interventional radiologist should be consulted in order to diagnose variceal bleeding and recommend a treatment plan accordingly.
Which are the best medicines for Variceal Bleeding?
- Vasoactive drugs: These drugs are usually given intravenously to reduce bleeding from the varices. Examples include octreotide, terlipressin, and somatostatin.
- Vasopressin analogues: These drugs work by narrowing the veins in the esophagus, reducing pressure on the varices and decreasing bleeding. Examples include vasopressin and terlipressin.
- Beta blockers: These medications slow down heart rate and reduce blood pressure, thereby decreasing pressure on the varices and reducing bleeding. Examples include propranolol, nadolol, and carvedilol.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be given to prevent infection of the ulcers caused by variceal bleeding. Examples include ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, and ceftriaxone.
- Endoscopic therapy: This involves using an endoscope to inject a sclerosing solution into the varices in order to reduce their size and decrease bleeding risk.
- Endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL): This procedure involves placing a band around the base of a varix in order to stop blood flow to it and reduce its size over time, thereby reducing its risk of rupturing and causing further bleeding episodes.
How long does it take to recover from Variceal Bleeding?
Generally, people who experience variceal bleeding can take weeks or months to fully recover, as they will need to receive specialized medical care and treatment.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The effects of treatment for variceal bleeding are not always lasting.
Treatment options typically focus on stopping the bleeding and preventing further episodes, rather than providing a permanent cure.
In most cases, treating the underlying condition causing the varices (portal hypertension, cirrhosis) will reduce the risk of recurrent bleeding and maintain a good quality of life.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Avoiding potential triggers of bleeding like alcohol consumption, heavy lifting, and straining during bowel movements.
- Maintaining an appropriate diet to lower the portal pressure, consisting of low-sodium meals rich in fiber and whole grains and eliminating processed foods.
- Taking medications like proton pump inhibitors or anticoagulants to reduce acid in the stomach and thin the blood, respectively.
- Avoiding smoking both before and after treatment to decrease chances of recurrence due to reduced blood flow caused by smoking narrowing veins and arteries over time.
- Following up regularly with a healthcare provider for appropriate monitoring of liver disease progression or other potential complications associated with variceal bleeding such as ascites or hepatic encephalopathy․
What is the cost of Variceal Bleeding treatments in India?
- Generally, endoscopic treatments are more expensive than medical treatments and can range from Rs. 5,000 to Rs. 50,000 per session.
- Pharmacotherapy treatments tend to be more cost-effective and may range from Rs. 500 to Rs. 5,000 per session.
- Surgery - such as a portocaval shunt or an endoscopic sclerotherapy - can cost up to Rs. 1 lac or more depending on the patient's condition and length of hospital stay required for the procedure.
What are side-effects of Variceal Bleeding treatments?
- Risk of infection: Variceal bleeding treatments can lead to an increase in the risk of developing an infection.
- Scarring and discomfort: Sclerotherapy for varices can cause scarring, soreness, and discomfort at treatment sites.
- Bleeding from puncture sites: Potential risks when the endoscopic esophagogastric varices ligation procedure is performed include bleeding from the puncture sites and trauma to the esophageal wall.
- Re-bleeding: Another possible side effect of treating variceal bleeding is a risk of re-bleeding, which may require additional medical intervention or procedures such as endoscopic banding ligation or liver transplantation
- Acute kidney failure: There is a risk of acute kidney failure with certain medications used to treat variceal bleeding, such as terlipressin or somatostatin analogues.
Variceal Bleeding - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you have any variceal bleeding symptoms, you should see a doctor in your area right away since they may lead to consequences including 'shock, hypoglycemia, and respiratory distress' for which treatment regimens can last anywhere from a few months to years, depending on how serious the issue is.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Hepatologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors