Vas Deferens (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 16, 2023
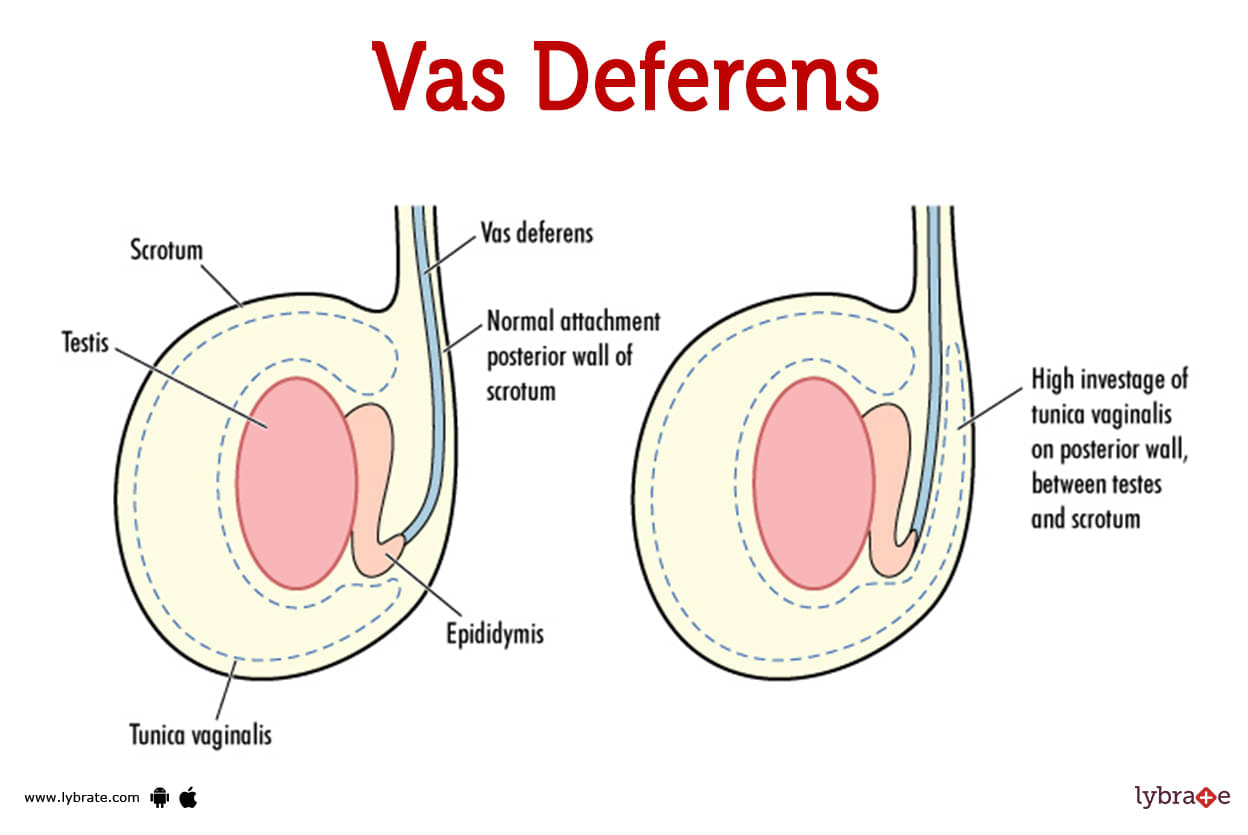
Vas Deferens Image
Each testicle has a vas deferens, commonly known as a sperm duct or ductus deferens. These ducts are responsible for extracting sperm from its testicular storage place. Scar tissue and infections can both affect the ducts. Before ejaculating, mature sperm are delivered to the urethra via the vas deferens (sperm duct).
The two vasa deferentia are part of the male reproductive system. The ductus deferens (or sperm duct) is another name for the vas deferens (singular). The ejaculatory duct is a muscular tube that extends from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity behind the bladder and connects to the urethra. The spermatic cord surrounds the vas deferens, which transports mature sperm to the urethra prior to ejaculation.
Where is the vas deferens located?
The vas deferens starts in the sac that holds your testicles, which is called the scrotum. The vas deferens goes from the testicle to the rest of your body. It keeps going until it connects to the duct of the seminal vesicle to make the ejaculatory duct.
How long is the vas deferens?
The vas deferens (also known as the ductus deferens) can range in length from around 30 centimetres (nearly 12 inches) to 45 centimetres (nearly 18 inches). It's coiled in places and straight in others. The tube's composition is classified as fibromuscular, which means it consists of both fibrous tissue and muscle.
Does a woman have a vas deferens?
No, but fallopian tubes perform a similar function in the female reproductive system. The tubes transport the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus, where they may be fertilised.
Vas Deferens Functions
In your testicles, sperm cells are created. Sperm then move into the epididymis, which is located on top of the testicle. The epididymis is in charge of maintaining sperm cells and developing them so they can fertilise eggs.
Muscle contractions transfer sperm from the epididymis to the vas deferens and then into the urethra when you are sexually aroused, allowing you to expel sperm from your body. Your body adds fluids to sperm cells throughout this procedure to make sperm.
Vas Deferens Conditions and Disorders
- Vasal aplasia (Congenital absence of vas deference): Male factor infertility is exacerbated by congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD), an uncommon obstructive condition. Despite the fact that the testes typically form and work correctly, sperm cannot go through the vas deferens to join the semen.
- Injuries of vas deference: Accidental injuries and its effects in the inguinal region often unavoidable and unpredictable, and iatrogenic lesions may affect the vas deferens' performance for extended periods of time.
- Vas deference stenosis: Congenital cysts, as well as inflammation and scarring caused by sexually transmitted diseases The vas deferens can become obstructed or damaged in men who have had bilateral hernia surgeries. This hinders normal sperm flow into the ejaculate.
- Duplication of vas deference: Duplication of the vas deferens, a rare congenital pelvic anatomical anomaly, is usually identified accidentally during spermatic cord surgeries such as inguinal hernia repair, varicocelectomy, orchidopexy, and vasectomy.
- Vasitis: This is a condition in which the vas deferens thickens as a result of infection and inflammation (swelling) in adjacent bodily tissues. This illness is also known as deferentitis or funiculitis.
- Infection of vas defence: Mycobacterium TB infection of the genitourinary tract can result in genitourinary tuberculosis. Genitourinary TB can restrict the vas (ductus) deferens through granuloma deposition or scarring. This can lead to azoospermia and infertility.
- Tonicity of vas deference: The tonicity of the medium has a significant impact on tension in the vas deference. Vas deference has grown rigid, with no room for flexibility.
Vas Deferens Tests
- Scrotal ultrasonography: It can tell the vas deferens apart from the other cord-like structures in the spermatic cord, and it has a distinct picture. Scrotal ultrasonography discovered and measured the diameter of all 50 typical guys.
- Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) for Vas deference: Magnetic resonance imaging is the most effective tool for detecting Vas deference abnormalities (MRI). Using weak signal intensity T1-weighted and maximum signal intensity T2-weighted images, normal Vas deference is represented as a long fluid-filled structure with small septa.
- Digital tomography of Vas deference: Computed tomography (CT) produces a tri picture of inside body anatomy using a series of planar cross-sectional scans. Vas deference appears on contrast-enhanced CT as fluid-filled structures with a thin septum. This approach is still the most effective for detecting various vas deference abnormalities.
Vas Deferens Treatments
- Vasectomy (vasoligation): It is a surgical treatment that can be used for male sterilisation or permanent contraception. During the surgery, the male vasa deferentia is cut and knotted or sealed, which aids in infection management.
- Transurethral endoscopic surgery for vas deference: It is a urological treatment approach. Transurethral excision of a prostrate (TUR-P) has been the standard treatment for vas deference infection and for past 60 years due to its efficacy, low risk of complications, and low cost.
- Laproscopy for vas deference: The most appropriate surgical treatment appears to be laparoscopic surgery. For vas deference cysts associated with ipsilateral renal agenesis, laparoscopic excision is extremely beneficial.
- Radical prostatectomy of vas deference: After a prostate cancer diagnosis, surgery to remove the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and vas deferens (and occasionally adjacent lymph nodes) is known as a radical prostatectomy. It is one option for treating patients with localised vas deferens infection.
- Local physiotherapy combined with systemic antibiotics: Drugs known as antibiotics are used to treat bacterial illnesses in both people and animals. They work by either getting rid of the germs or by making it impossible for bacteria to grow and multiply.
- Cryotherapy (also called cryosurgery): Using extremely low temperatures to freeze and kill cancer cells is known as cryotherapy. For this kind of procedure, spinal or epidural anaesthesia is required.
- Chemotherapy for vas deference: it is a medical practise that uses harsh chemicals to kill rapidly dividing cells in the body. Chemotherapy is the most common kind of cancer treatment because cancer cells expand and multiply more faster than the majority of normal cells in the body.
Vas deferens Medicines
- Antibiotics for vas deference: They kill germs or make it difficult for bacteria to thrive and multiply. Ampicillin sodium, Ticarcillin disodium, Penicillin procaine, Trimethoprim sulfa, Neomycin sulphate, Gentamicin, and Amikacin sulphate, Ciprofloxacin are examples of antibiotics.
- Antiviral agents for vas deference: Antiviral medications aid the body's defence against harmful viruses. The medications can lessen the severity of the symptoms and cut the length of time an infection caused by a virus lasts. Consider the antiretroviral medications Lamivudine, Zidovudine, Tenofovir, Nevirapine, and Abacavir as examples.
- Alpha blockers for vas deference: Alpha blockers are commonly used to dilate vessels. Prazosin, Terazosin, Doxazosin, Alfuzosin, Silodosin, and Tamsulosin are some examples.
- Nutritional supplements for vas deference: IIt promotes healthy sperm amount and quality, as well as overall male fertility. Lycopene, Selenium, Vitamin E, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Lecithin are a few examples.
- Chemotherapeutic agents for vas deference: Chemotherapeutic drugs can be utilised as an adjuvant treatment before surgery and in metastatic vas deferens adenocarcinomas. Vincristine, Actinomycin D, Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Fosfamide, and Etoposide are among examples.
- Muscles relaxants for stiffness in vas deference: These relax smooth muscles by altering the activity of K+ channels. For example, testosterone and androgens
What can I do to keep my vas deferens healthy?
The vas deferens, as well as the rest of your reproductive system, will benefit from your diligent attention to the self-care advice provided. You must aim for and try to keep a healthy weight and eat a wide variety of healthy foods and drink plenty of water.
You should do regular exercise, quit using tobacco products, and keep your sexual activity safe. When playing sports, it is important to always use safety gear. Learn what healthy genitalia feel like and look like. Get in touch with your doctor if you experience any changes.
Table of content
Find Urologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors