Wisdom teeth (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
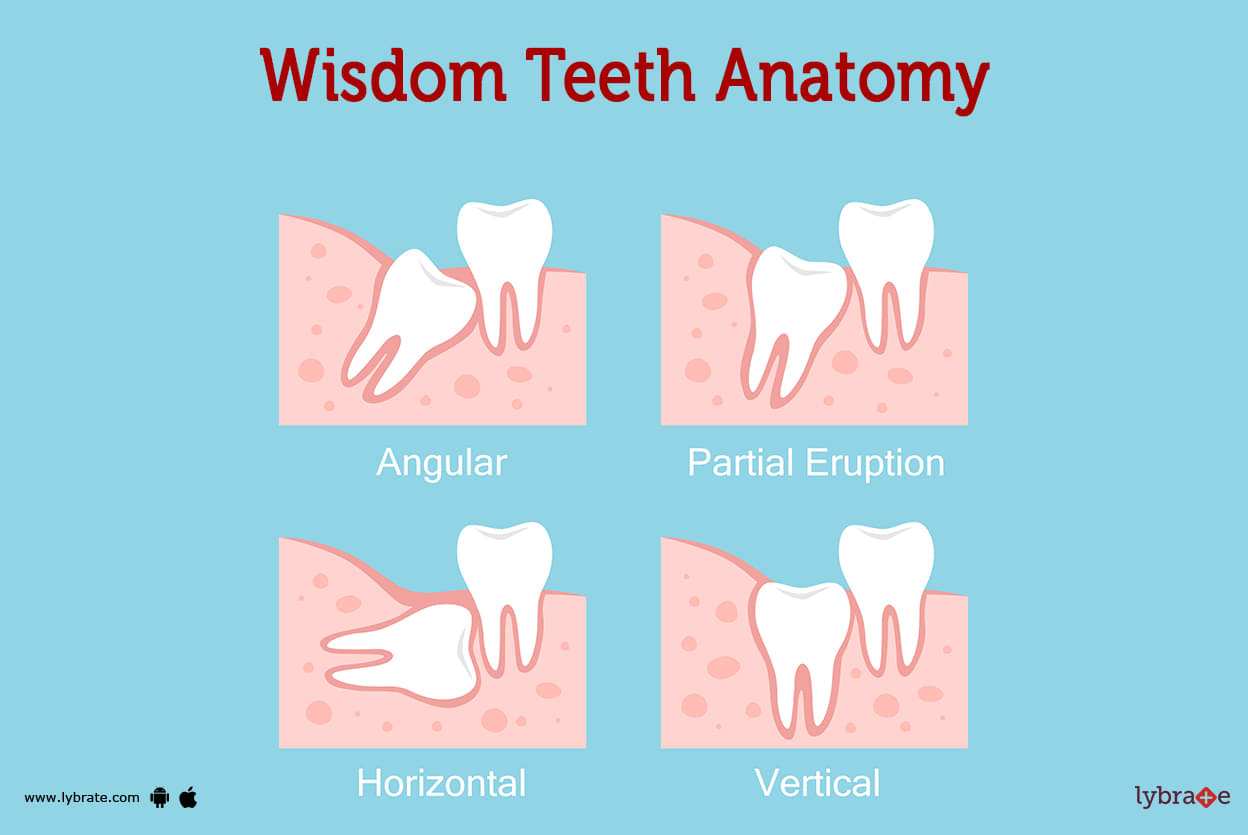
Wisdom Teeth Image
Wisdom teeth, commonly referred to as 'third molars,' are the last set of permanent adult teeth to erupt after the other molars. They can be found in the back of the mouth, close to where the tongue is situated. The eruption of a person's third molars typically begins around the age of 17, at which point most people begin to experience discomfort, infection, and other oral health problems.
It is common practise to recommend removing the third molar in order to avoid these complications. If the wisdom teeth become impacted within the gums or jawbone, it may be necessary to remove them surgically.
Wisdom teeth can occasionally erupt normally and cause no problems, but they can also become partially or completely impacted in the gums or jawbone, which can lead to infection, cavities, gum disease, and other oral health issues. Sometimes wisdom teeth can erupt normally without causing any problems. As a consequence of this, the removal of wisdom teeth is recommended by the majority of dentists.
Does everyone have wisdom teeth?
No, not everyone is born with all of their wisdom teeth in place. The wisdom teeth are the very last set of adult teeth to erupt, and some people are born without any of them.
When do wisdom teeth appear?
Do you have to remove wisdom teeth?
- Not always by any means. The wisdom teeth are the very last set of adult teeth to erupt, and while they can occasionally develop regularly and without any complications, this is not always the case. On the other hand, in the event that your wisdom teeth start to be tender or cause discomfort, you ought to think about getting them pulled.
- Your primary care provider will be able to guide you through the process of determining whether or not you need the extraction of your wisdom teeth.
- If it turns out that you do require their removal, your doctor will provide you with detailed, actionable instructions and may also write a prescription for pain medication. It is essential to carry out all of the directions to the letter if you want your mouth to recover as quickly as possible.
Where are my wisdom teeth located?
Positioned further back in the mouth, after the second molars, are your wisdom teeth. There is one wisdom tooth in each of your mouth's four corners. Third molars are another name for these teeth. There should be no discomfort or pain in the wisdom teeth, but if there is, you should see your dentist.
What are the first signs of wisdom teeth coming in?
One symptom could be jaw pain or tenderness, while another could be red, swollen gums behind the wisdom teeth. If your wisdom teeth are putting too much pressure on your nerves, you may also have facial pain.
Those tiny white spots you think you've been seeing behind your wisdom teeth might actually be something else. Your new teeth's crowns should now be visible above the gum line. If you see any of these issues, you should visit your dentist.
They can help you figure out if your third molars really are a problem and if you need to have them out. If that's the case, the dentist will advise you on what to do and may even prescribe pain medication. Following the instructions to the letter will aid in the healing of your mouth.
Wisdom Teeth Functions
The wisdom teeth, also called the third molars, are the last set of permanent teeth to come in. The average onset age is between 17 and 25. It's possible that our predecessors' diet required wisdom teeth because it consisted of harder, more chewy foods.
Wisdom teeth, with their increased chewing surfaces, were helpful for breaking down such difficult foods. However, diets today necessitate fewer wisdom teeth than they used to. When wisdom teeth are unable to erupt into their proper positions because of inadequate jawbone space, pain, infection, and other dental issues can develop. Therefore, it is no surprise that many people choose to have their wisdom teeth removed.
Wisdom teeth Conditions and Disorders
There is a risk of complications developing in certain individuals who have wisdom teeth that have not erupted properly or that have become impacted. Among these possible complications are the following:
- Wisdom teeth pain: Pain at the back of the mouth caused by erupting wisdom teeth is called wisdom tooth pain.
- Infection: Disease and tissue degradation are the results of an infection, which is defined as the presence of harmful bacteria or other germs in the body.
- Cavities: Cavities are caused by bacteria eating away at tooth enamel.
- Gum disease: Inflammation and infection of the gums and bone that support the teeth are the results of gum disease.
- Damage to neighboring teeth: Oftentimes, wisdom teeth cause harm to the teeth close to them due to constant friction.
- Cysts: Occasionally, fluid-filled sacs called cysts will grow in the gum tissue near or around the wisdom teeth.
- Tumors: Tumors are abnormal tissue growths that can develop anywhere in the mouth, including in the space occupied by the wisdom teeth.
- Trigeminal neuralgia: Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is a common cause of trigeminal neuralgia, a condition characterised by severe, sudden, and recurrent facial pain.
- Odontogenic carcinoma: To put it simply, odontogenic carcinoma is cancer that originates in the tooth's cellular structure or in the tissues immediately next to the tooth.
- Ameloblastoma: Growth of a benign tumour, called an ameloblastoma, in the jaw, most frequently in the area of the wisdom teeth.
Wisdom teeth Tests
- Dental X-rays: Dental X-rays are a type of imaging that make use of low doses of radiation in order to obtain clear images of the teeth and other oral structures that may be present.
- Biopsy: A diagnostic procedure known as a biopsy involves the removal of a very small sample of tissue from the patient's body and the subsequent examination of that tissue in order to establish whether or not it contains abnormal cells.
- CBC: A complete blood count, sometimes known as a CBC, is a test that measures the number of red, white, and platelet cells in the blood as well as sorts them.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan is a type of imaging test that creates comprehensive photographs of the inside of the body by employing a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to do the examination. This type of imaging test is also known as an MRI.
- Computed tomography: A computed tomography scan, sometimes known as a CT scan, is a diagnostic imaging method that provides inside images of the patient's anatomy by combining X-rays and a computer.
Wisdom teeth Treatments
The removal of the third molars is the treatment that is typically performed. The patient is typically sedated before to undergoing this procedure, which takes place in a clinic run by a dentist or an oral surgeon. On the other hand, if that is not possible for whatever reason, it can also be done in a hospital setting while the patient is under general anaesthesia.
The removal of one's wisdom teeth is a treatment that can be carried out at any age. However, in order to protect their oral health in the future, a significant number of people in their late teens and early 20s have their wisdom teeth pulled.
The typical amount of time needed for recovery following the extraction of your wisdom teeth is around one week. After the operation, your surgeon will give you a set of aftercare instructions to follow so that you can have a speedy and pain-free recovery. It is important that you follow these instructions exactly as they are written.
In comparison to the functions of one's other teeth, the wisdom teeth do not play a particularly significant role. Therefore, when they have been removed from their initial location, it is not necessary to replace them with new ones.
- Tooth removal: Tooth removal is the process of taking a tooth out of its place in the jawbone. Most of the time, this is done by a dentist or an oral surgeon.
- Sedation or anaesthesia: Sedation or anaesthesia is when drugs are used to make a patient feel calm or numb while dental work is done.
- Cold and heat therapy: Using a cold or hot compress to ease pain and swelling in the mouth.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a type of complementary and alternative medicine that involves putting very thin needles into certain parts of the body to relieve pain and speed up the healing process.
- Tea tree oil therapy : Tea tree oil therapy is the use of oil made from the leaves of the tea tree to treat oral infections and other health problems.
- Teeth fillings: Teeth fillings are things like amalgam, composite resin, and gold that are used to fill holes in teeth.
- Root canal: A root canal is a dental procedure that gets rid of diseased or damaged pulp tissue and cleans and seals the inside of the tooth.
- Chemotherapy for the jaw: Chemotherapy for the jaw is the use of medicines that kill cancer cells to treat cancer of the jaw. People often use carboplatin and 5-FU together.
Wisdom teeth Medicine
- Steroids are medications that can help make the area around your wisdom teeth less inflamed. Steroids are used for the purpose of reducing inflammation caused by wisdom teeth. This can be accomplished with the use of prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone, which are all types of steroids.
- Analgesics are a type of drug that can help alleviate pain in the region around the wisdom teeth and can be used to treat discomfort caused by wisdom teeth. To alleviate the discomfort associated with this type of pain, analgesics such as ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen, ketorolac, indomethacin, diclofenac, meloxicam, and celecoxib can be taken.
- Relaxants for the muscles around the wisdom teeth may be helpful in easing any stiffness that may be caused by the wisdom teeth. The muscle relaxants cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol, and tizanidine are just a few examples of those that could be used for this particular purpose.
- Antibiotics to treat an infection in the wisdom teeth: These medications may be helpful in the treatment of infections that affect the area around the wisdom teeth. Antibiotics such as vancomycin and cephalosporins are two examples of the kinds of drugs that could be utilised for this objective.
- DMARDs, or disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines, are medications that are used to treat pain and inflammation around the wisdom teeth. Among the DMARDs that could be utilised for this objective, some examples include sulfasalazine, methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib.
- Nutritional supplements for the relief of discomfort caused by wisdom teeth are substances that can either be taken orally or directly applied to the skin in order to assist in the reduction of discomfort caused by wisdom teeth. Dietary supplements like omega-3 fatty acids and ginger are two examples of foods that could be used for the goal of achieving this aim.
- Supplements for the promotion of growth of wisdom teeth are substances that can be taken orally to encourage the development of wisdom teeth. These supplements can be found in a variety of forms. Dietary supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin, vitamin D, and calcium are some examples of those that may be utilised for the aim of achieving this goal.
- Antiviral medications may be utilised in the treatment of viral infections in the region surrounding the wisdom teeth if it is determined that these infections are caused by the wisdom teeth. It is possible to treat this condition using antivirals such as amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, oseltamivir, ribavirin, acyclovir, and ganciclovir.
How can I care for my wisdom teeth?
- In the course of a routine dental examination, your wisdom teeth, if you still have them, will be scrutinised by your dentist. It is essential that you keep up with your basic dental care, but you should also do the following:
- It can be challenging to access the portions of the back surface of your wisdom teeth. Invest some effort and time into cleaning all of the areas that are difficult to access.
- At the very least once a day, clean your teeth. Cleaning the area in between your teeth thoroughly with floss is an efficient way to do so. Use a dental pick or an interproximal brush to clean the areas in between your teeth that just won't get clean no matter how hard you brush.
- You might want to try using an antibacterial mouthwash. Check to see that it doesn't have any alcohol in it. As a consequence of this, you will experience less of a tendency to have dry mouth.
Table of content
Find Dentist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors