Ovary (Human Anatomy): Image, Definition, Function, and Skin Diseases
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
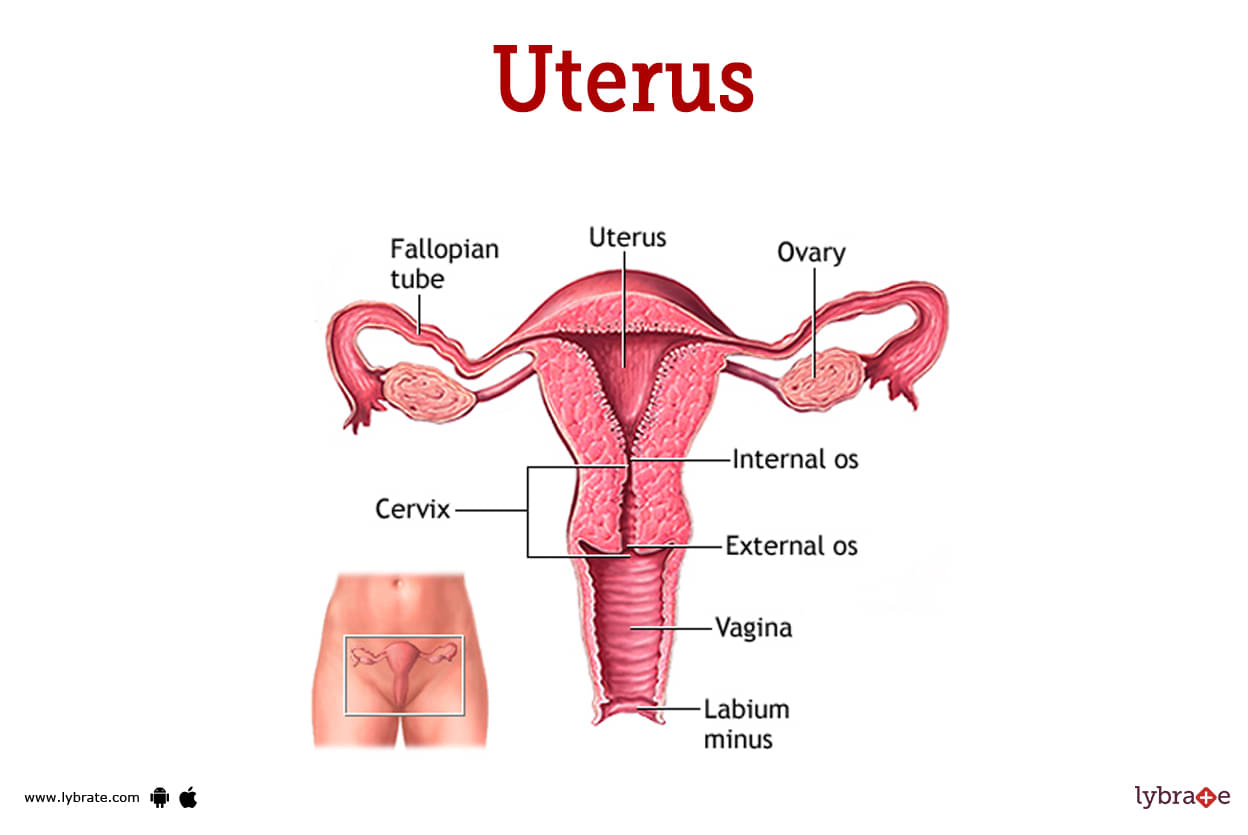
Ovary Image
The ovaries are two little oval-shaped glands on each side of the uterus. These regulate egg and hormone production. The fallopian tubes are tiny tubes that connect to the upper area of the womb and function as ova (egg cells) pathways from the ovaries to the uterus.
They are located in the lower abdomen on the right and left sides of the uterus and are held in place by various pelvic muscles and ligaments. The ovarian ligament connects your ovaries to your uterus, however they do not overlap.
They are oval in form, firm, and soft to the touch. They range in colour from mild grey to white.
Function of Ovary
They have several important functions, including:
- Production of eggs: The ovaries produce eggs, also known as ova, which are necessary for reproduction. The eggs mature in the ovaries and are released into the fallopian tubes during ovulation. They will continue to produce one egg with each menstrual cycle until they reach menopause. Menopause is characterized by the cessation of egg production. It is possible for it to release more than one egg on occasion, which may lead to multiple pregnancies. Ovaries stop producing eggs when a child is born.
- Hormonal production: The ovaries produce two main hormones, estrogen and progesterone, which play a critical role in the menstrual cycle and the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Estrogen is involved in the growth and maintenance of the female reproductive system, as well as the regulation of the menstrual cycle. Progesterone is responsible for preparing the uterus for pregnancy.
- Aromatase production: The ovaries also produce the enzyme aromatase which converts androgens to estrogens.
- Hormone balancing: The ovaries help to balance the levels of hormones in the body, including estrogen and progesterone, which are essential for the menstrual cycle and the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
- Menopause: Ovaries eventually stop producing eggs and hormone production, which leads to the onset of menopause.
Overall, the ovaries are essential reproductive organs that play a critical role in the production of eggs, the regulation of hormones, and the menstrual cycle. They are also important for maintaining the balance of hormones in the body and eventually lead to the onset of menopause.
Ovary Diseases
- Ovarian cysts: Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs inside or on the surface of the ovary. They feel little or no discomfort, and the cysts are perfectly harmless. Most cysts disappear on their own within a few months, but if not, they might pose problems.
- PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome): It is a hormonal condition that mostly affects women of reproductive age. In this disease, the ovaries of a woman may enlarge and create several harmless fluid-filled sacs (follicles). These follicles are undeveloped sacs that are designed to grow into eggs. When you have PCOS, your follicles fail to produce mature eggs.
- Ovarian cancer: It is a cancer that occurs in the ovaries. The cells reproduce rapidly and have the ability to penetrate and destroy healthy bodily tissue. Weight loss, stomach bloating, feeling full quickly, weight loss Pelvic pain, tiredness, and other symptoms. Back discomfort, gastrointestinal changes, constipation, and a frequent need to pee are among symptoms.
- Primary ovarian insufficiency: It is also known as premature ovarian failure, and it describes the condition that occurs when a woman's ovaries cease functioning properly before she reaches the age of 40.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: PID is a female reproductive organ infection.It usually occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to the womb (uterus), fallopian tubes, or ovaries.
- Ovarian tumors: Ovarian tumours are abnormal ovarian growths.Ovarian tumours can be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant).
- Endometriosis: Ovarian endometriomas, sometimes known as 'chocolate cysts,' are cysts that contain menstrual blood. They are a symptom of endometriosis, a disorder in which endometrial-like tissue migrates outside of the uterus.
- Germ cell tumour of the ovary: also known as dysgerminoma Germ cell tumours are cell growths that develop from reproductive cells. The tumours may or may not be malignant. The majority of germ cell tumours develop in the testicles or ovaries.
- Luteoma: A luteoma is a kind of tumour that develops in the ovaries during pregnancy. It is linked to an increase in sex hormones, most notably progesterone and testosterone.
- Ovarian remnant syndrome: Patients who have had an oophorectomy in the past might be said to suffer from ovarian remnant syndrome (ORS), which is defined as the existence of ovarian tissue in such patients.
- Female hypogonadism: Hypogonadism in women occurs when the ovaries in the female body generate very few or no sex hormones at all.
- Hyperthecosiss: the presence of nests of luteinized theca cells in the ovarian stroma due to differentiation of the ovarian interstitial cells into steroidogenically active luteinized stromal cellsOvarian torsion occurs when an ovary becomes twisted around the tissues that support it.
- Ovarian apoplexy: Ovarian apoplexy is a sudden rupture in the ovary, which usually happens at the site of a cyst. It is often accompanied by bleeding in the ovarian tissue and/or inside the abdomen.
- Choriocarcinoma: A malignant, fast-growing tumour that develops from trophoblastic cells, although the cases of ovarian cancer are small.
- Yolk sac tumours: These are malignant primitive germ cell tumors. They are also known as endodermal sinus tumors.
- Malignant Teratoma: Teratomas are tumours made up of tissues such as hair, muscle, and bone. They most often occur in the ovaries in women and in the testicles in men.
- Ovarian serous cystadenoma: A serous cystadenoma is a very common non-cancerous type of ovarian tumour. It develops from the cells on the surface of the ovary.
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: Mucinous cystadenocarcinomas are usually large, multiloculated cystic masses containing papillary projections and echogenic material. They can be found on the ovarian surface.
- Brenner's tumour: It is a rare ovarian tumour that is a part of the surface epithelial group of ovarian neoplasm. It is usually asymptomatic and is an unintentional pathological finding.
- Krukenberg tumor: A mucin-rich signet-ring cell-based disease that has spread to the ovaries. These tumours spread most likely through the lymphatic channels.
Test of Ovary
- Physical examination: During a pelvic exam, your provider can check your reproductive organs for masses, growths, or other changes.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can measure hormone levels. This testing can exclude possible causes of menstrual problems or androgen excess that mimic PCOS. You might have other blood testing, such as fasting cholesterol and triglyceride levels. A glucose tolerance test can measure your body's response to sugar (glucose).
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound can check the appearance of your ovaries and the thickness of the lining of your uterus. A wandlike device (transducer) is placed in your vagina. The transducer emits sound waves that are translated into images on a computer screen.
- Gene testing: Your doctor may recommend testing a sample of your blood to look for gene changes that increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Knowing you have an inherited change in your DNA helps your doctor make decisions about your treatment plan.
- Estrogen tests: they measure the level of oestrogen in the blood or urine. Estrogen can also be measured in saliva using an at-home test kit. If your estradiol or oestrogen levels are higher than normal, it may be due to a tumour of the ovaries.
- Laparoscopic diagnostic: During this procedure, your doctor makes tiny cuts in your abdomen and inserts a thin tube called a laparoscope. Using this tube, your provider can see the cyst, remove a sample of it for testing (biopsy), or remove it entirely.
- Blood count: People with ovarian endometriomas often have low red blood cell counts because of the heavy bleeding that comes with endometriosis.
- Urinalysis: A urine analysis can aid in the early detection of a number of kidney and urinary problems, such as diabetes, kidney stones, chronic kidney disease, and bladder infections.
- CT scan: This imaging technique utilises x-rays to capture pictures of the renal system. If a UTI spreads to the kidneys, however, it might have devastating effects .
- Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography CECT: In this scan X-rays are used for diagnosing specific diseases of the kidney the image is enhanced through intravenous contrast dye better gives better prognosis For this test, intravenous contrast dye may be used, which kidney patients may find concerning.
- MRI: Due to the combined importance of the anatomical and functional information offered, as well as the unique contrast patterns that may be detected non-invasively, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of healthy and diseased kidneys offers considerable potential. Imaging with several contrasts can reveal infiltrative kidney diseases.
- Estrogen tests1: Protein within foods you eat breaks down, producing urea nitrogen. BUN levels should be within 7 and 20. As renal function decreases, so does the amount of BUN in the blood.
- Ovary Biopsy: A kidney biopsy is a process in which a tiny piece of kidney tissue is surgically removed and studied under a microscope. You may use it to look for obstructions and structural flaws.
Ovary Treatment
- Laparoscopic ovarian drilling: It is a simple surgical procedure that uses heat or laser to destroy the tissues that produce male hormones like testosterone.
- Radiation therapy: This technique uses X-rays to kill cancer cells.If other techniques haven’t improved your symptoms and you don’t have plans to become pregnant, your provider may recommend that you have your ovaries removed.If both the ovarian and fallopian tissue are no longer viable, your doctor will use this laparoscopic procedure to remove them both. They may also recommend this procedure to prevent recurrence in women who are postmenopausal.
- Vaginal rings: The vaginal ring is a soft, flexible, transparent plastic ring that you insert into your vagina. This method is another long-acting reversible contraceptive that helps treat PCOS symptoms.
- Cryotherapy for preventing ovarian cancer: At abnormal areas of the ovaries an extremely cold probe is placed by which the abnormal cells are destroyed or killed through Freezing and the ovarian cancer chances are neglected.
- Laser therapy for preventing ovarian cancer: A laser of very high energy is used to burn the areas of abnormal cells in the ovaries. The abnormal cells are killed thus preventing them from ovarian cancer.
- Chemotherapy to kill ovarian cancer cells: Certain medications are injected into the vein. In case the cancer has spread already this therapy is given.Radiation therapy to treat ovarian cancer: radioactive rays are used to kill ovarian cancer cells. The rays are provided from outside the body or in small pellets implanted in the ovaries, known as brachytherapy.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays or particles to kill cancer cells. These x-rays may be given in a procedure that is much like having a regular x-ray.Chemo drugs called platinum compounds (usually cisplatin or carboplatin) and another type of chemo drug called a taxane, such as paclitaxel, are used to shrink the tumours to make them easier to remove. Aggressive chemotherapy is usually more effective as compared to radiation therapy
Ovary Medicine
- Antibiotics: Ampicillin-sulbactam plus doxycycline is effective against C. trachomatis, N. gonorrhoeae, and anaerobes for women with tubo-ovarian abscess.A single intramuscular or oral dose of penicillin can treat gonococcal PID that is not penicillin resistant; penicillin-resistant infection can be treated with a cephalosporin or ciprofloxacin. If chlamydia is a diagnostic consideration, a one-to two-week course of oral tetracycline or doxycycline (injectable-drug therapy is an alternative) should be added.
- Estrogen and progesterone therapy: Estrogen therapy can help prevent osteoporosis as well as relieve hot flashes and other symptoms of oestrogen deficiency. Your provider may prescribe oestrogen with the hormone progesterone, especially if you still have your uterus. Adding progesterone protects the lining of your uterus (endometrium) from precancerous changes that may be caused by taking oestrogen alone.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements: Both nutrients are important for preventing osteoporosis, and you might not get enough in your diet or from exposure to sunlight.
- Hormonal contraceptives: Birth control pills, patches, and vaginal rings help control the hormones responsible for the buildup of endometrial tissue each month. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) temporarily helps with pain from ovarian cysts.
- Ibuprofen (Advil): Ibuprofen inhibits the proliferation of ovarian theca interstitial cells; it lowers steroidogenesis; and it additionally has a positive effect on insulin and reduces oxidative stress.
- Naproxen (Aleve): Naproxen is a brand name for the drug naproxen sodium. Naproxen sodium is often tried in ovarian cysts as a painkiller, but the results are low.
- Oxycodone (OxyContin): Oxycodone is useful for moderate to severe pain. Morphine sulfate is used to treat severe pain in ovarian cysts.
- Oxycodone with acetaminophen (Percocet): to treat severe pain conditions, the combination of both is given
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics: Fluoro-quinolones (e.g.First-line therapy for acute, uncomplicated pyelonephritis is oral ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily for 7 days).
- Renal Specific antibiotics: Women who are pregnant and have urinary tract infections Antibiotics like nitrofurantoin, ampicillin, and the cephalosporins can be used with reasonable safety throughout the first trimester of pregnancy. Masculine urinary tract infections A fluoroquinolone or is advised for 7-14 days in treating a UTI in males with no evident complications.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of action of these drugs involves inhibiting the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to sites of cellular and tissue damage. Some of the important corticosteroids includes methylprednisolone
- Alkalyzers: For the treatment of hyperuricemia, hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis , and also in the case of renal stones alkalizer or alkalizing agents are used which increases the pH level of kidneys reducing the renal inflammation, some of the examples of alkalizing agents are sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium citrate, magnesium hydrogen carbonate, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are some ovarian diseases?
What causes ovary disease?
What are the symptoms of ovarian disease?
How do you check for ovary problems?
What can damage ovaries?
How do I keep my ovaries healthy?
How can I treat my ovary?
Table of content
Find Gynaecologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors